Scope of Enterprise IT
Microsoft Solutions Framework
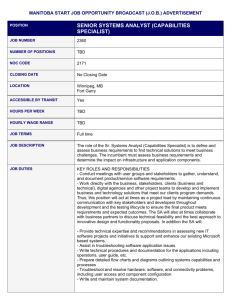
Overview
solution: [s&-‘lü-sh&n]
1: an action or process of solving a problem
2: an answer to a problem
DI Andreas Schabus
aschabus@microsoft.com
Academic Relations Manager
Microsoft Österreich GmbH
4
MSF
Framework: [‘frAm-“w&rk]
1: a basic conceptional structure (as of ideas)
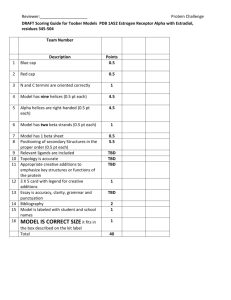
2: a skeletal, openwork, or structural frame
Challenges & Opportunities
Escalating business expectations of technology
Increasing business impact of technology
solutions
Risks are higher than ever before
Project Issues
Call to action
Adopt Key Concepts
Learn about MSF
Adopt MSF
Optimizing scarce resources
Skilled people, budget, time, and other assets
Rapid technology evolution
Many new opportunities, but they require new skills and
effective teams to take advantage of them
Symptoms of Challenged Projects
“It doesn’t meet
our expectations –
we’re not happy”
“The project
was late and
over budget”
“What was
built really
isn’t what
we needed”
“We didn’t
understand clearly
what we were
“We couldn’t get
supposed to do”
the information
“We were unaware
we needed to
of how the work of
do our work”
other team members
affected our work”
“We can’t get
it to operate
“It’s just too
well in our
“This thing is
difficult to use”
environment”
unpredictable – we
keep discovering
new problems”
Root Causes of Technology Project Failure
Disconnected stakeholders
No executive sponsorship
Limited user participation
Operations involved too late
Team environment
Team/culture issues
Perceived constraints
Not open and honest
Vague process
Unclear approach
Unstated goals
Managing scope
Success Hasn’t Come Easily
2000
1998
Failed
Challenged
Succeeded
23%
49%
28%
28%
1995
1994
46%
40%
31%
26%
33%
53%
27%
16%
This chart depicts the outcome of the 30,000 application projects in large, medium,
and small cross-industry U.S. companies tested by The Standish Group since 1994.
Source: The Standish Group International, Extreme Chaos, The Standish Group
International, Inc., 2000
Microsoft Solutions Framework
MSF offers guidance in how to organize
people and projects to plan, build, and
deploy technology solutions
successfully and effectively
Teamwork barriers
Responsibilities unclear
Conflicting language
Poor communications
Most causes are related to
“people and process” – not technology
Key goals for MSF:
Drive business success through business & technology
alignment
Ensure high quality solutions; handling the many facets of
quality as defined by multiple stakeholders
Accelerate delivery, reduce costs, minimize risks
Improve team effectiveness
Following a Solution Through the IT Lifecycle
M SF C h
ec
klist
Origi
n
Foun
dation P
rinciples
Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
Mode
Practice
ls
s
D i sci
Team
Proce
ss
plines
Optimizing Changing
Business
Need
Service
Delivered
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Supporting Operating
The Origin of MSF
Microsoft
Products
Groups
Microsoft
Services
Microsoft
Operations &
Technology
Group
Microsoft
Certified
Partners
M SF C h
Proven
Practices
Results from project teams and product groups are
analyzed
Analyzed results are contrasted with industry practices and
methods
Combined results are then organized and consolidated
into “people and process” guidance
ec
klist
; Origi
n
Foun
dation P
rinciples
Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
Mode
Practice
ls
s
D i sc i
Team
Proce
ss
plines
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
MSF Foundational Principles
Clear accountability, shared responsibility
Empower team members
Focus on business value
Shared project vision
Stay agile, expect change
Foster open communications
Learn from all experiences
Invest in quality
Scope
Scope – The parts of the vision that can be
accomplished within the solution constraints
Solution scope - The sum of the products and services
to be provided as a solution
Project scope – The work performed by the team to
deliver each item in the solution scope
Project
Scope
Project
Scope
Solution
Scope
Your project may not include
the entire solution
Example of a Vision
“I believe this nation should
commit itself to achieving the goal …
of landing a man on the Moon and
returning him safely to the Earth.
