Document
advertisement

Chapter 4 Microwave network analysis
4.1 Impedance and equivalent voltages and currents
equivalent transmission line model (b, Zo)
4.2 Impedance and admittance matrices
not applicable in microwave circuits
4.3 The scattering matrix
properties, generalized scattering parameters, VNA measurement
4.4 The transmission (ABCD) matrix
cascade network
4.5 Signal flow graph
2-port circuit, TRL calibration
4.6 Discontinuities and modal analysis
microstrip discontinuities and compensation
4-1
微波電路講義
4.1 Impedance and equivalent voltages and currents
• Equivalent voltages and currents
Microwave circuit approach
Interest: voltage and current at a set of terminals (ports), power flow
through a device, and how to find the response of a network
For a certain mode in the line, the line characteristics are represented by
it’s global quantities Zo, b, l.
Define: equivalent voltage (wave) transverse electric field
equivalent current (wave) transverse magnetic field
voltage (wave)/current (wave) = characteristic impedance or
wave impedance of the line
and
voltage current = power flow of the mode
→ use transmission line theory to analyze microwave circuit
performance at the interested ports
4-2
微波電路講義
• Impedance
characteristic impedance of the medium
wave impedance of the particular mode of wave
Et
Zw
Ht
V
characteristic impedance of the line Z o
I
input impedance at a port of circuit
4-3
Zin ( z )
V ( z)
I ( z)
微波電路講義
Discussion
1. Transmission line model for the TE10 mode of a rectangular
waveguide
V ( x, z ) E dl E y dy
y
: x dependent , non - unique value
x
transverse fields (Table 3.2, p.117)
x
x
Ey ( A e
A e ) sin
C1V sin
a
a
1
x
x
Hx
( A e jbz A e jbz ) sin
C2 I sin
ZTE10
a
a
jbz
ZTE10
P
E y
H x
jbz
k
Zo
b
1
*
E
H
dxdy
y
x
2
4-4
transmission line model
V Vo e jbz Vo e jbz
I I o e jbz I o e jbz
Vo jbz Vo jbz
e
e
Zo
Zo
Vo Vo
Zo
Io
Io
1
P Vo I o *
2
微波電路講義
(derivation of C1 and C2)
E y ( A e jbz A e jbz ) sin
Vo
A
A
, Vo
C1
C1
Hx
Io
x
x
C1 (Vo e jbz Vo e jbz ) sin
a
a
1
ZTE10
( A e jbz A e jbz ) sin
x
x
C2 ( I o e jbz I o e jbz ) sin
a
a
A
A
, Io
C2 ZTE10
C2 ZTE10
2
ab
1 a b
A
P E y H x*dxdy
4 ZTE10
2 0 0
ZTE10
2
A
2
1 *
*
C
C
Vo I o
1 2
ab
2C1C2* ZTE10
2
A C2 ZTE10
Vo
C2
=-1
Zo
C1
C1 A
Io
C1
2
2
, C2
ab
ab
4-5
微波電路講義
2. Ex.4.2
incident
wave
TE10 o
Zoa, ba
r
Z od Z oa
Z od Z oa
Z oa
Q: What if the incident wave is
from the other direction? “N”
ko o
k
, ko o k , k r ko
, Z od
bd
ba
b2a kc2 ko2 , bd2 kc2 k 2 , kc
Zod, bd
2f c
2 2f c
vp
a c
c / r
X band: a 2.286cm c 2a 4.472cm kc 137 m 1 f c ,a 6.56GHz, f c ,r 4.17GHz
if f 10GHz ko 2f / c 209m 1 , ba 158m 1 , r 2.54 k 333m 1 , bd 304m 1
Z oa 500, Z od 259.6, 0.316
