Intro to Business Chapter 2: Economic Systems UNIT TEST Name
advertisement
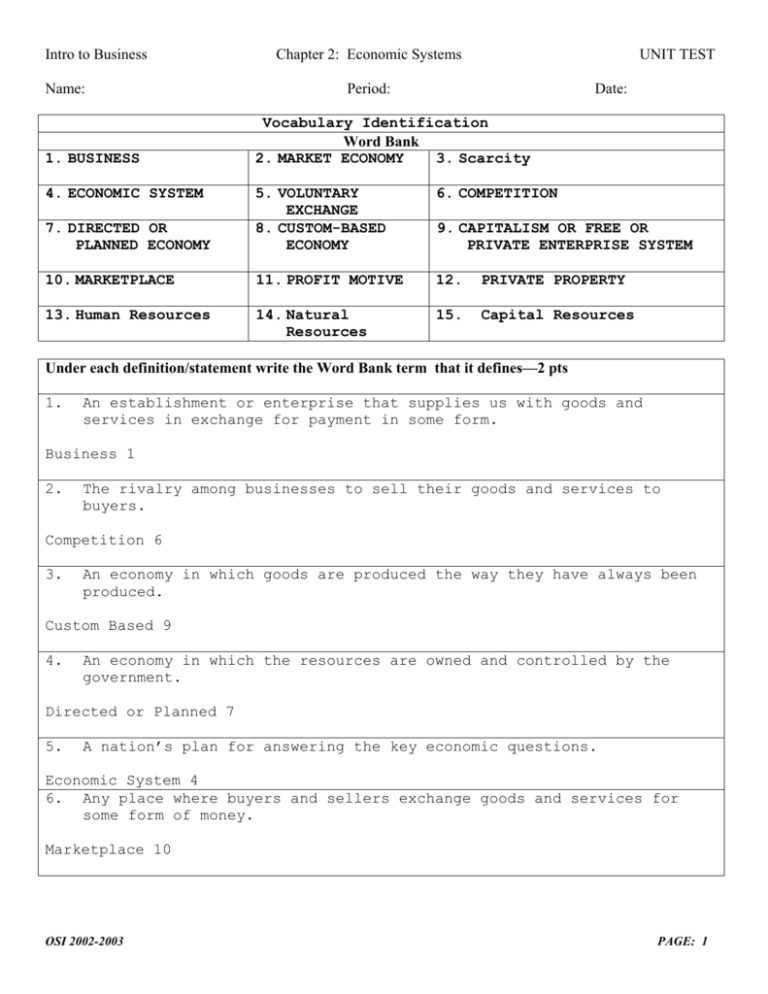
Intro to Business Name: 1. BUSINESS 4. ECONOMIC SYSTEM Chapter 2: Economic Systems UNIT TEST Period: Date: Vocabulary Identification Word Bank 2. MARKET ECONOMY 3. Scarcity 6. COMPETITION 7. DIRECTED OR PLANNED ECONOMY 5. VOLUNTARY EXCHANGE 8. CUSTOM-BASED ECONOMY 10. MARKETPLACE 11. PROFIT MOTIVE 12. PRIVATE PROPERTY 13. Human Resources 14. Natural Resources 15. Capital Resources 9. CAPITALISM OR FREE OR PRIVATE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Under each definition/statement write the Word Bank term that it defines—2 pts 1. An establishment or enterprise that supplies us with goods and services in exchange for payment in some form. Business 1 2. The rivalry among businesses to sell their goods and services to buyers. Competition 6 3. An economy in which goods are produced the way they have always been produced. Custom Based 9 4. An economy in which the resources are owned and controlled by the government. Directed or Planned 7 5. A nation’s plan for answering the key economic questions. Economic System 4 6. Any place where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services for some form of money. Marketplace 10 OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 1 Intro to Business Chapter 2: Economic Systems Name: Period: UNIT TEST Date: Vocabulary Identification Continued: 2 pts each 7. An economic system in which most economic resources are privately owned and decisions are largely made by free exchange in the marketplace. Capitalism or Free or Private Enterprise System 9 8. An economy in which individuals are free to engage in business transactions with buyers who are willing and able to buy and sellers who supply goods and services from which they earn a profit. Market Economy 2 9. The right to own, use, or dispose of things of value. Private Property 12 10. The desire to work hard and be creative to earn a higher profit. Profit Motive 11 11. Buyers and sellers make their own economic decisions to determine what the price will be for goods and services produced and sold. Voluntary Exchange 5 12. Basic Economic Problem—how does an economic system meet unlimited wants and needs with its limited resources. Scarcity 3 13. Materials (resources) that come from the earth, the water, or the air Natural Resources 14 14. The labor force, people who work to provide goods and services Human Resources 13 15. Tools, equipment, and machinery used to produce goods and services Capital Resources 15 OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 2 Intro to Business Name: Chapter 2: Economic Systems Period: UNIT TEST Date: True/False—2 pts each Directions: Mark a 9 in the corresponding True or False column to identify the statement as True or False: True False Statement: 1. A place where buyers and sellers come together to trade goods, services, and resources 9 is called a marketplace. 9 2. Voluntary exchange is controlled by the government. 9 3. Determining which of its citizens should benefit from the production of goods and services is something each nation must decide. 9 4. When the government or a business hires new employees, it is participating in the marketplace. 9 5. The basic economic problem, meeting unlimited wants and needs with limited resources is referred to as scarcity. 9 6. Scarcity is a problem that is faced by individuals, governments, and businesses. 9 9 7. In a system of capitalism, the government decides what will be produced with the resources available. 8. In a private enterprise system, you may start or invest in any business as long as it is legal to do so. 9 9. The profit motive is designed to allow lazy owners to become rich. 9 10. Freedom of choice is an important right included in a private enterprise system. 