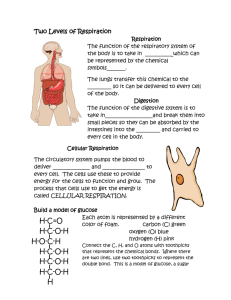
Respiration
advertisement

Respiration (Quick Questions) 1. In what part of cell does respiration take place? 2. What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? 3. What are the reactants of aerobic respiration? 4. What is a waste product of aerobic respiration? 5. How does oxygen get to cells in your body for respiration? 6. How does glucose get to the cells in your body for respiration? 7. Give 4 examples of what the body uses energy released from respiration for. 8. What is glycogen? 9. Name 3 body responses to exercise and explain why they happen. 10. How can you tell is someone is fitter from their breathing rate and heart rate? 11. What is the word equation or anaerobic respiration? 12. When does anaerobic respiration take place? 13. What happens to glucose in anaerobic respiration? 14. Which release more energy (more efficient): aerobic or anaerobic respiration? 15. How does anaerobic respiration differ from aerobic respiration? 16. Where lactic acid accumulate and what does it cause? Respiration (Quick Answers) 1. Mitochondria 2. Glucose + oxygen à carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) 3. Glucose and oxygen 4. Carbon dioxide 5. The oxygen comes the air around you and diffuses into your blood in your lungs. The heart then pumps the blood around the body to the body cells. 6. The glucose comes the food you eat and is absorbed into your blood in your small intestine. The heart then pumps the blood around the body to the body cells. 7. Building larger molecules (e.g. linking amino acids together to make protein molecules). To contract muscles. To maintain a steady body temperature. In plants to make amino acids from glucose. 8. Glycogen is a storage substance made up of many glucose molecules. It is stored in muscles tissues and converted to glucose when needed. 9. An increase in heart rate (to increase blood flow). An increase in breathing rate (to increase oxygen levels). Glycogen stores in muscles are converted to glucose for respiration. 10. Resting heart and breathing rate will be lower if they are fitter. The less your heart rate and breathing rate increase during exercise means the fitter you are. The quicker your breathing and heart rate returns to normal after exercise the fitter you are. 11. Glucose à lactic acid (+ little energy) 12. When the blood cannot supply oxygen to the muscles fast enough. 13. Glucose is not completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water so lactic acid is made instead. This is because there isn’t enough oxygen. 14. Aerobic respiration is more efficient. 15. Less energy is released, glucose is not completely broken down i.e. lactic acid made rather than carbon dioxide and water. 16. Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles and causes muscles pain and fatigue.