Demand and Supply Practice Problems
advertisement

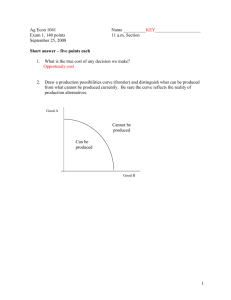
Practice Problems for Demand and Supply If you decide to put one on the board then please clearly indicate the number and part and put up all relevant information. 1.) ( Millions lbs. ) Given: P ($) Qd Qs Price 10 Problem 1. a 8.5 A. Construct graph of D & S. 7.5 Su p Do the following: pl y 4 35 15 5 30 20 6 25 25 7 20 30 8 15 35 9 10 40 6.5 5.5 em D d an 4.5 3.5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Quantity Su pp ly B.) Supposing that Qd increased by 20 million lbs. at all prices (i.e. parallel shift), Construct change on your graph and show new equilibrium. 1. b 10 8.5 New Equilibrium (35, 8) 6.5 5.5 em d an 4.5 3.5 d lD n ma na igi De Or w Ne Price 7.5 0 10 20 30 Quantity 40 50 65 igi na Su pp ly lS up ply 1. c 10 C. Suppose that Qs increases by 20 million lbs. at all prices instead of a change in Qd as in B above; Construct change ( start with graph from part A and not part B). Ne w Or 8.5 Price 7.5 6.5 an m De 5.5 d 4.5 New Equilibrium (35,4) 3.5 0 10 20 30 40 Quantity D. Suppose instead of B or C, that Qs falls relative to values in table by 20 million lbs. at all P > 5 And at P ≤ 5 Qs = 0 Show changes.(start with graph from part A and not part B). Or igi Su Ne w 8.5 7.5 Price na pp ly lS up ply 1. d 10 New Equilibrium (15,8) 6.5 nd ma De 5.5 4.5 3.5 0 10 20 30 Quantity 40 50 65 50 65 2.) In the above figure, in order for price to remain constant, but quantity to increase the A) supply and demand curves both would have to shift leftward. B) supply curve would have to shift leftward and the demand curve would have to shift rightward. C) supply curve would have to shift rightward and the demand curve would have to shift leftward. D) supply and demand curves both would have to shift rightward . Clearly both supply and demand would have to increase for Q to rise and they would have to do so by the same amounts for P to remain constant. D is the best response in this case. 3.) Let Qd stand for the quantity demanded, Qs stand for the quantity supplied, and P stand for price. If Qd = 20 – 2P and Qs = 5 + 3P, solve for the equilibrium quantity and price. The easiest way is to find the values at equilibrium, at which Qd = Qs. Since at this point Price is the same set the expressions equal to each other and solve: 20 – 2P = 5 + 3P 15 = 5P 3 = P and then substitute 3 for P in either of the above to find Q 20 - 2(3) = Q 14 = Q 4.) Given P = 1/50 Q + 2 and P = -1/50 Q + 6 What is Ep and Eq ? The easiest way is to find the values at equilibrium, at which Qd = Qs. Since at this point Price is the same set the expressions equal to each other and solve: 1/50 Q + 2 = -1/50 Q + 6 thus 2/50 Q = 4 Q = 100 and then substitute 100 back into either to find P P = 1/50(100) + 2 = 4 What effect will P = 1/50 Q + 4 have? i.e.: This is a movement in what ? What is new Ep and Eq? This is a shift in S and in fact is a decrease in Supply. Thus price should rise and quantity should fall. 1/50 Q + 4 = -1/50 Q + 6 2/50 Q = 2 Q = 50 and then substitute 50 back into either to find P P = 1/50 (50) + 4 = 5 What happens if Demand now moves to P = - 1/50 Q + 10 ? This is an increase in Demand so Price should rise and quantity should rise. 1/50 Q + 4 = -1/50 Q + 10 2/50 Q = 6 Q = 150 and then substitute 150 back into either to find P P = 1/50 (150) + 4 = 7 5.) Given P = Q/4 - 25 and P = - Q/2 + 125 Find mkt. P & Q. The easiest way is to find the values at equilibrium, at which Qd = Qs. Since at this point Price is the same set the expressions equal to each other and solve: Q/4 - 25 = - Q/2 + 125 3Q/4 = 150 3Q = 600 Q = 200 now substitute 200 back into either expression and find P. P = 200/4 - 25 = 50 - 25 = 25