Calculus II (Math 102)
advertisement

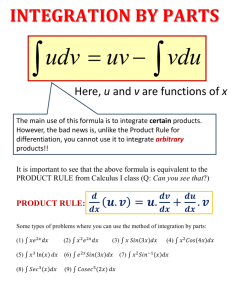
QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 1. Major Course Information Course Syllabus Math 102 (Calculus II) Girls Spring Semester 2013 1.1 Course Data Course Number: Math 102 Course Title: Calculus II Course Section: L54 Course CRN: 24878 Credit Hours: 3 Contact hours: 4 Pre-requisite : Calculus I Course Status: Major compulsory First day of Classes: February 10, 2013 Last day of Classes: May 23, 2013 Time: Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 and Sundays 11:00-11:50. Location: D-210 College of Arts and Sciences Female Building. Required Text: Calculus by James Stewart, 6th Edition, 2008, Brooks/Cole 1.2 Faculty Information Name: Dr. Safeer Hussain Khan E-mail: safeer@qu.edu.qa Office Phone: 4403 4614 Office Location: C 216 (male) OFFICE HOURS: Sundays 12-1 PM Monday Wednesday 1230-130 PM By appointment Office hours in Room A210 College of Arts and Sciences Female Building. CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page1 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 1.3 Course Description MATH 102 is the second course in a three-course calculus series (CALCULUS I-III) which is required for Science and Engineering students. It starts from the study of transcendental functions. Then a very important part covers the techniques of integration. Parametric equations and polar coordinates are studied and applied to find area in polar coordinates. Finally the sequences and series are taken into account. A number of tests for convergence are learned in this course. Taylor and Maclaurin’s series are applicable series. 1.4 Course Contents 1. Transcendental Functions: Inverse trigonometric functions. Hyperbolic functions. Inverse hyperbolic functions. Derivative of inverse hyperbolic functions. Integrals involving inverse trigonometric and inverse hyperbolic functions. 2. Techniques of Integration: Integration by parts. Integrals involving trigonometric functions. Trigonometric substitutions. Partial fractions. Rationalizing substitutions. Improper Integrals. 3. Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates: Polar coordinates. Curves defined by parametric equations. Tangent lines and length for parametric and polar curves. Area in polar coordinates. 4. Sequences and Infinite Series: Sequences. Infinite series. Convergence tests. Absolute and conditional convergence of alternating series. Power series. Taylor series CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page2 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 1.5 Course Objectives The course aims at: 1. To introduce trigonometric inverse functions and their properties. 2. To introduce Hyperbolic functions and their inverses. 3. To develop skills to evaluate integrals using different integration techniques. 4. To introduce improper integrals and methods for their evaluation. 5. To introduce sequences and use it to develop the study of properties of infinite series. 6. To introduce infinite series and develop skills to determine their convergence. 7. To introduce power series and expansion of functions in Taylor series and Maclaurin series. 8. To introduce polar coordinate system and find the tangent lines and arc length for parametric and polar curves. 9. To find area in polar coordinates. 1.6 Educational Outcomes By the end of the course, the students should be able to: 1. Identify the properties of inverse trigonometric functions, hyperbolic, and inverse hyperbolic functions. 2. Find the derivatives and integrals of inverse trigonometric, hyperbolic, and inverse hyperbolic functions. 3. Evaluate the indefinite and improper integrals by using different integration techniques. 4. Identify the properties of sequences and their limits. 5. Use various tests to determine convergence of series. 6. Perform standard operations with convergent power series, including the method of differentiating and integrating term by term. 7. Use Taylor and Maclaurin series to approximate functions. 8. Sketch the graphs of parametric and polar equations. 9. Use parametric and polar equations to solve applied problems including area and arc length. CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page3 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 1.7 Distribution of Contents Lectures schedule Week 1 Date FEB 10—FEB 14 Sec. 6.6 Topics 6.