if f 6GHz k r ko 201m 1 kc in r , bd 147 m 1 ,
ko 126m 1 kc in air , ba j54m 1 , TE10 " non exist "
4-6
微波電路講義
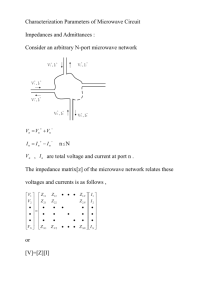
4.2 Impedance and admittance matrices
V1+, I1+
reference plane V1¯, I1¯
for port 1
Z o1 V1, I1
(plane for
V1 0 )
t1
port 1
N-port
network
port N
Vi Vi Vi
I i I i I i
VN+, IN+
VN¯, IN¯
IN ,VN Z on
tN
1
(Vi Vi )
Z oi
Vi Vi
Z oi
Ii
I i
1
1
Pinc ,i Re{Vi I i *}, Pin ,i Re{Vi I i *}
2
2
4-7
reference plane
for port N
(plane for
VN 0 )
微波電路講義
• Impedance matrix
V1 Z11
V Z
2 21
V Z I ,
VN Z N 1
Z12
ZN 2
Z1N I1
Z 2 N I 2
V
, Z ij i
Ij
Z NN I N
I k 0, k j
responsei
source j
I k 0, k j
• Admittance matrix
I1 Y11 Y12
I Y
2 21
I Y V ,
I N YN 1 YN 2
Y1N V1
Y2 N V2
I
, Yij i
Vj
YNN VN
4-8
Vk 0, k j
responsei
source j
Vk 0, k j
微波電路講義
Discussion
1. Reciprocal network
Z Z t ,
Y Y t ,
Zij Z ji
, Z and Y : symmetric matrix
Yij Y ji
(derivation)
source
port 1
port 2
a
V1a, I1a
V2a, I2a
b
V1b, I1b
V2b, I2b
reciprocity theorem: V1aI1b + V2aI2b =V1bI1a + V2bI2a
V1 Z11 Z12 I1
V Z
2 21 Z 22 I 2
( Z11I1a Z12 I 2 a ) I1b ( Z 21I1a Z 22 I 2 a ) I 2b ( Z11I1b Z12 I 2b ) I1a ( Z 21I1b Z 22 I 2b ) I 2 a
Z12 I 2 a I1b Z 21I1a I 2b Z12 I 2b I1a Z 21I1b I 2 a
( Z12 Z 21)( I 2 a I1b I 2b I1a ) 0 Z12 Z 21
4-9
微波電路講義
2. T and Πnetworks
Z1
Z2
Z11-Z12
Z22-Z12
Z12
Z3
I2=0
(derivation)
V1 Z11
V Z
2 21
Z11
Z 22
V1
I1
V2
I2
Z1
Z12 I1
Z 22 I 2
Z1 Z 3 , Z 21
I 2 0
I1
V2
I1
V1
Z2
V2
Z3
Z 3 Z12
I1=0
I 2 0
Z1
Z 2 Z3
V1
I1 0
Z 3 Z12 , Z1 Z11 Z12 , Z 2 Z 22 Z12
4-10
Z2
Z3
V2
I2
微波電路講義
Y1
Y2
-Y12
Y11+Y12
Y3
I1 Y11 Y12 V1
I Y Y V
2 21 22 2
I1
I
Y1 Y2 , Y21 2
V1 V 0
V1
2
I
Y22 2
V2
I2
I1
(derivation)
Y11
Y22+Y12
V1
Y1
Y2
Y3 V2=0
Y1 Y12
V2 0
I2
I1
Y1
Y1 Y3
V1 0
V1=0
Y1 Y12 , Y2 Y11 Y12 , Y3 Y22 Y12
4-11
Y2
Y3
微波電路講義
V2
3. Impedance matrix and T-network of a lossless transmission line section
I1
V1
(derivation)
0
Z1
I2
Zo , b
V2
Z2
Z3
l
Z1 Z 2 jZ o (cot bl csc bl )
Z3 jZo csc bl
z
V ( z ) Vo e jbz Vo e jbz , I ( z ) Yo (Vo e jbz Voe jbz ), B.C. V1 V (0), I1 I (0),V2 V (l ), I 2 I (l )
1
(V1 Z o I1 )
2
1
1
V2 Vo e jbl Vo e jbl (V1 Z o I1 )e jbl (V1 Z o I1 )e jbl V1 cos bl jZ o I1 sin bl.....(1)
2
2
1
1
I 2 Yo (Vo e jbl Vo e jbl ) Yo [ (V1 Z o I1 )e jbl (V1 Z o I1 )e jbl ] jYoV1 sin bl I1 cos bl.....(2)
2
2
(2) V1 jZ o I1 cot bl jZ o I 2 csc bl.....(3)
(3)
cot bl csc bl
(1) V2 jZ o I1 cos bl cot bl jZ o I 2 cot bl jZ o I1 sin bl Z jZ o
csc bl cot bl
= jZ o I1 csc bl jZ o I 2 cot bl
Z1 Z11 Z12 jZ o (cot bl csc bl ) Z 2 , Z 3 Z12 jZ o csc bl
V1 Vo Vo , I1 Yo (Vo Vo ) Vo
4-12
微波電路講義
4. Reciprocal lossless network
Re{Z ij } 0
5. Problems to use Z- or Y-matrix in microwave circuits
1) difficult in defining voltage and current for non-TEM lines