9 11. The economic system in the United States is primarily considered to be a Market Economy. 9 12. Most economies are composed of a mixture of characteristics from the three economic systems: Market, Planned or Directed, and Custom based. This concept is described as a Mixed Economy. 9 13. The economic system in the United States is pure capitalism with not government invention or regulation involved. 9 14. A place where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services for some form of money is called the marketplace. 9 15. An establishment or enterprise that supplies goods and services in exchange for some form of payment is called a business. OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 3 Intro to Business Chapter 2: Economic Systems Name: Period: UNIT TEST Date: Multiple Choice—2 pts each Directions: Write the letter of the answer that best completes each statement in the corresponding answer column Answer Column Statement: B 1. A market economy is one in which: a) Buyers and sellers operate according to government guidelines b) Individuals are free to exchange in business transactions (voluntary exchange) c) Stores stay open until late at night only when they are given permission d) There is a central market committee that solves problems D 2. Which of the following are goods? a) jackets b) CD players c) gasoline d) all of the above A 3. The means through which goods and services are produced are called: a) factors of production b) natural resources c) production materials d) human resources A 4. Which of the following are considered to be natural resources? a) fish b) farmer c) teacher d) school building C 5. The person who checks out purchases at the supermarket is part of : a) natural resources b) capital resources c) human resources d) none of the above OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 4 Intro to Business Name: Chapter 2: Economic Systems Period: UNIT TEST Date: Multiple Choice—2 pts each Directions: Write the letter of the answer that best completes each statement in the corresponding answer column Answer Statement: Column A 6. Members of a family might not be able to afford the things they want because an economic factor called: a) the basic economic problem—scarcity b) the family economic problem c) multiple greed d) human desires B 7. What step is defining the problem in the decision making process? a) second b) first c) last d) third A 8. Which of the following describes a situation in which scarcity can be a problem? a) a city wants to give fire fighters a large pay increase b) a business wants to enlarge its plant c) a family wants to extend its vacation d) all of the above B 9. Things you can see and touch are called: a) services b) goods c) scarcity d) none of the above D 10. Examples of raw materials include: a) oil b) water c) diamonds d) all of the above OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 5 Intro to Business Name: Chapter 2: Economic Systems Period: UNIT TEST Date: Identification: 5 pts The three questions every economic system must answer in its efforts to solve the basic economic problem (Scarcity) are: Write your answers below ??? 1—WHAT TO PRODUCE 2—HOW TO PRODUCE 3—FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE Identification: 5 pts What are the FIVE CHARACTERISTICS of a market economy: 1—Private enterprise 2—Private property 3—Profit 4—Competition 5—Freedom of choice 10 point Bonus Question LIST THE SIX STEPS IN THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS: 1. Identify the Problem 2. Identify the choices 3. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each choice 4. Choose 5. Act 6. Evaluate the outcome OSI 2002-2003 PAGE: 6