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions, Derivatives and Integrals Involving Inverse Trigonometric Functions. Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions. Derivatives and Integrals Involving Inverse Hyperbolic Functions. 2 FEB 17—FEB 21 7.1 7.2 Integration by Parts Trigonometric Integrals 3 FEB 24—FEB 28 Trigonometric Substitution 4 MAR 3—MAR 7 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.8 8.1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Integrating Rational Functions by Partial Fractions Strategy for Integration Improper Integrals Arc Lengths Review for Exam 1 First Exam; Saturday March 16, 14--16 8.2 MAR17-MAR 21 Area of surface of revolution 8.3 Applications to Physics and Engineering MAR10-MAR14 MAR 24-MAR 28 10.1 10.2 APR 21--APR 25 11.3 11.4 Curves Defined by Parametric Equations Calculus with Parametric Curves March 31 — April 6 Spring Break Polar Coordinates. 10.3 APR 7—APR 11 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates 10.4 11.1 APR 14—APR 18 Sequences 11.2 Series The Integral Test and Estimates of Sums The comparisons Tests 11.5 APR 28--MAY 2 Alternating series Review for Exam 2 Second Exam; Saturday April 27, 14--16 11.6 MAY 5—MAY 9 Absolute Convergence and the Ratio and Root Tests 11.7 Strategy for Testing Series 11.8 MAY 12-MAY 16 Power Series 11.9 Representations of Functions as Power Series 11.10 MAY 19-MAY 23 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Final Exam: Sunday, May 26, 14-16 CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page4 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM Delivery Methods We will use different types of teaching methods including: Presentation explaining material. Problem solving. Discussion - actively involving students in learning by asking questions that provoke thinking and verbal response. Using Math packages explaining some material. The lecture will be posted on the e-learning tool Blackboard, so pay your full attention to the class and try to understand everything. 1.8 Learning Resources & Media In class we will use Digital Camera to explain mathematical formulas Data show will be used also to visualize some important graphs in the three dimension space We will use some math packages including MATHEMATICA. Blackboard will be used frequently: http://mybb.qu.edu.qa/ The Student companion site for the text: http://www.stewartcalculus.com/media/7_home.php CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page5 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 1.9 Additional Sources Online Sources The Student companion site for the text: http://www.stewartcalculus.com/media/7_home.php http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/ http://www.mathword.wolfram.com Google and other search engines Printed Sources Calculus by H. Anton, I. Bivens and S. Davis, 8th Edition, 2005, Wiley. Calculus, by Swokowski, Sixth Edition 1994,PWS Publishing Company, Boston. Calculus with Analytic Geometry, by H. Edwards and D. E. Penny, 5th Edition, 1998, Prentice Hall. Calculus, by R.T. Smith and R.B. Minton, 2nd Edition, 2002, McGraw-Hill. Calculus: One and Several Variables by S. L. Salas, G. J. Etgen and E. Hille; 10th Edition, 2007, John Wiley & Sons. Calculus, Early Transcendentals by J. Stewart, 6th Edition, 2008, Brooksw/Cole. Non-Printed Sources Course notes will be posted on the blackboard system: http://mybb.qu.edu.qa/ CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page6 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 2.5 Assessment Policy and Tools Grades for the course will be assigned as follows: Percent grade Letter grade Earned Points 90 100 A 4.0 85 - 89 80 - 84 B+ 3.5 B 3.0 75 79 C+ 2.5 70 - 74 65 - 69 60 - 64 below 60 C 2.0 D+ 1.5 D 1.0 F 0.0 Description of Exams: 1. Exams: (80%) There will be three major exams: 1. First Exam: 22.5%, Saturday, 16 March 2013 2. Second Exam: 22.5%, Saturday, 27 April 2013 3. Final Exam: 35%, Sunday, 26 May 2013 14:00 - 16:00 14:00 - 16:00 14:00 - 16:00 Each exam will consist of comprehensive questions; there will be partial credits, so students are required to show all their work to maximize their grades. 2. Quizzes (10%) Approximately a total of 4 quizzes during the course. Quizzes will be announced in advance. Each quiz will normally consist of 2 - 3 questions. No make-up quizzes in any case. Best 3 out of 4 will be chosen for evaluation. 