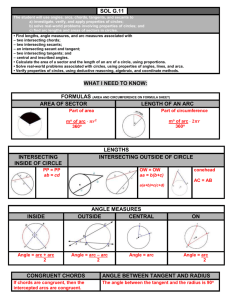
Geometry: Arcs & Angles Worksheet - High School

NAME
Practice A
For use with pages 613-620
Find the measure of the indicated arc or angle.
1. mBC= ?
2. mBC=
B
DATE
3. m!-BAC = ?
160°
C
4. mBC = ?
A
5. m/_BAC =
6. m/_BAC = ?
Find the measure of the arc or angle in
7. mAQMP
9. m~PNO
11. m@O
13. mP@
8. mANMO lO.m~@Np
12. mNOP
14. mO@N
24°
Decide whether a circle can be circumscribed about the quadrilateral
Find the value of each variabHe.
19.
Chapter I 0 Resource Book
20.
Copyright © McD0ugal Littell Inc.
All rights reserved.
NAME.
Practice B
For use with pages 613-620
Find the measure of the indicated arc or angle in
1. m/_BAC= ?
2. mBC = ?
B A
DATE
3. mA.BAC= ?
Find the measure of the arc or angle in ®0, given
mCD = 108° and roBE = ~lO0°.
4. m/_ABC 5. mACED
6. mA.BDE
7. mACBD
8. mAABD 9. m/-.BCE
10. mAD 11. nv~BC
Find the value of x.
A
E
D
2x+ 13)°
16. (3x- 8)° 17.
18, Archeology Archeologists found a portion of a circulm" dinner plate.
Describe a method to determine the diameter of the plate,
Copyright © McD0ugal Littett Inc.
All rights reserved,
(~eometry
Chapter 10 Resource Book
DATE NAME
Pr~~*i~e A
Far use with pages 621-627
Find the measure of L1.
1.
172°
170° ~
1
34~
8, 92o~
131°
Write an equation that can be used to so~ve for x. Then solve the equation for x.
105°
97°
Use the diagram of ®A to write the m/_l, m!_2, and m/_3 in order of increasing measure.
13.
14.
Geometry
Cha~ter 10 Resource Book
Copyright © McD0ugal Litt~tl inc.
A ~ ght~ i~d.
I
~1
NAME
Practic~ B
For use with pages 621-627
Find the measure of/_1.
DATE
5, 1~)
194°
241° ~
Write an equation that can be used to serve for x. Then solve the equation for x.
13.
Aerial V~ew You are flying across the plains of Kansas at an altitude of 32,000 feet,~.or approximately 6 miles. It is a clear day.
Find the measure of CD that represents the part of Earth that you can see.
B
Copyright © McDougal Littell Ins,
All rights reserved.
not drawn to scale
Geometry
Chapter 10 Resource Book
Lesson 10.2
continued
5. Sample answer: Construct perpendicular bisectors of D’--~ and ~. We may label the bisectors ~ and ~, where C is the center of the circle, K is the midpoint of DG and L is the midpoint of ~-~. Then CK ~ CL, because congruent chords are equidistant from the center,
mad CJ ~ C J, by the Reflexive Property of
Congruence. Therefore, by the HL Congruence
Theorem, AKJC .~ ALJC; this gives
!.D J1 ~ / HJI becaus.~e correspond~ag parts of
~Asare~-. 6. roDE = 50°,reEF= 130°,
mFG=50°,mGD= 130° 7. 73 8. 12 9. 13
Lesson 10.3
Warm-~Jp Exercises
1. 22.5 2. 18 3. 32 4. (40, 20)
Daily Homework (~uiz
1. major arc 2, minor arc 3. 78° 4. 220°
5. 28
Lesson Opener
Allow 15 minutes.
1. Sample answer:
Pract[ce B
1. 66° 2. 54° 3. 43° 4. 90° 5. 54°
6. 50° 7. 54° 8. 36° 9. 50° 10. 72°
11. 180° 12. 23.5 13. 7 14. 102
15. 13 16. 23.25 17. 8
18. Sample answer: Draw a chord, construct ± bisector; draw a second chord and construct ± bisector. Where ± bisectors intersect is the center.
Measure radius. Double for diameter.
Practice C
1. 74° 2. 132° 3, 43.5° 4. 56° 5, 19°
6. 21° 7. 90° 8. 43° 9. 47.5° 10. 43°
1!. 47° 12. 47.5° 13. 94° 14. 180°
15, 20 16, 7 17. 36
18.
Statements
1. /_MEI~ /.GED
2. m/.IMD = ~ miD
3. m!.IGD = ~ miD
4. m/_IMD = m/.IGD
1, Vert. Angles Tl~m.