2) no equipment available to measure voltage and current in
complex value (eg. sampling scope in microwave range,
impedance meter <3GHz)
3) difficult to make open and short circuits over broadband
4) active devices not stable as terminated with open or short circuit
4-13
微波電路講義
4.3 The scattering matrix
t1’
V1’+
t1
V1’¯
V1+
V1¯
q1=bl1
port 1
N-port
network
port NVN¯
tN
tN’
VN+
VN’¯
VN’+
qN=blN
V1 S11 S12
V2 S21
V S V ,
V S
N N1 S N 2
S1N
S2 N
S NN
4-14
V1
V2
Vi
responsei
, Sij
Vj
source j
V
0,
k
j
k
V
N
Vk 0, k j
微波電路講義
Discussion
1. Ex 4.4 a 3dB attenuator (Zo=50Ω)
Z in 8.56 41.44 50
Z in Z o
V1
S11
0( ) V1 0 V1 V1 V1 V1
Z in Z o
V1
41.44
50
1
1
0.707V1
V1
V1 S 21V1
41.44 8.56 50 8.56
2
2
1
0
reciprocal S 21 S12
2
: lossy
S
symmetric S11 S 22
1
0
2
V2 0, V2 V2 V1
1 V1
incident power to port 1:Pinc ,1
2 Zo
transmitted power from port 2: Ptrans ,2
2
1 V2
2 Zo
input match
attenuator design
R1 , R2
attenuation
value
2
1
V
1 2 1
2
Zo
4-15
2
2
1 1 V1
: 3dB attenuation
2 2 Zo
微波電路講義
2. T-type attenuator design
Zo
R1
Eth
R1
V1
R2
V2
Zo
Z in
Zin R1 Zo // R2 R1 Zo
R2 // R1 Z o
Zo
V2
S21
V1 R1 R2 // R1 Z o R1 Z o
3dB attenuator
1
2
1
Zo
1
2
R2
Zo
1 2
R1
1
2 1
Zo
Zo
1
2 1
2
R2
Zo 2 2Zo
1 2
R1
4-16
微波電路講義
3. Relation of [Z], [Y], and [S]
S Z U 1 Z U , Y Z 1
(derivation)
Let Z on 1,
Vn Vn Vn
I n Vn Vn
V Z I V V Z (V V )
Z V V Z V V
( Z U ) V ( Z U ) V
V S V ( Z U ) S V ( Z U ) V
S ( Z U )1 ( Z U )
4-17
微波電路講義
4. Reciprocal network
S S t, S : symmetric matrix
(derivation)
Vn Vn Vn Vn (Vn I n ) / 2
Let Z on 1,
I n Vn Vn
Vn (Vn I n ) / 2
1
1
V (V I ) ( Z U ) I
2
2
1
1
V (V I ) ( Z U ) I
2
2
V ( Z U )( Z U ) 1 V S ( Z U )( Z U ) 1
S
t
from 3
(( Z U ) ) ( Z U ) ( Z U ) ( Z U )
1 t
t
4-18
1
S
微波電路講義
5. Lossless network (unitary property)
i j
1
S S U , S S
k 1
0
N
t
*
*
ki kj
i j
(derivation)
Let Z on 1
lossless (incident power=transmitted power) net averaged input power
P
in ,i
i
Pin
*
*
1
1
t
*
Re(V I ) Re[( V V )t ( V V )]
2
2
Im
t
*
t
*
t
*
t
*
1
Re[ V V V V V V V V )] 0
2
t
*
t
V V V V
V S V
*
V S S V
t
t
*
*
S S U
t
*
N
6. Lossy network
S
k 1
*
S
ki ki 1
4-19
微波電路講義
=0
0.150o 0.85 45o
S =
0
0
0.85
45
0.2
0
7. Ex.4.5
S :not symmetric a non-reciprocal network
S11 S 21 0.745 1 a lossy network
2
2
port 1 RL 20 log S11 16.5dB
port 2 RL 20 log S 22 14dB
IL 20 log S 21 1.4dB
port 2 terminated with a matched load L 0
in S11 0.15, RL 20 log 0.15 16.5dB
port 2 terminated with a short circuit L 1
in S11
S12 S 21 L
0.452, RL 6.9dB
1 S 22 L
4-20
微波電路講義
8. Shift property
t1’
V1’+
t2’
t1
V1’¯
V1+
V1¯ port 1 port 2 V2¯
V2+
V2’¯
t2 q2=bl2
q1=bl1
S '11 e j 2q1 S11 , S '21 e jq1 S21e jq2 , S '12 e jq2 S12e jq1 , S '22 e j 2q2 S22
e jq1
0
j q2
0
e
'