3. Assignments (5%) Approximately 3-4 assignments, students are required to answer all problems. Late submission leads to deduction of marks. 4. Mathematica (5%) Mathematica assignments carry 5% marks. CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page7 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 2.6 Methods of Student Evaluation Marks are awarded on the basis of both presentation and concept. Students should show all their work to maximize their grades. Three examinations will be given: First Major Exam, Second Major Exam and the Final Exam. The final exam is comprehensive. Make-up for final examination only under official permission by the university. Four or Five quizzes will be given. As a matter of principle, no quiz will be repeated. Best three will be counted towards evaluation. Four or Five assignments will be given and best three will be chosen for evaluation. Assignments are to be returned on time. Late submission will result in loss of marks. A presentation of the assignment problems may be required in the class and carries marks. Special assignment involving use of Mathematica carries five percent marks. The exam dates and times and the due dates and times for the home works, that we agree upon cannot be and will not be changed. Exam 1 and Exam2 may be re-taken only under a genuine reason like proven illness or mishap. A certificate of the same is required before the make-up exam. 2.7 Learning Activities and Tasks Basically students are responsible for their own ongoing learning process. They need to do their assignments independently unless they are allowed to work in groups. Different activities for learning are done and tasks are given both in and outside the class. Students are involved in the lecture by asking different related questions. A quick revision helps the students in continuity of the material. They are made to think and give their opinion. Practice problems help them to learn more about the topic. Assignments give them a deeper vision. Presenting their assignments gives them a chance to share the ideas. Post-exam discussions make their concepts and presentations better. CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page8 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 2.8Practice Problems "Practice makes a man perfect" is a well-known saying. It is particularly true for mathematics students. Following are the Recommended Practice Problems from the text book. These problems are meant for the least practice. They only show the type of the problems you will encounter in this course. You are strongly urged to solve much more problems to get an excellent skill. Recommended Problems in the Textbook, to be attempted by the students LIST OF SELECTED PROBLEMS 7.1: 1 - 27 (odd), 29 – 41 (odd) 7.6: 1 – 13 (odd), 23 – 39 (odd), 43 – 46, 59-70 7.7: 1 – 23 (odd), 31 – 47 (odd), 54, 55, 57 – 65 8.1: 1 – 37 (odd), 43, 44, 45(a,b), 47 – 53 (odd) 8.2: 1 – 49 (odd), 57, 62, 67, 69 8.3: 1 – 31 (odd) 8.4: 1 – 51 (odd) 8.5: 1 – 79 (odd) 8.8: 1 – 39 (odd), 49 – 57 (odd) 9.1: 3-17 (odd) 9.2: 1 – 15 (odd), 27, 29, 33 9.3: 1 – 17 (odd), 29, 31, 35, 41, 45 11.1: 1 – 21 (odd), 24, 28, 31, 33, 41 11.2: 1 – 7 (odd), 11 – 19 (odd), 25, 31, 33, 39, 41, 44 11.3: 1 – 47 (odd), 49, 55, 59, 63, 65, 69 11.4: 1 – 41 (odd) 12.1: 1 – 45 (odd), 54, 61 – 65 (odd), 80 12.2: 1, 9, 11 – 51 (odd), 52, 55, 59, 65, 71 12.3: 3 – 29 (odd), 33, 39 12.4: 1, 2, 3 – 35 (odd), 39, 40, 41, 42 12.5: 1 – 19 (odd), 23, 25, 27, 29 12.6: 1 – 33 (odd) 12.7: 1 – 37 (odd) 12.8: 1 – 31 (odd) 12.9: 1 – 17 (odd), 23, 26, 27, 29, 35, 37 12.10: 1 – 37 (odd), 45, 47-50, 53, 57, 59, 63, 67 Edition 6 CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page9 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM Recommended Problems in the Textbook, to be attempted by the students LIST OF SELECTED PROBLEMS 6.1: 1 - 27 (odd), 29 – 41 (odd) 6.6: 1 – 13 (odd), 23 – 39 (odd), 43 – 46, 59-70 6.7: 1 – 23 (odd), 31 – 45 (odd), 54, 57, 59 – 67 7.1: 1 – 42 (odd), 47, 48, 49(a,b), 51 – 58 (odd) 7.2: 1 – 49 (odd), 57, 62, 67, 69 7.3: 1 – 31 (odd) 7.4: 1 – 51 (odd) 7.5: 1 – 81(odd) 7.8: 1 – 39 (odd), 49 – 57 (odd) 8.1: 3-17 (odd) 8.2: 1 – 15 (odd), 27, 29, 33 8.3: 1 – 17 (odd), 29, 31, 35, 41, 45 10.1: 1 – 21 (odd), 24, 28, 31, 33, 41 10.2: 1 – 7 (odd), 11 – 19 (odd), 25, 31, 33, 39, 41, 44 10.3: 1 – 45 (odd), 47, 53, 57, 61, 63, 65 10.4: 1 – 41 (odd) 11.1: 1 – 55 (odd), 64, 71 – 78 (odd), 92 11.2: 1, 9, 17 – 63 (odd), 64, 67, 73,79, 85 11.3: 3 – 31 (odd), 37, 43 11.4: 1, 2, 3 – 35 (odd), 39, 40, 41, 42 11.5: 1 – 19 (odd), 23, 25, 27, 29 11.6: 1 – 31 (odd),35 11.7: 1 – 37 (odd) 11.8: 1 – 31 (odd) 11.9: 1 – 19 (odd), 25, 28, 29, 31, 37, 39 11.10: 1 – 37 (odd), 45, 47-50, 53, 57, 59, 63, 69 Edition 7 CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page10 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM 2.9 Some instructions for the students Classroom Discipline The use of mobile telephones inside the classroom and during examinations is NOT allowed. Anyone found using mobile will be asked to leave the class. If you do it twice, you will counted absent for one day. Any disciplinary issues, which may arise, will be referred to the Head of the Department. General i n s t r u c t i o n s . Feel free to ask any question related to the course material inside the class, in the designated office hours, on-request office hours or by email. Prior to class, look over the section that will be covered. Check blackboard site http://mybb.qu.edu.qa for announcements and some class material like class notes, assignments, syllabus, assignments and exams solutions, etc. Only a limited use of calculators is allowed in the examinations. Such use is announced during the examination. Homework Problems will be assigned, and students are strongly urged to solve much more problems than indicated by the instructor. Department of Mathematics, Statistics and Physics provides syllabi very close to the ones of the most international universities. Deducting and cutting short this syllabus is impossible and the students should understand this in advance. 2.10 Course Regulations . Class attendance is compulsory. In accordance with University regulations, a student’s absence cannot exceed 25% of the total number (entire semester) of class meetings. If your absence rate exceeds 25%, including both excused and unexcused absences, you will NOT be allowed to take the final examination and will receive an ‘F barred’ grade for the course Students are expected to be punctual in class attendance and to conduct themselves in an adult and professional manner. Every 3 late class arrivals will be counted as one class absence. Homework assignments should be worked independently. While exchanging ideas is permitted orally, any kind of copying is not. CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page11 QATAR UNIVERSITY / COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MATH, STAT AND PHYSICS/MATH PROGRAM Homework assignments should be submitted in an organized way and any late assignments may be assessed and corrected but the grade may be reduced even to zero. 2.11 Plagiarism (Academic Dishonesty) All students are expected to turn in work that is their own. Any attempt to pass off another's work as your own will constitute an "F" in the entire course. Using part of, or the entire work, prepared by another or turning in a homework assignment prepared by another student or party are examples of plagiarism. You may discuss assignments and projects with each other, but you should do the work yourself. In the case of group projects, you will be expected to do your share of the work. If you use someone else's words or ideas, you must cite your sources. Plagiarism is considered a serious academic offence and can result in your work losing marks or being failed. QU expects its students to adopt and abide by the highest standards of conduct in their interaction with their professors, peers, and the wider University community. As such, a student is expected not to engage in behaviours that compromise his/her own integrity as well as that of QU. You may discuss assignments and projects with each other, but you should do the work yourself. In the case of group projects, you will be expected to do your share of the work. If you use someone else's words or ideas, you must cite your sources. Plagiarism includes the following examples and it applies to all student assignments or submitted work: Use of the work, ideas, images or words of someone else without his/her permission. Use of someone else's wording, name, phrase, sentence, paragraph or essay without using quotation marks. Misrepresentation of the sources that were used. For further information see: http://www.plagiarism.org/ The instructor has the right to fail the coursework or deduct marks where plagiarism is detected... CourseSyllabusCalculusIIDr.SafeerHussainKhan Spring2013 Page12