Cell Structures and Functions
advertisement

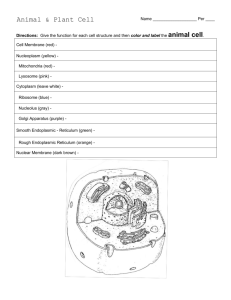
Cell Structures and Functions Animal Cell Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Cell Membrane 1. Function: allows certain materials in and out of the cell. Nickname: “The Gate” Structure that forms the outer boundary of the cell Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Cytoplasm 2. Function: to hold all organelles in place to allow them to carry out the life processes of the cell. Structure: gel-like material that is found inside the cell membrane and the outside of the nucleus. Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Nucleus 3. Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA Parts: 1. 2. Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes Nucleus Membrane: is a double membrane that surrounds to nucleus Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Ribosomes 4. Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 4. Nickname: “Roads”, “Conveyer belt” Function: To move materials from one part of the cell to another The ER extends from the nucleus to the cell membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types: 1. Rough ER: 2. Rough appearance because it has ribosomes Function: helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes Smooth ER: NO ribosomes Function: makes fats or lipids Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Golgi Apparatus 5. Nickname: “The shippers” or “FedEx” Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Lysosomes Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Lysosomes: circular, but bigger than ribosomes) 5. Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: to break down food into particles the rest of the cell can use and to destroy old cells Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Lysosomes Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Mitochondria 7. Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Structure: Bean shape and has two membranes Function: Energy formation Breaks down food to make ATP ATP: is the major fuel for all cell activities that require energy Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Centrioles Lysosomes Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 8. Centrioles Function: During animal cell division, the centrosome divides and the centrioles replicate (make new copies). Not in plant cells. Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Reticulum Centrioles Golgi Bodies Lysosomes Vacuoles Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Section 7-2 Plant Cell Vacuole Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Vacuoles 9. Function: Temporary storage of water, foods, pigments, waste or other materials. In plants: Bigger in plant cells than animal cells. This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts Now let’s talk about structures only found in PLANT Cells!! Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Chloroplasts 10. Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment Chloroplasts Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Cell Wall 11. Function: provides support and protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Plant Cell Cytoplasm Vacuole Smooth ER Ribosomes Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleolus Golgi Bodies Nucleus Mitochondria Rough ER Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal