Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth
advertisement

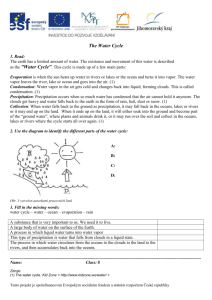
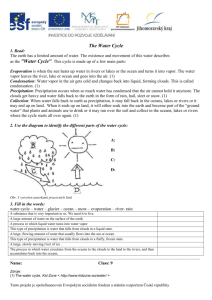
Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 1: How Can the Oceans Be Described? Hydrosphere The water on or surrounding the surface of the globe, including the water of the oceans and the water in the atmosphere. Sea Level The level of the surface of an ocean. Salinity A measure of the amount of salt in water. Oceans 5 Oceans 1. Pacific Ocean 2. Atlantic Ocean 3. Indian Ocean 4. Arctic Ocean 5. Southern Ocean The deeper we go in the oceans, the colder and higher the pressure. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 2: Where is Fresh Water Found? Aquifer The layer of rock and soil that groundwater flows through. Water Table The top level of the groundwater in an aquifer. Watershed The area from which water drains into a river. Reservoir Usually an artificial lake that forms behind a dam. Pollutant Any substance, as certain chemicals or waste products, that renders the air, soil, water, or other natural resources harmful or unsuitable for a specific purpose. Glacier An extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over the years. Drinking Water Water that comes from lakes, glaciers, dams, and underground springs. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 3: What Are Some of California Water Sources? Aqueduct A system of pipelines that carries water from a river or lake to the area where it is needed. Reclamation Waster water from homes or businesses that is carried to a waster water treatment plant to be used again for purposes other than drinking water. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 4: What Is the Water Cycle ? Water Cycle Repeated movement of water through the environment in different forms. Also known as the hydrologic cycle. Evaporation (3) The process by which particles leave a liquid and become a gas (water vapor). Condensation(2) The process by which particles leave a gas (water vapor) and become a liquid. Precipitation(4) Water that falls from clouds as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. Snow Hail Sleet Ice Crystals Sublimation The act of changing from solid ice directly to water vapor. Water Vapor The gas form of water. It forms when water molecules evaporate from the Earth’s surface. Run-Off Water moving downhill. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 5: How Do Clouds Form? Cirrus High altitude clouds that are thin, wispy, and white. Thunderheads Vertical clouds that often cause thunderstorms. Altocumulus Mid-altitude clouds that look like small, puffy balls. Stratus Low-altitude clouds that cover the whole sky. Sleet Frozen raindrops that fall as precipitation. Fog Tiny droplets of water on ice. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 1: How Does Air Move? Atmosphere All of the air around the Earth. Atmospheric Pressure The weight of air pushing down on an area (air pressure). Convection Current The rising and sinking of matter in a circular pattern cause by temperature differences. Uneven Heating Weather is different in places around the Earth because the surface of our planet is heated by the sun unevenly. Wind A movement of air that happens because of differences in air pressure caused by temperature differences (Convection currents) Latitude A measure of how far a place is north or south of the equator, which has a latitude of 0 degrees. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 2: What Are Air Masses? Air Masses A large body of air with similar properties all through it. Warm Front When warm air moves against cooler air, the warm air rises above the cooler air. Cold Front When colder air is brought into an area, it forces the warmer air to move up quickly. Cyclone A wind that spirals inward around an area of low pressure. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 3: What Causes Severe Weather? Hurricane A strong cyclone that forms over warm ocean waters Monsoon A wind that changes direction with the seasons. Tempered Describes air that is warmed in winter and cooled in summer because it is near a large body of water. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 4: How Are Weather Forecasts Made? Barometer A tool that measures air pressure. Hygrometer A tool that measures moisture in the air. Anemometer A tool that measures wind speed. Rain Gauge A tool that measures the amount of rain that has fallen. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 2: Why Do Planets Revolve Around the Sun? Sun A star composed of helium and hydrogen and is located in the center of our solar system. It is the largest body in our solar system. Star A huge ball of hot gas that gives off energy. Solar System A system that includes the Sun and its planets, along with many moons, asteroids, and comets. Orbit The curved path described by a planet, satellite, or spaceship around a celestial body such as the sun. Satellite An object that orbits another object in space. Gravity A force that exists between two things that have mass. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 3: What Are the Inner Planets? Inner Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are referred to as the inner planets because they are closest to the sun. They are small, rocky planets. Meteorite A mass of stone or metal that has reached the Earth from outer space. Asteroid A rocky object up to several hundred kilometers wide that revolves around the sun. Comet A frozen mass of ice and dust with a tail up to 80 million kilometers long that is in orbit around the sun. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 4: What Do We Know About the Outer Planets and Beyond? Outer Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are referred to as the outer planets. Their orbits are beyond the asteroid belt. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 1: How Can the Oceans Be Described? Hydrosphere-The water on or surrounding the surface of the globe, including the water of the oceans and the water in the atmosphere What do you see in the picture? The picture is showing examples of the _______. What does the Greek root hydro in the word hydrosphere mean? Hydro means ________, which tells me that hydrosphere is water _____________________. Sea Level-The level of the surface of an ocean. What do you see in the picture? The picture shows _______, which is the level ________________. What does the word level mean? Level means having the ________ height. Salinity- A measure of the amount of salt in water. What does salinity mean? Salinity is the _______ of _______ in ________. What does the Latin root word saline means in the word salinity must mean? Saline means anything that contains __________. Oceans- The deeper we go in the oceans, the colder and higher the pressure. 5 Oceans 1. Pacific Ocean 2. Atlantic Ocean 3. Indian Ocean 4. Arctic Ocean 5. Southern Ocean What does the picture show? The picture shows the five ______ of the _______, which are the _____ Ocean, the _____ Ocean, the _____ Ocean, the _____ Ocean, and the ____ Ocean. The deeper we go in the oceans, the _______ and _____ the pressure. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 2: Where is Fresh Water Found? Aquifer-The layer of rock and soil that groundwater flows through. What do you see in the picture? The picture shows an _______, which is a layer of rock and ______ that groundwater ________ through . The word aquifer means to carry water. It has the Latin roots aqua, which means ______, and ferre, which means to ______. Water Table-The top level of the groundwater in an aquifer. What is the picture showing you? The picture shows a ______, which is the top _______ of the ______ in an aquifer. Watershed-The area from which water drains into a river. What is a watershed? A watershed is the _____ from which _____ drains into a _________. Reservoir- Usually an artificial lake that forms behind a dam. What is a reservoir? A reservoir is usually an ______ lake that _____ behind a dam. How are watersheds and reservoirs different? A watershed is water that drains into a _____, while a reservoir forms behind a _______. Pollutant-Any substance, as certain chemicals or waste products, that renders the air, soil, water, or other natural resources harmful or unsuitable for a specific purpose. What do you see in the picture? The picture shows different ________, which can be _____ or waste products that are harmful. Glacier-An extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over the years. What is a glacier? A glacier is an extended mass of _____ formed from ______ falling and ________ over the years. Drinking Water-Water that comes from lakes, glaciers, dams, and underground springs. Where do we get drinking water from? Drinking water comes from _____, _______, _____, and _______. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 3: What Are Some of California Water Sources? Aqueduct- A system of pipelines that carries water from a river or lake to the area where it is needed. What is the purpose of an aqueduct? An aqueduct carries water from a _____ or _____ to the area where it is needed. If an aqueduct is a “pipe that carries water”, the Latin root aque means ______, while the suffix –duct means ___________. Reclamation- Waster water from homes or businesses that is carried to a waster water treatment plant to be used again for purposes other than drinking water What is the root word of Claim reclamation? What does the prefix re mean? To do again What does reclamation mean? To claim or use water again Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 4: What Is the Water Cycle ? Water Cycle- Repeated movement of water through the environment in different forms. Also known as the hydrologic cycle. What do you know about cycles? Cycles mean something that _________. What is the water cycle? The water cycle is the _______ movement of ______ that never stops. Evaporation- The process by which particles leave a liquid and become a gas ( water vapor). (3) What is evaporation? Evaporation is a step of the _____ cycle, in which the liquid form of water changes to a ______, which is also called water vapor. Condensation- The process by which particles leave a gas (water vapor) and become a liquid. (2) What is condensation? When air cools, the gas, which is called ____ vapor, turns into a liquid. What do some of the water droplets turn into? The water droplets turn into _______ or fog. Precipitation- Water that falls from clouds as rain, hail, sleet, or snow. (4) What step of the water cycle is the arrow pointing to? The picture is showing ________, which is when water falls from clouds as ____, ____, ___, or _____. How is precipitation different from condensation? _________ is the change from a gas to a liquid, while ______ is when water falls from the clouds. Sublimation- The act of changing from solid ice directly to water vapor. What is the picture showing? The picture shows the changing of solid _____ directly to water vapor, which is called sublimation. Water Vapor- The gas form of water. It forms when water molecules evaporate from the Earth’s surface (sublimation). What is water vapor? Water vapor is the ____ form of water, which is called sub__________. In which step of the water cycle does sublimation occur? Sublimation occurs during _______ , which is the changing of liquid to water vapor. Run Off-Water moving downhill. What is the picture showing? The picture is showing a runoff, which is when ______ is moving ______. Where does water run off into? Water runs off the land into streams and rivers, that flow into ______ and ________. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 5: Water on Earth Lesson 5: How Do Clouds Form? Cirrus- High altitude clouds that are thin, wispy, and white. What type of clouds does the picture show? The picture shows ______ clouds. How could you describe cirrus Cirrus clouds are high altitude, clouds? _____, _____, and _______. Thunderheads- Vertical clouds that often cause thunderstorms. What type of clouds does the picture show? The picture shows ______ clouds. How could you describe Thunderheads are vertical thunderhead clouds that often cause clouds? _______. Altocumulus- Mid-altitude clouds that look like small, puffy balls. What type of clouds does the picture show? The picture shows ______ clouds. How could you describe altocumulus clouds? Altocumulus clouds are mid-altitude clouds that look like ____, ____ balls. Stratus- Low-altitude clouds that cover the whole sky. What type of clouds does the picture show? The picture shows ______ clouds. How could you describe stratus clouds? Stratus clouds are lowaltitude clouds that ______ the whole ______. Sleet- Frozen raindrops that fall as precipitation. What is sleet? _______ is frozen raindrops that fall as precipitation. Fog- Tiny droplets of water on ice. What is fog? _______ is tiny droplets of water on ice. Fog occurs during the ______ step of the water cycle (gas to liquid). Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 1: How Does Air Move? Atmosphere- All of the air around the Earth. What does atmosphere mean? The _______ is all of the ____ around the ______. Atmospheric Pressure- The weight of air pushing down on an area (air pressure). What is atmospheric pressure? Atmospheric pressure is the weight of ____ pushing _____ on an area. The higher you go in the atmosphere, the air pressure will ________ Convection Current-The rising and sinking of matter in a circular pattern cause by temperature differences. What is a convection current? A convection current is the _____ and _____ of matter in a circular pattern. During the day, the _____ air causes the ___ air to rise. Uneven Heating- Weather is different in places around the Earth because the surface of our planet is heated by the sun unevenly. What is the picture showing? The picture is showing how the ____ affects the Earth’s surface unevenly, therefore the _______ is different in places around the Earth. Wind- A movement of air that happens because of differences in air pressure caused by temperature differences (Convection currents) What causes wind? Wind occurs because of the differences in air ______ caused by temperature _______. Latitude- A measure of how far a place is north or south of the equator, which has a latitude of 0 degrees. What is latitude? Latitude is a measure of how ____ a place is ____ or ____ of the equator. Places closest to the equator get _____ energy from the Sun than do places near the North or ____ poles. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 2: What Are Air Masses? Air Masses- A large body of air with similar properties all through it. What is an air mass? An air mass is a large ____ of _____ with similar properties all through it. Air has mass, therefore it takes up ______. Warm Front- When warm air moves against cooler air, the warm air rises above the cooler air. What causes a warm front to occur? A warm front occurs when ______ air moves against _____ air, the warm air rises above the cool air. A warm front brings ______ air into an area. Cold Front- When colder air is brought into an area, it forces the warmer air to move up quickly. What causes a cold front to occur? A cold front occurs when ______ air is brought into an area, it forces the ____ air to move _____ quickly. A cool front brings ______ air into an area. Cyclone- A wind that spirals inward around an area of low pressure. What is a cyclone? A cyclone is a ____ that spirals _____ around an area of ____ pressure. Cyclone comes from the Greek word cyclone meaning circle. I know that cycle means _____, which means A cyclone moves in a _______ pattern . Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 3: What Causes Severe Weather? Hurricane- A strong cyclone that forms over warm ocean waters. What is a hurricane? A hurricane is a strong ____ that forms over ____ ocean waters. Monsoon- A wind that changes direction with the seasons. What causes a monsoon? A monsoon is a ____ that _____ direction with the seasons. Tempered- Describes air that is warmed in winter and cooled in summer because it is near a large body of water. What is tempered air? Tempered air is warmed in the ______ and cooled in the _____ because it is near a large body of water. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 6: Weather Lesson 4: How Are Weather Forecasts Made? Barometer- A tool that measures air pressure. What does a barometer measure? A ______ is a tool that measures air ______. Barometer has the suffix –meter meaning “ to measure”. I know that barometer means a device used for _______. Hygrometer-A tool that measures moisture in the air. Hygrometer has the suffix –meter meaning “ to measure”. I know that a hygrometer must be a device used to ______ something. What is a hygrometer? A hygrometer is a ____ that measures ____ in the ______. Rain Gauge- A tool that measures the amount of rain that has fallen. What is a rain gauge? A rain gauge is a tool that _____ the amount of ____ that has fallen. How is a rain gauge different from a hygrometer? A rain gauge measures the amount of ____ that has fallen, where a hygrometer measures the ______ in the air. Anemometer-A tool that measures wind speed. What does the picture show? The picture shows a _____, which is a tool that ____ wind speed. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 2: Why Do Planets Revolve Around the Sun? Star- A huge ball of hot gas that gives off energy. What is a star A star is a huge ball of hot _____ that gives off _______ . Sun-A star composed of helium and hydrogen and is located in the center of our solar system. It is the largest body in our solar system. Where is the Sun located? The Sun is located in the _____ of the solar system. What is the Sun a star? The Sun is a star because it is a huge ball of ___ that gives off ______. Solar System- A system that includes the Sun and its planets, along with many moons, asteroids, and comets. What is a solar system? A solar system includes the _____ and its planets, along with many moons, ________, and comets. Orbit- The curved path described by a planet, satellite, or spaceship around a celestial body such as the sun. What does orbit mean? Orbit means a path that a _____, satellite, or spaceship takes around something. The picture shows the _____ orbiting the _____. Satellite-An object that orbits another object in space. What is a satellite? A satellite is an object that _____ another object in space. The moon is a satellite of _______. Gravity is a force that exists between two things that mass. What is gravity? Gravity is a force that ____ between two things that have ____. Why will the apple for on his head? The apple will fall on his head because _____ exists between ____ and the ____. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 3: What Are the Inner Planets? Inner Planets- Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are referred to as the inner planets because they are closest to the sun. What are the inner planets? ______, ______, ______, and _____ are known as the inner planets. What are they called the inner planets? They are known as the inner planets because they are _____ to the ____. Meteorite- A mass of stone or metal that has reached the Earth from outer space. What is a meteorite? A meteorite is a _____ from outer space that has reached _____. Asteroid- A rocky object up to several hundred kilometers wide that revolves around the Sun. What is an asteroid? An asteroid is a _____ object that ____ around the ____. Comet- A frozen mass of ice and dust with a tail up to 80 million kilometers long that is in orbit around the sun. What is a comet? A comet is a mass of _____ and dust with tail that orbits the ______. Grade 5 Science Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 7: The Solar System Lesson 4: What Do We Know About the Outer Planets and Beyond? Outer Planets- Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are referred to as the outer planets. Their orbits are beyond the asteroid belt. Which planets are known as the outer planets? _____, _____, _____, and _____ are referred to as the outer planets.