No single space project … will be more
impressive to mankind, or more
important for the long-range
exploration of space… .”
President John F. Kennedy
Speech to U.S. Congress
May 25, 1961
M SF C h
D i sc i
Solution
Scope
Project
Scope
A single solution may spawn
several serial or concurrent projects
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
Mode
Practice
ls
s
Team
Proce
ss
plines
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Key Concepts and Proven Practices
M SF C h
Key concepts
D i sc i
Proven practices
Goals for Successful Projects
Related Project Goal
for Success
Deliver within project
constraints
?
“What was built really isn’t what we
needed”
“This thing is unpredictable – we keep
discovering new problems”
“We can’t get it to operate well in our
environment”
Build to specifications
?
Release with issues identified
and addressed
Deploy smoothly and prepare
well for ongoing operations
?
“It’s just too difficult to use”
Enhance user effectiveness
“It doesn’t meet our expectations –
we’re not happy”
Satisfy customers
?
?
“Needed information is not shared
timely to all who need it”
Establish good communications
?
?
plines
MSF Team Model
Goal
Ownership
“The project was late and over
budget”
Team
Proce
ss
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Use small, interdisciplinary teams
Enable teams to work together at a single site
Create a solution design through total team
participation
Typical Symptom
of Challenged Project
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
Mode
Practice
ls
s
Team of peers
Customer-focused mindset
Product mindset
Zero defect mindset
Willingness to learn
Delivering the solution
within project constraints
Satisfied
customers
Program
Management
Product
Management
Building to
specification
Development
Communication
User
Experience
Enhanced user
effectiveness
Test
Release
Management
Smooth deployment and
ongoing operations
Approval for release only
after all quality issues are
identified and addressed
MSF Team Model: Functional Areas
The Extended Project Team
Project management
Solution architecture
Process assurance
Administrative services
Program
Management
Business value
Marketing
Customer advocacy
Product planning
Product
Management
Business Focus
Users
Technology consulting
Implementation architecture
and design
Application development
Infrastructure development
Help
Desk
Product
Management
User
Experience
Development
Customer
Test
Project Team
User
Experience
Operations
and
Support
Groups
Test
Accessibility
Internationalization
User advocacy
Training/support material
Usability research and testing
User interface design
Test planning
Test engineering
Test reporting
Release
Management
Infrastructure
Support
Operations
Logistics
Commercial release
management
Lead team
Program
Management
Release
Management
Test
Test
Feature teams
Release
Management
N
N
P
P
U
N
U
U
P
N
N
N
P
P
Development
Development
N
N
Test
Test
P
U
N
User
Experience
P
U
N
P
Release
Management
U
P
N
P
Release
Management
Development
Site Engine &
Design
User
Experience
N
Fulfillment
Program
Management
Test
Program
Management
Program
Management
Development
User
Experience
Technology Architects and
Steering Committees
Program
Product
Development
Management Management
Product
Management
Test
Catalog
User
Experience
Project
Sponsor
Scaling Down – Combining Roles
for Smaller Teams
Development
User
Experience
Program
Management
Program
Management
Roles may be combined, but some combinations pose risks
Product
Management
User
Experience
Release
Management
Technology Focus
Using Sub-Teams for Large Projects
Function team
Development
P Possible
U Unlikely
N Not Recommended
U
U
Sample: Project Team
Example: Small Team
Project
ProjectExecutive
Executive
Small team, combined roles
3 x tbd
3 x tbd
Project
ProjectBoard
Board