n-port network: S
0
0
e jq1
0
0
j q2
0
0
e
S
e jqN
0
0
0
0
jq N
e
9. S-matrix is not effected by the network arrangement.
4-21
微波電路講義
V2’+
Ii
10. Power waves on a lossless transmission line with Zoi
Vi
incident (power) wave : ai
Z oi
=
Vi Z oi I i
2 Z oi
Vgi
Vi
V Z oi I i
reflected (power) wave : bi
= i
Z oi
2 Z oi
b
V S V b S a , Sij i
aj
Pin ,i
ak 0 ,k j
Vi Z oj
V j Z oi
ZL
Pin,i
Vk 0 ,k j
1
1 2 1 2
2
Re{Vi I i*} ai bi Pinc ,i Prefl ,i Pinc ,i (1 Sii ) PL
2
2
2
(derivation)
+
ai =
Zoi Vi
Vi
,b i =
V i-
,V i = V i+ +V i- = Z oi (a i + b i ),I i =
V i+ -V i- a i - b i
=
Z oi
Z oi
Z oi
Z oi
2
2
1
1
1
Pin ,i = Re{V i I i* }= Re{(a i + b i )(a i - b i ) *}= Re{ a i - b i + a *i b i - a i b i* }
2
2
2
2 1
2
2
1
bi
= a i - b i =Pinc ,i - Prefl ,i = Pinc ,i (1- S ii ),S ii =
2
2
a i a k=0 ,k¹i
V i+
2
1
= Re{Pi+ - Pi- } ® Pi+ =
= ai
2
Z oi
2
,Pi- =
V i-
4-22 Z oi
Im
2
= bi
2
微波電路講義
11. Two-port device with its S-matrix
S11
S 21
S12
S 22
b1
a1
b2
a1
b1
a2
b2
a2
: reflection coefficien t at port 1 with port 2 matched
a2 0
: forward transmission coefficien t with port 2 matched
a2 0
: reverse transmission coefficien t with port 1 matched
a1 0
: reflection coefficien t at port 2 with port 1 matched
a1 0
b1 S11
b S
2 21
b1 a1 S11 a 2 S12
S12 a1
S22 a2
b2 a1 S 21 a 2 S 22
4-23
微波電路講義
12. Reflection coefficient and S11, S22
Zg
g
in
Zo, b out
Zin
in
L ZL
Zout
Zin Z g
Zout Z L
Z L Zo
g , out
L , if Z g Zo then L
Zin Z g
Zout Z L
Z L Zo
Zo
S11
two-port
network
Zo
Zin Z o
S11
Zin Z o
Zo
two-port
network
S22
4-24
Zo
S22
Z out Z o
Z out Z o
微波電路講義
13. RL and IL
RL at port 1: - 20 log
b1
-20 log S11
a1
b2
IL from port 1 to port 2: - 20 log
-20 log S21
a1
PL1
insertion loss IL(dB) 10log
PL 2
a1
a1
Zg
b2
Zg
PL1
PL2
b1
Zo
usually Zg=Zo
4-25
two-port
network
Zo
微波電路講義
14. Two-port S-matrix measurement using VNA
V1
V1
DUT
V2
V2
Zo
a1
b1
b2
a2
→ S11
→ S21
15. Advantages to use S-matrix in microwave circuit
1) matched load available in broadband application
2) measurable quantity in terms of incident, reflected and
transmitted waves
3) termination with Zo causes no oscillation
4) convenient in the use of microwave network analysis
微波電路講義
4-26
16. Generalized scattering parameters
incident power wave ai
reflected power wave bi
Vi Z ri I i
