Biology Chapter 5 Practice Test: Cell Division & Cycle
advertisement

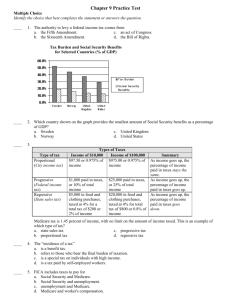
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. If a cell cannot move enough material through its membrane to survive, then the ratio of its surface area to volume is a. too large. b. just the right size. c. too small. d. growing too quickly. ____ 2. Before a cell can proceed to mitosis from the gap 2 stage of the cell cycle, it must a. double in size. b. complete a full cell cycle. c. undergo cytokinesis. d. pass a critical checkpoint. ____ 3. During interphase a cell grows, duplicates organelles, and a. copies DNA. b. divides the nucleus. c. divides the cytoplasm. d. produces a new cell. ____ 4. Why do the cells lining the stomach divide more quickly than those in the liver? a. They are much smaller cells. b. They have fewer chromosomes. c. They need much more surface area. d. They undergo more wear and tear. ____ 5. During which of the following stages shown in Figure 5.1 does the cytoplasm of a cell divide? a. b. c. d. gap 1 synthesis gap 2 mitosis 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 6. Kinases and cyclins are internal factors that a. cause apoptosis. b. control the cell cycle. c. cause cancer cells to break away. d. prevent mitosis. ____ 7. Proteins from outside a cell that stimulate it to divide are called a. oncogenes. b. stem cells. c. cyclins. d. growth factors. ____ 8. Which statement describes the chromosome shown in Figure 5.2? a. b. c. d. ____ It is made up of two histones. It is made up of two chromatids. It is made up of two centromeres. It is made up of two telomeres. 9. In a single-celled organism, mitosis is used for a. development. b. reproduction. c. growth. d. epair. ____ 10. Which of the following is true of malignant tumors? a. They do not require treatment. b. They are easily removed through surgery. c. They can cause tumors in other parts of the body. d. They contain cells that stay clustered together. ____ 11. One difference between a cancer cell and a normal cell is that a. cancer cells divide uncontrollably. b. normal cells divide uncontrollably. c. cancer cells cannot make copies of DNA. d. normal cells cannot make copies of DNA. ____ 12. Which statement about the process of binary fission is true? a. It does not involve the division of cytoplasm. b. It does not require any duplication of DNA. c. It does not take place in multicellular organisms. d. It does not produce genetically identical offspring. 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 13. A plant's leaf consists of a. a group of organs. b. various types of tissue. c. organs that form a system. d. many identical cells. ____ 14. Cells in a developing embryo differentiate based on a. their location in the embryo. b. symmetry in the first division. c. their particular DNA. d. secretions from the embryo. ____ 15. Which organism is capable of reproduction through asexual mitosis? a. horse b. oak tree c. bacterium d. starfish ____ 16. What does a cell make during the synthesis stage of the cell cycle? a. more organelles b. a copy of DNA c. daughter cells d. greater surface area ____ 17. Before a cell can move from the G or G stage to the next stage of the cell cycle, it must grow and a. double in size. b. duplicate its DNA. c. complete interphase. d. pass a critical checkpoint. ____ 18. The gap 1, gap 2, and synthesis stages of the cell cycle make up a. interphase. b. telophase. c. cytokinesis. d. mitosis. ____ 19. Molecules that control the stages of the cell cycle in all eukaryotes are similar. This fact suggests that a. binary fission and mitosis are the same. b. rates of cell division are uniform. c. cells of eukaryotes rarely divide. d. eukaryotes share a common ancestry. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 20. During which of the following stages shown in Figure 5.1 does cytokinesis take place? a. b. c. d. gap 1 synthesis gap 2 mitosis ____ 21. Which of the following is an example of an internal factor that controls the cell cycle? a. growth factor b. kinase c. cell-cell contact d. erythropoietin ____ 22. A hormone present in the blood can stimulate the growth of certain cells. The hormone is acting as a(n) a. oncogene. b. carcinogen. c. daughter cell. d. external factor. ____ 23. Which statement is true of the chromosome shown in Figure 5.2? a. b. c. d. Its telomeres have been shortened due to repeated cell division. Its left and right halves carry identical genetic information. Its sister chromatids have spindle fibers attached. Its centromere has been lost during the copying of DNA. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 24. Multicellular organisms use mitosis for growth, development, and a. apoptosis. b. repair. c. reproduction. d. interphase. ____ 25. If a tumor is malignant, then cancer cells from the tumor a. are harmless. b. remain clustered together. c. can form more tumors. d. create more carcinogens. ____ 26. One difference between a cancer cell and a normal cell is that a. cancer cells can divide in the absence of growth factors. b. cancer cells continue in the G0 stage indefinitely. c. cancer cells cannot copy DNA during the synthesis phase. d. cancer cells are killed by radiation and chemotherapy ____ 27. Offspring that are genetically unique are the result of a. mitotic reproduction. b. mitotic reproduction. c. sexual reproduction. d. vegetative reproduction. ____ 28. Which phrase best describes fragmentation? a. parent organism produces eggs and sperm, which form a new organism. b. parent organism sends off runner that grows into new organism. c. parent organism splits into pieces, each of which forms a new organism. d. parent organism sprouts projection that becomes new organism. ____ 29. In vertebrates, differentiation of cells is influenced by a. whether the cell is apical or basal. b. how rapid the first divisions are. c. variations in the organisms' DNA. d. where the cells migrate. ____ 30. Which of the following reproduce asexually through mitosis? a. many multicellular eukaryotes b. most unicellular prokaryotes c. only unicellular eukaryotes d. some multicellular and unicellular eukaryotes 5 ID: A CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: STA: TOP: 2. ANS: TOP: 3. ANS: STA: NOT: 4. ANS: STA: NOT: 5. ANS: STA: NOT: 6. ANS: TOP: 7. ANS: TOP: 8. ANS: STA: NOT: 9. ANS: STA: TOP: 10. ANS: TOP: 11. ANS: TOP: 12. ANS: TOP: 13. ANS: STA: NOT: 14. ANS: STA: TOP: 15. ANS: STA: NOT: 16. ANS: TOP: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.8 | KY 9-12.7.2.6 Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 TOP: Ch 5 Test - A 978-0-618-78317-5 D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 | KY 9-12.6.1.5 TOP: 978-0-618-78317-5 D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 TOP: Ch 5 Test - A 978-0-618-78317-5 B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 TOP: 978-0-618-78317-5 B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 | KY 9-12.6.1.5 Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 C PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 B PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 TOP: Ch 5 Test - A 978-0-618-78317-5 A PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 Ch 5 Test - A NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 D PTS: 1 DIF: Level A REF: KY 9-12.4.2.6 TOP: Ch 5 Test - A 978-0-618-78317-5 B PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 1 act0976aaf18007e0ef_202 act0976aaf18007e0ef_210 act0976aaf18007e0ef_218 act0976aaf18007e0ef_226 Ch 5 Test - A act0976aaf18007e0ef_234 act0976aaf18007e0ef_243 act0976aaf18007e0ef_251 act0976aaf18007e0ef_259 Ch 5 Test - A act0976aaf18007e0ef_268 act0976aaf18007e0ef_276 act0976aaf18007e0ef_284 act0976aaf18007e0ef_292 act0976aaf18007e0ef_300 act0976aaf18007e0ef_308 act0976aaf18007e0ef_316 act0976aaf18007e0f0_14 ID: A 17. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_22 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 18. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_30 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 19. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_38 STA: KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.1.6 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.9 | KY 9-12.4.2.11 | KY 9-12.5.1.2 | KY 9-12.5.2.1 | KY 9-12.SC-HS-3.5.1.a | KY 9-12.SC-HS-3.5.1.b TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 20. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_46 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 21. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_54 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 22. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_62 STA: KY 9-12.1.1.7 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 23. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_70 STA: KY 9-12.4.1.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 24. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_79 STA: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 | KY 9-12.6.1.5 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 25. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_87 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 26. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_95 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 27. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_103 STA: KY 9-12.4.2.6 | KY 9-12.SC-HS-3.4.5.a | KY 9-12.SC-HS-3.4.5.b TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 28. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_111 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 29. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_119 STA: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.2 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 30. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Level B REF: act0976aaf18007e0f0_127 STA: KY 9-12.4.1.1 | KY 9-12.4.2.3 TOP: Ch 5 Test - B NOT: 978-0-618-78317-5 2 CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 [Answer Strip] C _____ 1. D 20. _____ B 24. _____ B _____ 6. B 13. _____ D _____ 7. A 14. _____ C 25. _____ B _____ 8. D 15. _____ A 26. _____ D _____ 2. B 16. _____ A _____ 3. D 17. _____ D _____ 4. B 21. _____ D 22. _____ C 27. _____ C 28. _____ B _____ 9. A 18. _____ D _____ 5. B 23. _____ D 29. _____ C 10. _____ D 19. _____ A 11. _____ C 12. _____ D 30. _____ ID: A