3 x tbd
3 x tbd
Project
ProjectDirector
Director
Project
ProjectOffice
Office
tbd
tbd
3x tbd
3x tbd
Product
Product
Logistics
Logistics
44 xx tbd
tbd
tbd
tbd
Logistics
Logistics
Alliance
Alliance
Engineer
Engineer
tbd
tbd
Supportability
Supportability
tbd
tbd
Program
Management
Test
Dev
Dev
Program
Program
tbd
tbd
tbd
tbd
Architect
Architect
tbd
tbd
Dev
Dev
33 xx tbd
tbd
Core
Exchange
Test
Test
22 xx tbd
tbd
Dev
Dev
55 xx tbd
tbd
Program
Program
Portal
Test
Test
Dev
Dev
33 xx tbd
tbd
55 xx tbd
tbd
Integration
Program
Program
tbd
tbd
Test
Test
44 xx tbd
tbd
Program
Program
tbd
tbd
22 xx tbd
tbd
MSF Process Model
ecklist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
Mode
Practice
ls
s
; Team
Proce
ss
plines
tbd
tbd
Development
Release
Management
M SF C h
Performance
Performance
tbd
tbd
tbd
tbd
D i sci
Test
Test
tbd
tbd
22 xx tbd
tbd
Build
Build
Product
Management
Leads
User
User XP
XP
User
User XP
XP
User
Experience
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Deployment
Complete
Deployment Stabilized
Site Deployments Complete
Core Technology Deployed
Release Readiness
Approved
Pilot Complete
Pre-Production
Testing Complete
Release Candidates
Core Team Organized
Vision/Scope Baselined
Vision/Scope
Approved
Technology Validation Complete
Functional Specifications Baselined
Master Project Plan Baselined
User Acceptance Testing Complete
Zero Bug Bounce
Bug Convergence
Scope
Complete
Master Project Schedule Baselined
Development/Test Environment Set Up
Project Plans
Approved
Proof of Concept Complete
Internal Release 1
Internal Release 2
Internal Release nn
The MSF Process Model Is Iterative
Functionality
Minimize risks by breaking large projects into multiple versions
Version 3
Version 2
Different Roles Drive Different Phases
Milestone
MSF Role Cluster
Vision/scope approved
Product management
Project plans approved
Program management
Scope complete
Development
User experience
Release readiness approved
Testing
Release management
Deployment complete
Release management
Version 1
Time
MSF Team Roles Through the Phases
Envisioning
Phase
Product
Management
Program
Management
Planning
Phase
Overall goals
Identify
customer
requirements
Vision / scope
document
Design goals
Solution
concept
Project structure
Development
Prototypes
Development
and technology
options
Feasibility
analysis
Developing
Phase
Conceptual
design
Business
requirements
analysis
Communication
s plan
Conceptual and
logical design
Functional
specification
Master project
plan
Master project
schedule
Budget
Technology
evaluation
Logical and
physical design
Development
plan / schedule
Development
estimates
Customer
expectations
Stabilizing
Phase
Communication
s plan execution
Launch
planning
MSF Team Roles Through the Phases
Envisioning
Phase
Deploying
Phase
Customer
feedback,
assessment,
signoff
User
Performance
needs and
implications
User
Experience
Planning
Phase
Functional
specification
management
Project tracking
Plan updating
Project tracking
Bug triage
Solution / scope
comparison
Stabilization
management
Test
Testing
approach
Test
acceptance
criteria
Developing
Phase
Usage
scenarios / use
cases
User
requirements
Localization /
accessibility
requirements
User
documentation,
training plans
and schedules
Design
evaluation
Testing
requirements
Test plan and
schedule
Code
development
Infrastructure
development
Configuration
documentation
Bug resolution
Code
optimization
Problem
resolution
Escalation
support
Release
Management
Deployment
implications
Operations
management
and
supportability
Operations
acceptance
criteria
Design
evaluation
Operations
requirements
Pilot and
deployment
plan and
schedule
Stabilizing
Phase
Training
Training plan
updates
Usability testing
Graphic design
Functional
testing
Issues
identification
Documentation
testing
Updated test
plan
Rollout