2 Re Z ri
Ii
Zgi
, Z ri : reference impedance
Vgi
Vi Z ri * I i
Vi
ZL
2 Re Z ri
power wave reflection coefficient Sii
power reflection coefficient Sii
2
b
i
ai
2
bi Vi Z ri * I i Z L Z ri *
ai
Vi Z ri I i
Z L Z ri
Pin,i
2
Z Z ri *
L
, conjugate match Z L Z ri * Sii
Z L Z ri
2
0
1
1
2
2
Re{Vi I i *} ( ai bi ) PL
2
2
Ref: K.Kurokawa,"Power waves and the scattering matrix", IEEE-MTT, pp.194-201, March 1965
traveling wave along a lossless line with real Z 0
Pin ,i
Vi
Vi
Vi Vi ai bi
ai
, bi
, Vi Vi Vi Z oi (ai bi ), I i
Z oi
Z oi
Z oi
Z oi
ai bi
Sii
Vi
Z oi
, ai bi I i Z oi ai
Vi Z 0 I i
2 Z0
, bi
Vi Z 0 I i
2 Z0
bi Vi Z oi I i Z L Z oi
,impedance match Z L Z oi Sii 0
ai Vi Z oi I i Z L Z oi
4-27
Ii
Zoi Vi
ZL
微波電路講義
Ii
Vgi
ZL
Vi Vgi
, Ii
Z L Z gi
Z L Z gi
PL
Zgi
Vgi
2
gi
V
Re Z L
1
Re{Vi I i *}
2
2 Z Z
L
gi
ai
if Z L Z ri *
Vi Z ri I i
2 Re Z ri
bi
2 Re Z ri
PL Pin ,i
2
Pin,i
Vgi
Vi Z ri * I i
ZL
Vi
ZL
1
Z ri
Z L Z gi
Z L Z gi
Vgi
2 Re Z ri
Z L Z ri *
Vgi
ZL
1
Z ri *
Z L Z gi
Z L Z gi
2 Re Z ri
Re Z ri
Z L Z gi
0 Sii 0
Re Z ri
Vgi2
1 2
ai Pinc ,i
2
2 Z Z 2
L
gi
2
1 Vgi
if Z L Z g * PL =
:maximum power trasfer from source
8 Re Z L
4-28
微波電路講義
a F (V Z r I )
b F (V Z r * I )
0
Z r1 0 .
0 . 0 0
Z r
0 0 .
0
0
0
0
Z
rN
Re Z r1
0
1
F
0
2
0
0
.
0
.
0
0
0
.
0
0 0
Re Z rN
,
V Z I b F ( Z Z r *)( Z Z r ) 1 F
S F ( Z Z r *)( Z Z r ) 1 F
4-29
1
a
1
微波電路講義
4.4 The transmission (ABCD) matrix
• Cascade network
I1
V1
+
_
I2
A
C
B
D 1
V2
+
_
I3
A
C
B
D 2
V3
+
_
B V2 A
B A
B V3
V1 A
D 1 I 2 C
D 1 C
D 2 I 3
I 1 C
Discussion
1. ABCD matrix of two-port circuits (p.190, Table 4.1)
2. Reciprocal network AD-BC=1
3. S-, Z-, Y-, ABCD-matrix relation of 2-port network (p.192,
Table 4.2)
4. Ex. 4.6 ABCD(Z)
微波電路講義
4-30
(derivation) Z (ABCD)
V1 Z11 Z12 I1 V1 A B V2
V Z Z I , I C D I
2
2 21 22 2 1
Z11
Z12
V1
I1
I 2 0
V1
I2
AV2 A
CV2 C
I1 0
AV2 BI 2
I2
V
A 2
I2
I 0
1
B, I1 0 CV2 DI 2
I1 0
D
AD BC
A( ) B
C
C
Z 21
V2
I1
Z 22
I 2 0
V2
I2
V2
CV2 DI 2
I1 0
I 2 0
V2 D
I2 C
symmetrical network
Z11 Z 22 A D
1
C
reciprocal network
D
, I1 0 CV2 DI 2
C
4-31
Z12 Z 21
AD BC 1
AD BC 1
C
C
微波電路講義
(derivation) S (ABCD)
V1 (V1 Z o I1 ) / 2
b1 S11 S12 a1 V1 A B V2 V1 V1 V1
b S S a , I C D I ,
I
(
V
V
)
/
Z
V1 (V1 Z o I1 ) / 2
2 1
2 21 22 2 1
1
1
o
V Z I
AV BI 2 Z oCV2 Z o DI 2
