MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
advertisement

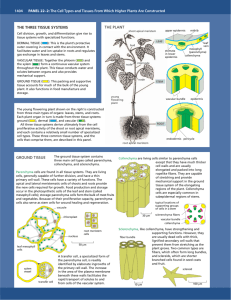
Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Plants that do not develop persistent woody parts above the ground are called: A. B. C. D. E. monocots. dicots. herbaceous. deciduous. perennials. 2. From the group of plants below, select which are annuals. A. B. C. D. E. corn geranium sunflower marigold All of these. 3. A plant that requires two years to complete its life cycle is referred to as: A. B. C. D. E. a biennial. an annual. a perennial. a dicot. a monocot. 4. All woody plants are: A. B. C. D. E. annuals. biennials. perennials. deciduous. evergreen. 5. A main function of a plant’s root system is to: A. B. C. D. E. photosynthesize. absorb dissolved nutrients and water. absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide. capture sunlight. bear seed-containing fruits. 6. Which tissue system of the plant body is largely responsible for photosynthesis? A. B. C. D. E. ground tissue system vascular tissue system dermal tissue system primary tissue system secondary tissue system 7. The bulk of the herbaceous plant’s body is its _________________________ system. A. B. C. D. E. vascular tissue ground tissue dermal tissue xylem tissue All of these. 32 - 1 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 8. Which one of the following is mismatched? A. B. C. D. E. ground tissue—photosynthesis vascular tissue—storage dermal tissue—covering of plant body ground tissue–—storage vascular tissue—transport 9. Roots, stem, leaves, flower parts, and fruits are referred to as: A. B. C. D. E. apical meristems. dermal tissues. vascular tissues. organs. ground tissues. 10. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma are classified as: A. B. C. D. E. dermal tissues. vascular tissues. ground tissues. primary tissues. secondary tissues. 11. A secondary cell wall would be located: A. B. C. D. E. inside the cytoplasm. embedded within the primary wall. embedded within the plasma membrane. inside the plasma membrane. outside the primary wall. 12. Parenchyma cells: A. B. C. D. E. may be either photosynthetic or non-photosynthetic. can differentiate into other kinds of cells in response to an injury to the plant. may contain various storage materials, such as starch grains, oils, or water. must be living cells in order to function. All of these. 13. The extremely flexible tissue that provides support in soft, nonwoody plants, allowing them to grow upward, is: A. B. C. D. E. parenchyma tissue. collenchyma tissue. sclerenchyma tissue. dermal tissue. meristematic tissue. 14. The soft part of a plant body, such as a potato, consists largely of _____________ tissue. A. B. C. D. E. sclerenchyma collenchyma parenchyma phloem xylem 32 - 2 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 15. In plants, parenchyma cells secrete: A. B. C. D. E. resins. hormones. tannins. enzymes. All of these. 16. Which of the following tissues is dead at maturity? A. B. C. D. E. parenchyma. sclerenchyma. collenchyma. epidermis. lignin. 17. Sclereids are cells that: A. B. C. D. E. are found in wood and bark. conduct water and dissolved minerals. are usually found in nut shells and pits of stone fruits. conduct dissolved sugars. form cytoplasmic connections between cells. 18. The most abundant polymer in the world is: A. B. C. D. E. cellulose. glucose. hemicellulose. lignin. pectin. 19. What two tissues transport materials throughout the entire plant body? A. B. C. D. E. sclerenchyma and xylem phloem and xylem parenchyma and xylem sclerenchyma and collenchyma epidermis and xylem 20. What tissue conducts water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the stems and leaves? A. B. C. D. E. collenchyma epidermis periderm xylem phloem 21. Xylem is composed of all of the following cell types except: A. B. C. D. E. tracheids. vessel elements. fibers. parenchyma. sieve tube elements. 32 - 3 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 22. Mature vessel elements: A. B. C. D. E. form sieve tubes in the vascular tissue. have pits in their walls, which allow water to be transported laterally. are alive and contain cytoplasm. are given support by companion cells. occur in pairs, forming stomata in the epidermis. 