checklists
Rollout and pilot
plan updates
Site preparation
checklists
Deploying
Phase
User
documentation
stabilization
Training
materials
Testing
Bug reporting
and status
Configuration
testing
Pilot setup and
support
Deployment
planning
Operations and
support training
Training
Training
schedule
management
Performance
testing
Problem
resolution
Site deployment
management
Change
approval
MSF Project Trade-off Matrix
The Tradeoff Triangle
The MSF tradeoff matrix is an early agreement
made between the team and stakeholders
Fixed
Chosen
Adjustable
Resources
Schedule
The Tradeoff Triangle represents the
variable relationship between
resources, schedule, and features
Features
The Tradeoff Matrix - an agreement between the team and
customer to set default priorities for tradeoff decisions
Establishing Traceability
Ensuring that end
results meet initial
business goals and
requirements
Business
Goal
M SF C h
Requirements
User Profiles
Solution Concept
Conceptual Design View
Logical Design View
Physical Design View
Functional Specification
Plans
Solution
Schedule
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
; Mode
Practice
ls
s
D i sc i
; Team
; Proce
ss
plines
Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
MSF Project Management Discipline
Project management is an area of knowledge, skills, tools,
and techniques to achieve project objectives within project
constraints
In MSF, project management is a service, with many responsibilities
shared among roles
Does not equate to “being the boss”
Is especially critical for scaled-up project teams
MSF was designed to work in conjunction with several
industry project management standards around the world
including:
The Project Management Institute (PMI) Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
The International Project Management Association (IPMA)
Prince2
MSF enhances generic PM practices with techniques,
milestones, and practices specifically appropriate for
technology projects
Project Management Knowledge Areas
Project integration management
Project scope management
Project schedule management
Project cost management
Project staff resource management
Project communications management
Project risk management
Project procurement management
Project quality management
Definitions
M SF C h
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
; Mode
Practice
ls
s
D i sci
; Team
; Proce
ss
plines
; Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Risks
“Possibility of loss or injury,” Webster’s
Collegiate Dictionary, 10th edition
An anticipated problem or future potential
for adverse outcome, loss, or harm
Risk management
Process of identifying risks and managing
those that are most threatening to the
project
Risk Management in MSF
Project Risk – The possibility of a
negative outcome that is assumed in
order to pursue an opportunity for gain in
the project
MSF risk management discipline
Distinguishes risks from issues or problems
that exist already (“known problems”)
Defines a risk management process for
proactively identifying, analyzing, and
addressing risks
Increases the likelihood of success in a
project by minimizing the potential for failure
Foundational Principles Applied to
MSF Risk Management
Stay agile, expect change
Embrace change and turn it into opportunity
Continuously assess and proactively manage
risks
Foster open communications
Encourage a no-blame culture
Discuss risks openly to enable better informed
decision-making
MSF Risk Management Discipline
Key Concepts
Assume risk is inherent in any project or
process
View risk identification as a positive
activity
Specify risks first, then manage them
Assess risks continuously
Use proactive risk management
Do not judge value of project simply by
the number of risks
Foundational Principles and MSF
Risk Management (cont.)
