Introduction to Electric Circuits 1
advertisement

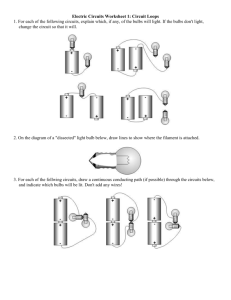
Introduction to Electric Circuits Introduction to Electric Circuits1 ! Electricity is an important and necessary component to our daily lives. Electricity delivers energy to many of our appliances/electronics and an electric circuit describes the pathway it takes. ! In this first activity, students will focus on what is needed/ required for electrical devices to work. For example, what do we need to make a light bulb light up? ! Physical Sciences Connection: Conservation of Energy and Energy Transfer (PS3.B) Initial thoughts: Imagine you have a small light bulb. What do you think is required to make the light bulb light up? or For the arrangements below, predict whether the light bulb will light up. ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Prediction: Observation: 1 Prediction: Observation: Prediction: Observation: Some of the material here is taken from Physics and Everyday thinking by Fred Goldberg. 1 Introduction to Electric Circuits What information did you use to make your predictions? What made you decide whether the light bulb would light or not light up? ! ! ! ! ! ! Discuss your thoughts and ideas as a class. ! ! Activity 1: What is needed to light the light bulb? In this activity you will construct an electric circuit to determine in what instances the light bulb will light up. ! What you will need: • • • ! ! One battery One light bulb Two wires or Part 1: Comparing different electric circuit arrangements Using the materials given to you, recreate each of the arrangements an figure out If the bulbs lights up, write “yes” next to “observation” and “no” if it does not light up. ! ! Part 2: A new circuit arrangement Think of another arrangement where the light bulb will light up. ! Draw the arrangement below in the box below. What does your electric circuit have in common to the electric circuits drawn above? 2 Introduction to Electric Circuits Look over the arrangements that allow the bulb to light and answer the following questions. ! Which parts of the battery need to be part of the electric circuit? ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Does a wire or part of the bulb need to touch the positive end of the battery only? Or can it touch any part of the positive end of the battery? ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Which parts of the bulb must be part of the electric circuit? ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Part 3: New tools for constructing an electric circuit It can be awkward to hold the battery, wires, and bulb to build an electric circuit. To make things easier, there are special holders to help us construct these circuits! ! Construct the circuit to the right. Does the lightbulb light up? ! ! The lightbulb should light up like before, but hopefully it was easier to do this time. ! 3 Introduction to Electric Circuits Activity 1 Recap: For a lightbulb to light up we have discovered the following: • A battery is needed • Wires are needed to connect the light bulb to the batter • The positive and negative sides of a battery are both used • The bottom and side of the light bulb are used ! ! Activity 2: Understanding what parts of the battery need to be connected in an electric circuit. ! What you will need: ! ! • • • Two batteries One light bulb Two wires The evidence form the past few sections suggest that one side the light bulb needs to be connected to the positive end of the battery and the other side of the bulb needs to be connected to the negative end of the battery. ! ! But do the two sides of the bulb need to be connected to the positive and negative ends of the same battery? ! ! ! ! ! Do you think the lightbulb will light up? Why? 4 Introduction to Electric Circuits ! Part 1: Construct the arrangement above. ! Does the bulb glow? ! ! ! Do the two ends of the bulb need to be connected to the two ends of the same battery for the circuit to work? ! ! Activity 2 Recap: • The positive and negative parts of a battery need to come from the same battery otherwise the lightbulb will not light ! ! ! Activity 3: Understanding the different parts of a light bulb ! Construct an electric circuit as shown here: ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Which part of the light bulb is actually glowing? ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! 5 Introduction to Electric Circuits Below is a sketch showing the various parts of a bulb: ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Starting at one end of the battery, draw connecting lines that go from the two wires to the filament support, then to the filament. ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! The connections from the battery form a continuous pathway to the filament (the part that lights up) then back to the battery. We’ll look into this more in the next activity. ! Activity 3 Recap: • Only one part of the light bulb lights. This part is called the filament. • The connections from the battery form a loop. ! ! 6 Introduction to Electric Circuits Summarizing Questions ! 1. ! ! The picture below shows one electronic circuit that was constructed by a student. Do you think the light bulb will light? ! ! ! ! Using what you have discovered about electric circuits, explain why the light bulb will or will not light. 7