b1
V1
S11
1 o1
2
a1 a 0 V1 V 0 V1 Z o I1 V 0 AV2 BI 2 Z oCV2 Z o DI 2 V 0
2
2
2
2
I2
A BYo CZ o D
V2 0
A BYo CZ o D
Z o V2 I 2 Z o , I 2 V2Yo
V2
b
S 21 2
a1
V2 V2
V2
V2
2V2
V1 V 0
(V1 Z o I1 ) / 2 AV2 BI 2 Z oCV2 Z o DI 2
a 0
I 2 V2Yo
2
2
2
A BYo CZ o D
4-32
微波電路講義
b
S12 1
a2
a1 0
V1
V2
V1 0
V2 V2 V2
V2 (V2 Z o I 2 ) / 2
,
I 2 (V2 V2 ) / Z o V2 (V2 Z o I 2 ) / 2
V1 V1
V 1 D B V1
V1
, 2
I , AD BC
I
(V2 Z o I 2 ) / 2 2 C A 1
2V1
2V1
( DV1 BI1 Z oCV1 Z o AI1 ) / DV1 BYoV1 CZ oV1 AV1
2Δ
A BYo CZ o D
Zo
b
S 22 2
a2
I2
V1
V2 V1 I1Zo , I1 V1Yo
V Z I DV BI1 Z o (CV1 AI1 )
V2
2 o 2 1
V2 V 0 V2 Z o I 2 DV1 BI1 Z o (CV1 AI1 )
a 0
I1 V1Yo
I1
1
1
DV1 BYoV1 Z o (CV1 AYoV1 ) A BYo CZ o D
DV1 BYoV1 Z o (CV1 AYoV1 ) A BYo CZ o D
4-33
symmetrical
S11 S 22 , A D
reciprocal
S12 S 21, 1
微波電路講義
5. Example
t1
Zoc
t2
coaxial-microstrip transition
(a linear circuit)
[S]
Zom
[S] representation can be obtained from
measurement or calculation.
L
Zoc
C1
C2
Zom
one possible equivalent circuit
4-34
微波電路講義
4.5 Signal flow graphs
• 2-port representation
a1
a1
b1
a2
b2
[S]
port 1
b1 S11
b S
2 21
S22
a2
S12
b1 a1 S11 a 2 S12
S12 a1
S22 a2
RL at port 1: - 20 log
b2
S11
b1
port 2
S21
b2 a1 S 21 a 2 S 22
b1
-20 log S11
a1
IL from port 1 to port 2: - 20 log
4-35
b2
-20 log S21
a1
微波電路講義
Discussion
1. Source representation
Zs
as
} a1
b 1 s
b1
s
Vs
es Vs
as
Zo
e
, as s
Zo Z s
Zo
1
a1
s
b1
2. Load representation
b2
b2
L ZL
L
a2
a2
3. Series, parallel, self-loop, splitting rules (p.196, Fig.4.16)
4-36
微波電路講義
4. 2-port circuit representation
as
Zs
Vs
s
in
[S]
out
LZL
a1 S21 b2
s
b1 S12
b1 a1S11 a1S21 Γ L S12 (1 S22 Γ L ...) a1S11 a1
Γ in
S12 S21 Γ L
1 S 22 Γ L
b1
S S Γ
S11 12 21 L
a1
1 S22 Γ L
Γ out
as
a2
a1
s
b2 a2 S 22 a2 S12 Γ S S21 (1 S11 Γ S ...) a2 S22 a2
S S Γ
b2
S 22 12 21 S
a2
1 S11 Γ S
in
b1
S12 S21 Γ S
1 S11 Γ S
b2
out
4-37
L
S11 S22
L
a2
微波電路講義
5. TRL (Thru-Reflect-Line) calibration
Find [S]DUT from 2-port measurement using three calibrators
DUT
[S]
x
ao
y
b1
e10
e00 e11
e01
a2
S21
S11 S22
S12
b3
e32
e22 e33
e23
bo
a1
b2
a3
6 unknowns of [S]x and [S]y to be calibrated to acquire [S]DUT
T: Through 3 eqs., R: Reflection 2 eqs., L: Line 3 eqs.
R () and line length (l) can be unknown
微波電路講義
4-38
Calibrators
T: Through
3 eqs.
x
R: Reflection
2 eqs.
