Organic Chemistry - vishal publishing co.
advertisement
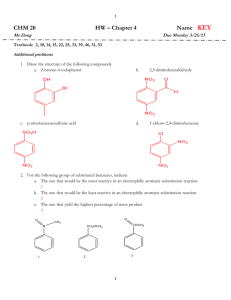
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry for [Second Year B.Sc. (Main) Students of M.G. University, Kerala] III Semester (This Book is an outcome of “Modern Organic Chemistry” by M.K. Jain & S.C. Sharma duly recommended by M.G. University.) M.K. JAIN S.C. SHARMA M.Sc., Ph. D. (Glasgow) Former, Professor, National Dairy Research Institute (Deemed University), KARNAL (Haryana) M.Sc., Ph.D. Former-Head Deptt. of Chemistry V.B.R.I. P.G. College, UDAIPUR (Rajasthan) VISHAL PUBLISHING CO. Future for WINNERS JALANDHAR – DELHI CONTENTS Chapter No. Title 1. CLASSIFICATION NOMENCLATURE COMPOUNDS* Page No. Chapter No. & IUPAC OF ORGANIC 1-22 1.0. Classification 1 1.1. IUPAC or Geneva names 3 Title Page No. 2.2. Types of reagents 24 1. Nucleophiles 24 2. Electrophiles 25 3. Free radicals 25 2.3. Types of organic reactions 25 1.2. Rules of IUPAC system of nomenclature for acyclic compounds 3 [A] Substitution reactions 25 [B] Addition reactions 26 1.3. IUPAC system of nomenclature for substituted alkanes 4 [C] Elimination reactions 27 [D] Rearrangement reactions 27 1.4. Alkenes, alkynes and substituents 9 1.5. IUpac nomenclature of cycloalkanes and its derivatives 10 1.6. IUPAC nomenclature of bicycloalkanes and related compounds 11 1.7. IUPAC nomenclature of bicyclic spiro compounds 12 2.4. Homolytic and Heterolytic Cleavage of a covalent bond (formation of reactive intermediates) 28 1. Carbocations / Carbonium ions 28 2. Carbanions 30 3. Free Radicals 32 2.5. Electron Displacement effects 33 1.8. IUPAC nomenclature of alkyl halides 12 1.9. IUPAC nomenclature of alcohols 13 1. Inductive or inductometric Effect 34 13 2. Electromeric Effect 37 1.11. IUPAC nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones 14 3. Resonance and Resonance Effect 39 4. Resonance theory 41 1.12. IUPAC nomenclature of acids 14 5. Mesomeric effect 46 1.13. IUPAC nomenclature of acid derivatives 15 6. Hyperconjugation 46 1.14. IUPAC nomenclature of amines 7. Steric effects / Inhibition / Hindrance 49 1.10. IUPAC nomenclature of phenols 16 1.15. IUPAC nomenclature of nitro compounds17 1.16. Procedure for writing the structure of a compound with a given IUPAC name 18 Questions 2. FUNDAMENTALS OF REACTION MECHANISM-I 2.0. Introduction 19 ORGANIC 23-54 23 2.1. Notations used to show Electron Migration 23 1. Curved arrow notation 23 2. Double Headed Arrow(s). 24 3. Half-headed Arrow (Fish hook arrow) 24 Questions 3. FUNDAMENTALS OF REACTION MECHANISM-II 52 ORGANIC 55-79 3.0. Introduction 55 3.1. Addition Reactions 55 1. Electrophilic Additions to double bond 55 3.2. Polymerisation 60 1. Types of Polymerisation Reactions 61 3.3. Aliphatic Substitution Reactions 66 1. Detailed Mechanisms Of aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions 66 Chapter No. Title Page No. Chapter No. 3.4. Elimination Reactions 4.9. Properties of Diastereomers 71 2. Orientation In Elimination Reactions (hofmann & saytzeff elimination) 74 95 97 4.9.1. Distinction Between Diastereomers And Enantiomers 97 72 1. Mechanisms Of Elimination Reactions 72 Page No. or two asymmetric/chiral carbon 2. Factors Influencing Rates Of aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions 70 3. SN1 vs. SN2 Mechanisms Title 4.10. Fischer projections 97 4.10.1. Specifying R–S Configurations on Fischer Projection 100 3. Substitution vs. Elimination 77 4.11. Erythro and threo