Topic 13: P1.5.1 (continued) The Origins of the
advertisement

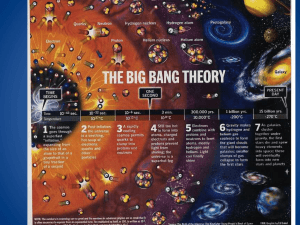
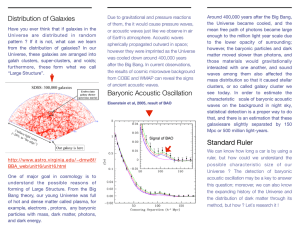
Topic 13: P1.5.1 (continued) The Origins of the Universe The origins of the universe hub We estimate that there are 125 billion galaxies in the universe. Our galaxy (the Milky Way!) contains about 100 billion stars. Our planet orbits a very average, middle aged yellow dwarf star, called Sol. spiral arm The nearest star to us is proxima centauri which is about 3 light years away. 10 The farthest galaxies are 13 billion (1.3x10 ) light years away. one light year is the distance that light travels in one year The Big Bang Theory About 13.7 billion years ago all matter and energy in the universe was concentrated into a small dense ball (according to the theory). This expanded and cooled rapidly, creating the universe as it went. Evidence for the Big Bang ­ Red Shift ­ but first a reminder on how to spot high and low frequency waves Eeeeeeeeeeeeeee ­ ­ Yowwwwwwwww Sound and stationary objects The siren is producing a single note which has a single frequency ...is the same as the frequency here The frequency here... ...and this is now high frequency Sound and moving objects The sound is crunched up in front of the ambulance, and stretched out behind the ambulance. Waves scrunched up = high frequency EEEEEEEyowwww This is now low frequency... We call this effect the DOPPLER SHIFT Waves stretched out = low frequency "Shift" refers to the shift in frequency No shift Stationary shorter wavelength Thrusters to station keeping longer wavelength Doppler shift also happens with light waves No shift When the ship moves, the light waves get scrunched in front, and stretched behind. Full impulse Waves scrunched Mr Sulu! up Waves stretched out • shifted to a lower frequency • shifted towards the red end of the spectrum (red shift) • shifted to a higher frequency • shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum (blue shift) Object moving away = red­shift, Object moving towards = blue­shift When we pass light from a star in a different galaxy through a prism the light splits up in to a spectrum. There are chemicals R floating in the atmosphere of stars that absorb certain frequencies/colours of light making thin dark bands. O Y G B I V Red shift makes these bands shift towards the red end of the spectrum so the galaxies (and the stars in them) are all moving away from us. Every single galaxy is red­shifted. They are all moving away from us! Also, the further away the greater the red­shift We explain this by saying that the whole universe is expanding away from the site of the big bang. Red­shift supports the Big Bang theory Problem: We have recently discovered that the expansion of space is getting faster!!!!!!!!! The Big Bang theory, in its current form, can't explain this (so, as a piece of wild speculation, we have invented dark energy to push the galaxies apart [and no, we don't have a clue what that is!]) Evidence for the Big Bang ­ Cosmic Microwave background radiation The original electromagnetic radiation produced by the big bang would have been gamma rays. Over the last 14 billion years, the gamma rays have mellowed, and become less energetic. Their frequency has dropped to that of microwaves: high energy low energy visible light gamma X­ray UV VIBGYOR IR Microwaves Radio waves high frequency original Big Bang radiation low frequency present day "cosmic background" radiation picked up by RADIOTELESCOPES Summary ­ Big Bang evidence • galaxies are red­shifted. The farther away they are, the more they are red­shifted (they are moving away quicker) • there is a background hiss of microwave radiation in the universe ­ but don't forget the accelerating expansion problem! R O Y G B I V All galaxies show red­shift Microwave hiss is is found in every direction