L: Line
y
x
y
exp(l)
3 eqs.
x
y
Requirement: connectors and line have same characteristics for 3 calibrators
Limitation: operation bandwidth 20°≦βl≦160°
微波電路講義
4-39
(brief derivation )
R matrix (wave cascade matrix)
b1 R11 R12 a 2
a R
1 21 R22 b2
R11 R12
1 S12 S21 S11S22 S11
R
S22
1
S21
R21 R22
x12
x
y11
error matrices Rx 11
,
R
y y
x21 x22
21
0 1
1 0
Through: ST
R
T
0 1
1 0
0
Line: S L l
e
Reflection:
Thru measurement:
Line measurement:
e l
0
e l
RL
0
y12
y22
1 / e l
0
RmT Rx RT R y Rx
RmL Rx RL Ry
4-40
R y
微波電路講義
M Rx Rx RL ,
Ry N RL Ry ,
M RmL RmT
1
N RmT
1
reflection measurement at port 1 mx
RmL
e11 , e22 , e10e01 , e23e32
e00,
e33,
e01e10
e11
e23e32
e22
e10e01
e00
1 e11
reflection measurement at port 2 my e33
Γ mx
Γ my
Γ mT
S21mT
S12 mT
e23e32
1 e22
e10e32 , e23e01
e10 , e01 , e23 , e32
Γ, e l
4-41
微波電路講義
(det ailed derivation )
m11 m12 x11
M
R
R
R
x x L
m21 m22 x21
x12 x11
x22 x21
x12 e l
0
x22 0 1 / e l
m11 x11 m12 x21 x11e l
x11 2
x11
x11
e10e01
m
(
)
(
m
m
)
m
0
a
e
21
22
11
12
00
l
x21
x21
x21
e11
m21 x11 m22 x21 x21e
l
x12
m11 x12 m12 x22 x12 / e m21 ( x12 ) 2 ( m22 m11 ) x12 m12 0
b
e00
m21 x12 m22 x22 x22 / e l
x22
x22
x22
root choice : e10e01 0 a b, e00 e11 1 a b
y
R y N RL R y 11
y21
y12 n11 n12 e l
0 y11
y22 n21 n22 0 1 / e l y21
y12
y22
y11n11 y12n21 y11e l
y11 2
y11
y11
e23e32
n
(
)
(
n
n
)
n
0
c
e
12
22
11
21
33
l
y12
y12
y12
e22
y21n11 y22n21 y12e
l
y21
y11n12 y12n22 y12 / e n12 ( y21 ) 2 ( n22 n11 ) y21 n21 0
d
e33
y21n12 y22n22 y22 / e l
y22
y22
y22
root choice : e23e32 0 c d , e22 e33 1 c d
4-42
微波電路講義
e10e01 Γ
1 b Γ mx
Γ
e
Γ
00
mx
1 e11 Γ
e11 a Γ mx
e23e32 Γ
1 d Γ my
Γ
e
Γ
my
33
1 e22 Γ
e22 c Γ my
e e e
1 b Γ mT
Γ mT e00 10 01 22 e11
1 e11e22
e22 a Γ mT
b Γ mx c Γ my b Γ mT
1 b Γ mT
2
e11
, e22
, e10e01 (b a )e11 , e23e32 =( c - d )e22
a Γ mx d Γ my a Γ mT
e11 a Γ mT
e10e32
S
21mT 1 e e
11 22
e10e32 S21mT (1 e11e22 ), e23e01 =S12 mT (1 e11e22 ) e10 , e01 , e23 , e32
e
e
S12 mT 23 01
1 e11e22
1 b Γ mx
m
Γ
...(also for e11 selection), e l m11 12
e11 a Γ mx
a
4-43
微波電路講義
4.6 Discontinuities and modal analysis
• equivalent circuit components
E C, H L
constant E (V) parallel connection
constant H (I) serial connection
Discussion
1. Microstrip discontinuities
Cg
Cp
Coc
open-end
Cp
gap
4-44
微波電路講義
L
L
C
step
L1
L2
C
L3
L
L
T-junction
C
bend
4-45
微波電路講義
2. Microstrip discontinuity compensation
w
a
r
a=1.8w
r>3w
swept bend
mitered bends
mitered step
mitered T-junction
4-46