nomenclature (notation) of configurations 101 Questions 77 4.12. Resolution 4. STEREOCHEMISTRY-I 80-106 4.0. Introduction 80 4.1. Stereoisomerism 80 4.2. Types of Stereoisomers 80 4.3. General Stereochemistry 80 4.3.1. Concept of Chirality 80 4.3.2. Tetrahedral Carbon 81 4.3.3. Chirality and Enantiomerism 81 4.3.4. Wedge and Dashed Bond Drawing of Organic Molecules (Perspective Drawings) 82 4.3.5. Asymmetric Carbon Atom and Related Terms 82 4.3.6. Elements of symmetry 83 4.3.7. The Asymmetric Carbon Atoms And Molecular Chirality 85 4.4. Optical activity 86 4.5. Acyclic molecules with one asymmetric/chiral carbon or stereogenic centre 87 4.6. Enantiomers And Related Aspects 89 4.6.2. The Racemic Modification 90 4.7. Configuration 4.13. Asymmetric (Stereogenic Centre) Synthesis 104 4.14. Walden Inversion 104 4.15. Retention and racemisation 105 5. STEREOCHEMISTRY-II 90 4.7.1. Relative Specification of Configuration ‘D’ and ‘L’* Notation 91 4.7.2. Specification of Configuration R and S notation 93 4.8. Compounds with two Stereogenic Centres 107-128 5.0. Geometric isomerism (cis-trans isomerism) 107 1. Concept of Hindered Rotation About a Carbon-Carbon Double Bond and Geometric Isomerism 107 2. Geometric Isomers as Diastereomers 108 3. Structure of Alkenes and Geometric Isomerism 108 4. Extended Isomerism 5. Assigning Configuration to Geometric Isomers 110 Scope of Geometric 109 5.1. E-Z System of Nomenclature for Cis-trans Isomers 110 1. 88 4.6.1. Properties of Enantiomers 102 Relative Stabilities of cis-trans Isomers 114 5.2 Conformation Of Alkanes (conformational analysis) 114 5.3. Factors Influencing Conformational Stability 118 5.4. Conformational Analysis Of Cyclohexane 120 1. Axial And Equatorial Bonds* In Cyclohexane 122 Chapter No. 2. Title Page No. 1, 3-Diaxial Interactions In Cyclohexane Derivatives 122 5.5. Conformational Isomers vs Configurational Isomers 123 Questions Chapter No. Title 7.3.1. Bimolecular Mechanism Page No. Displacement 158 7.3.2. Benzyne Intermediate Mechanism (Elimination Addition Mechanism) 160 123 Questions 6. ARENES AND AROMATICITY 129-147 6.0. Introduction 129 6.1. Structure Of Benzene 129 6.2. Aromatic Sextet And Orbital Picture 133 6.3. Resonance And Molecular Orbital Structure Of Naphthalene 133 I. Resonance Structure 6.4. Resonance Anthracene and M.O. 134 Structure of 135 (1) Resonance Structure. 135 (2) Molecular Orbital Structure. 135 6.5. Concept Of Aromaticity 136 6.6. Aromaticity/Aromatic Character 136 6.7. Hückel Theory Of Aromaticity 136 (1) Benzenoids (2) 137 Non-Benzenoid Aromatic Compounds/ Ions 137 6.8. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions 140 6.9. General Pattern Of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 142 6.10. Reactivity Of Naphthalene 143 Questions 145 7. ORIENTATION OF SUBSTITUTION IN ARENES 148-164 7.0. Introduction 7.1. Orientation Electrophilic Substitution Reactions. 148 Aromatic 148 7.1.1. Effect Of Activating Groups 149 7.1.2. Effect Of Deactivating Groups 152 7.2. Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 155 7.3. Mechanisms 157 8. PERICYCLIC REACTIONS 162 165-173 8.0 Introduction 165 8.1 Salient features of Pericyclic reactions 165 8.2 Classification of Pericyclic reactions 165 8.2.1 Electrocyclic reactions 8.2.2 Cycloaddition reactions (Diels-Alder reaction) 170 8.2.3 Sigmatropic rearrangements 8.3 The Frontier orbital method Questions Model Question Papers University Question Paper 166 171 172 173 175-180 181-184