Establish clear accountability, shared
responsibility
Hold program management role accountable for risk
management activities
Share responsibility for participating in the risk
management process among all team members
Share responsibility for assigned risks and action
items among individual team members
Learn from all experiences
Apply learning to achieve continuous improvement
and greater success
MSF Risk Management Discipline
Creating Risk Statements
Identifying, analyzing, and addressing risk
proactively
Risks must be clearly stated
To manage risk proactively
Anticipate problems
vs. Fixing them when they occur
Address root causes
vs. Addressing symptoms of the cause
Risk Statement
Root
Cause
Condition
Prevent and minimize vs. Reacting to consequences through
risk
mitigation
Prepare for
consequences
vs. Reacting to a crisis
to minimize impact
Use a known and
structured process
vs. Using an ad hoc process
Deriving Risk Sources from Risk
Classifications
Risk classifications can be used to stimulate thought
regarding risk sources
Risk
Classifications
The development and
test roles have been
combined in this project
Customers, end users, stakeholders, personnel,
organization, skills, and politics
Process
Mission and goals, decision-making, project
characteristics, budget, costs, schedules,
requirements, designs, building, and testing
Technology
Security, development and test environments, tools,
deployment, support, operations environment, and
availability
Environment
Laws, regulations, competition, economy, technology,
and business
Therefore
…we may ship with
more bugs
Arriving at the Initial Risk List
Classification
Root Cause
Technology
Technology
change
Risk Sources
People
Consequence
Total Loss
or
Opportunity Cost
People
Condition
Developers
to work with
new shipping
technology
Consequence
Development
time will take
longer due to
the need for
developers to
learn
Organization Development Communicatio
team is divided n among the
between
team
London and
members will
Los Angeles
be difficult
Downstream
Effect
We get to the
market later
and lose
market share
to competitors
Delays in
product
shipment with
additional
rework
Arriving at a Prioritized Master Risk List
Priority
1
2
Condition
Developers to
work with
new shipping
technology
Consequence Probability Impact Exposure
Development
30%
2
.6
time will take
longer due to
the need for
developers
to learn
Communication
Development
20%
2
.4
among the team
team is divided
between London members will be
and Los Angeles difficult
The MSF Risk Management Process
Analyze and
Prioritize
Risk
Statement
Identify
Control
Risk
Knowledge Base,
Concepts,
and Processes
Learn
Master
Risk List
Top n
Risks
Track and
Report
Plan and
Schedule
Documenting Risk Action Plans
Condition
Developers
to work with
new
shipping
technology
Consequence
Development
time will take
longer due to
need for
developers
to learn
Development
team is
divided
between
London and
Los Angeles
Communicatio
n among the
team will be
difficult
Mitigation
Provide
technical
training to
developers
Contingency
Revert
back to
previous
version
Trigger
Owner
Developers
Brenda
have not
Diaz
passed related
technology
exam by project
plan approval
Erik
Hold a weekly Establish an Lack of
team meeting internet-based communication Ismert
via
communication results in
teleconference portal for
schedule
between
posting
slippage
London
important
and Los
project
Angeles
information
M SF C h
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
; Mode
Practice
ls
s
D i sc i
; Team
; Proce
ss
plines
; Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
; Risk
Manage
m e nt
Read
iness M
a na g e m
e nt
Treat readiness
planning as positive
vs.
React to shortfalls in
knowledge, skills, abilities
Use a known and
structured process
Anticipate and schedule
readiness needs
Develop and use a
knowledge
management system
vs.
Using and ad hoc process
or none at all
Conduct training or fix
gaps as they occur
Unknown knowledge
assets
vs.
vs.
Every project is a learning opportunity
The MSF Readiness Management
Process
Define
Assess
Knowledge
Skills
Abilities
Skill Building
Readiness Management: A Proactive Approach
Proactive
vs.
Reactive
Defining the Type of Project for
Skills Requirements
Skill Maintenance
MSF Readiness Management Discipline
Strategic
High
Potential
Critical to sustain
future business
opportunity
Important to
achieve future
success
Key
Operational
Support
Dependency for
current success
Valuable, but not
critical to success
Proactive
M SF C h
Change
ec
klist
; Origi
n
; Foun
dation P
rinciples
; Key C
oncepts
/ Proven
; Mode
Practice
ls
s
; D i sci
Evaluate
Reactive
Source: Based on the Cranfield Information Systems Research Centre’s Application Portfolio Planning
; Team
; Proce
ss
plines
; Proje
ct Mana
g e m e nt
; Risk
Manage
m e nt
; Read
iness M
http://w
a na g e m
e nt
ww
.micros
oft.com
/msf
Maybe i
nterestin
g
?
http://w
ww.micr
osoft.com
ation
/austria
/educ
http://d
e.thespok
e.net
http://Im
agine.th
espoke.n
http://w
et
ww.stud
entoptio
http://re
ns.com
search.m
icrosoft.c
http://b
om
logs.ms
dn.com/
bloggers
.aspx
© 20032003-2004 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
This presentation is for informational purposes only. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, in this summary.