23. ____________________________, which are a type of xylem, are extremely efficient in conducting water. A. B. C. D. E. Sieve tube elements Companion cells Tracheids Sclereids Vessel elements 24. Sugar is conducted in solution through specialized cells known as: A. B. C. D. E. fibers. companion cells. sieve tube elements. tracheids. vessels. 25. _________________ are one of the few eukaryotic cells that can function without nuclei. A. B. C. D E. Sieve tube elements Companion cells Tracheids Sclereids Vessel elements 26. ____________ are living cells that do not conduct sugar themselves but play a crucial role in assisting the movement of sugars. A. B. C. D. E. Sieve tube members Sieve plates Tracheids Vessel elements Companion cells 27. ____________ are tiny pores in the epidermis that facilitate the diffusion of carbon dioxide into leaves or herbaceous stems. A. B. C. D. E. Stomata Guard cells Tracheids Sclereids Trichomes 28. Special epidermal outgrowths that remove excess salt accumulated in seashore plants are an example of: A. B. C. D. E. plasmodesmata. guard cells. stomata. sclereids. trichomes. 32 - 4 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 29. In both stems and leaves, photosynthetic tissues lie beneath the ____________________. A. B. C. D. E. cortex periderm pith epidermis None of these. 30. What tissue comprises the outer bark of woody plants? A. B. C. D. E. ground tissue epidermis phloem periderm xylem 31. Which of the following is not considered a secondary tissue? A. B. C. D. E. secondary xylem secondary phloem epidermis periderm None of these, all are secondary tissues. 32. Which organelle increases in size, causing plant cells to elongate? A. B. C. D. E. chloroplast mitochondrion nucleus ribosome vacuole 33. The plant growth process that allows cells to become specialized is: A. B. C. D. E. cell division. cell elongation. cell differentiation. primary growth. secondary growth. 34. Which of the following statements about meristematic tissue is false? A. B. C. D. E. It is found at the tips of all roots. It is found at the tips of all stems. It is capable of continually dividing throughout the life of the plant. Its cells are incapable of differentiating. Its cells are dead at functional maturity. 35. Growth that results in an increase in the length of a plant is referred to as: A. B. C. D. E. horizontal growth. longitudinal growth. primary growth. radial growth. secondary growth. 32 - 5 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 36. Growth that results in an increase in stem or root length occurs in which specific area of the plant? A. B. C. D. E. lateral meristem apical meristem vascular cambium cork cambium periderm 37. A root cap: A. B. C. D. E. protects the fragile meristematic cells at the root tip. pushes the root tip deeper into the soil. protects the cells located in the lateral meristem. arises from the stem apical meristem. will differentiate into primary tissues of the adult plant. 38. Growth that results in an increase in the girth of a plant is referred to as: A. B. C. D. E. horizontal growth. longitudinal growth. primary growth. radial growth. secondary growth. 39. The stem apical meristem gives rise to: A. B. C. D. E. leaf primordia. lateral meristems. root caps. root hairs. All of these. 40. Dividing cells are found in all of the following except: A. B. C. D. E. 41, 42. apical meristems. lateral meristems. vascular cambium. cork cambium. fiber cells. Use the figure on the next page to answer the corresponding questions. 41. In the accompanying figure, the region that is composed of secondary xylem is: A. B. C. D. E. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 42. The labeled structure that is responsible for secondary growth is: A. B. C. D. E. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 32 - 6 Name__________________________________________________________________Period______ Mrs. Laux Take Home Test #13 on Chap. 32 AP Biology DUE: MONDAY, MARCH 7, 2011 43. If you place your hand on the trunk of a tree that is 3 feet in diameter, the tissue you would be touching is: A. B. C. D. E. epidermis. secondary xylem. cork cambium. cork parenchyma. cork. 44. I have purchased a review book. a. yes b. no 32 - 7