微波電路講義
Solved Problems
Prob. 4.11 Find [S] relative to Z0
port
1
Z
port
1
port
2
Z
port
2
é
ù
éY ù = ê 1/ Z -1/ Z ú,DY = (Y o +Y 11 )(Y o +Y 22 ) +Y 12Y 21 = Z + 2Z o
Z Z
2
ë û
ZZ o2 Z Z Z , Z ( Z o Z 11 )( Z o Z 22 ) Z 12 Z 21 2Z o Z Z o
ë -1/ Z 1/ Z û
é (Y -Y )(Y +Y ) +Y Y
ù
2Z 12 Z o
( Z 11 Z o )( Z 22 Z o ) Z 12 Z 21
-2Y 12Y o
o
11
o
22
12 21
ê
ú
Z
Z
DY
DY
ú S
éS ù = ê
ë û ê
2Z 21Z o
( Z 11 Z o )( Z 22 Z o ) Z 12 Z 21
-2Y 21Y o
(Y o +Y 11 )(Y o -Y 22 ) +Y 12Y 21 ú
ê
ú
Z
Z
DY
DY
ë
û
2
Z o
2Z
2ZZ o Z o
ù
é
ù é
2
Z
2Z
o
2 / ZZ o ú ê
Z o 2Z Z o 2Z
Z
Z
ú
ê 1/ Z o
,1 S 11 S 21
2
2Z
Z o
Z + 2Z o Z + 2Z o ú
ê
ê
DY
DY
ú
2
ZZ
Z
o
o
=
=
,1- S 11 = S 21
Z
ú
ê 2 / ZZ
Z Z o 2 Z Z o 2Z
Z
1/ Z o2 ú ê 2Z o
o
ú
ê
ú ê
DY
ë DY
û êë Z + 2Z o Z + 2Z o úû
Prob. 4.12 Find S21 of [SA] in cascade of [SB]
S21A
S11A
S21
S21B
S22A
S11B
S12A
S22B
S12B
4-47
S21 AS21B
1 S22 AS11B
微波電路講義
0.17890 0
0
0.645
0.445 0
0
Prob. 4.14
0.645 0
0
0
0.3 45 0
0.445 0
0
0
0.5 45 0
0
0.3 45 0
0.5 45 0
0
(1) S12 S 42 0.8 1 lossy
2
2
(2)[ S ] symmetrical reciprocal
(3)return loss at port 1 20 log S11 20 log 0.1 20dB
(4)insertion loss between port 2 and port 4 20 log S 24 20 log 0.4 8dB
phase delay between port 2 and port 4 450
(5)reflection at port 1 as port 3 is connected to a short circuit
b1 0.17890 0
b 2
0
0.6
45
b 3 0.445 0
0
b 4
b 3 0.445 0 a 1
0.645 0
0.445 0
0
0
0
0
0.3 45 0
0.5 45 0
a1
0.3 45 0 0
0.5 45 0 b 3
0
0
0
b1 0.17890 0 a 1 0.445 0 b 3 0.17890 0 a 1 0.1690 0 a 1 0.01890 0 a 1
S 11
b1
0.018 j
a1
4-48
微波電路講義
Prob. 4.19 given [Sij] of a two-port network normalized to Zo, find
its generalized [S’ij] in terms of Zo1 and Zo2
incident (power) wave : ai
reflected (power) wave : bi
Vi
Z oi
Vi
Z oi
=
Vi Z oi I i
=
2 Z oi
Vi Z oi I i
2 Z oi
b
V S V b S a , Sij i
aj
S11' S11 , S12' S12
Zo2
Z o1
'
, S21
S21
4-49
Z o1
Zo2
ak 0 ,k j
Vi Z oj
V j Z oi
Vk 0 ,k j
'
, S22
S 22
微波電路講義
Prob. 4.28 find P2/P1 and P3/P1
0
S
12
0
P1
S12
0
S 23
a1
0
S 23
0
P2
Γ2
Γ3
b1
S12
S23
S23
P3
2
2
2
b3 (1 3 )
P3 b3 a3
2
2
2
2
P1
a1 b1
a1 (1 in )
2
2
2
S12 (1 2 )
2
2
2
1 23 S
S12
2
2 2
23
2
1 23 S
(1
S 2
2
2
1 23 S
2 2
23
)
S 23 (1 3 )
2
2 2
23
S12 (1 2 )
2
2
12
2
(1
2
S 2
2
12
Γ2
a2
b3
Γ3
a3
S S
S122 2
S12
b1 a1
a1in , b2 a1
, b3 a1 12 2 232
2
2
1 2 3 S 23
1 2 3 S23
1 2 3 S23
b2 (1 2 )
P2 b2 a2
2
2
2
2
P1
a1 b1
a1 (1 in )
b2
S12
2
1 23 S
2 2
23
)
2
2
2
1 2 3 S23
S122 2
S12
2
2
2
2
S 23 (1 2 )
2
2
2
1 2 3 S23
S122 2
ADS examples: Ch4_prj
4-50
微波電路講義
2
2