2. Measure of inscribed/- = ½ measure of intercepted arc.
3. Measure of inscribed/- = ½ measure of intercepted arc.
4. Trans. Prop. of -------
2. m/_ADB = m/_BCA; The rays that form each angle intersect the circle at A and B, the endpoints of arc AB. 3. m!-DAC = m/-CBD; arc CD
4, MP = MQ
6. AMEI~ AGED 6. AA Similarity
Postulate
Regeach~ng with Practice
I, 34 2. 23 3, 43 4. 50 5. 25 6. 11
7. x=40, y=93 8. x=56, y=20
9. x=30, y~59.3
Practice A
1. 76° 2. 156° 3. 80° 4. 180° 5. 12°
6. 16° 7. 60° 8. 110° 9. 35° 10. 30°
11. 130° 12. 180° 13. 60° 14. 250°
15. no 16. yes 17. yes
18. x= 180, y=90 19. x=55, y=55
20. x = 75
Reel-Li~e Application
1. /-BDC 2. 4400 miles 3, 25° 4. 50°
5. 8 6. about 3666 miles
Challenge: Skills and Applications
1. Sample answer: Draw D--~. Since D--ff is a dianaeter, !.DGF is a right angle inscribed in ®C; therefore, DG ± FG. So, we have FG -~ GE
(given), !.DGF ~ !.DGE (all right angles are
Copyright © McD0ugal Littell Inc.
All rights reserved,
Geome’~ry
Chapter 10 Resource Book
Lesson 10.3
continued
congruent), and DG ~ DG (Reflexive Property of
Congruence). By the SAS Congruence Postulate,
ADGF ~ ADGE, so DF -~ DE (corresponding parts of = As are ~.) and ADEF is isosceles.
2. Sample answer: Draw PR, PS, and PT. Since
PR is a diameter of ®Q,/-PSR is a right angle inscribed in ®Q; therefore, PS ± RT. APSR and
APST are right triangles, PR ~ PT (radii of a circle are congruent), and PS =-- PS (Reflexive
Property of Congruence). Therefore,
APSR ~ APST by HL Congruence Theorem, and so RS -=- ST (corresponding parts of ~- As are ~).
3. Sample answer: Draw ~. Note that W’Z II ~, so by the Alternate Interio.o_.rr Angles Theorem,
/_WZX ~ !_YXZ. But mWX = 2m/_WZX and
mYZ = 2m/_YXZ, so mWX ~ YZ. Since two minor arcs in the same circle are congruent if and only if their corresponding chords are congruent, we conclude that WX ~- YZ, so WXYZ is an isosceles trapezoid.
4, a. OR = c, PS = c-a b. right triangle
PS PQ co Sample answer: -- = --
PQ RP c-a b d. Sample answer: b c + a’
b2 = (c-a)(c+a)=c~- a2,soa~ + b~=ca.
Quiz I ent~ li~Ss~t ~the~xadi~u&dr &wn~tn o~~ the point of tangency. 2. 15; two tangent segments with the same exterior endpoint are congruent. 3. 60° 4. 60° 5. 180° 6. 240°
7. 120° 8. 300° 9. 102.8°
Practice A
1. 90° 2. 86° 3. 116° 4. 39° 5. 82°
& 74° 7. 40° 8. 24.5° 9. 36°
10. 38° = ½(180° - x°); 104
11. 115° = ½(105° + x°); 125
12. 96° = ½(360° - x°); 168
’l& m/_3, m/_2, m/-1 ~4. m~l,m~2, m~3
Practice ~
1. 63° 2. 148° 3. 33° 4. 49° 5. 13.5°
6. 48° 7. 104°=½(360°-x°);152
8. 22° = ½(125 - x°); 81
9. 38° = ½(x° + 69°);7
10. 45° = ½(360 - x° - x°); 135
1~. 17° = ~(x° - 42°);76
12. 138°=~(360-x)°;84 ~3. ~6.3°
Practice C
1.
1.
142° 2. 65°
6. 52° 7.
Statements
2. BC ~ CD
4. mBC = mCD
3. 40°
20° 8. 100°
C is midpt, of BD m~BAC = mBC m/-CAD = ~ mCD
~. mA_BAC = mZ_CAD
4. 28° 5. 57.5°
Reasons
1. Given
2. Def. of midpoint
3. In a ®, measure of inscribed/- = ½
4. Congruent arcs have = measure
5. Mult. Prop. of
Equality
& Substitution
7. AC bisects Z_BAD 7. Def of Z_ bisector
Warm-Up l=xercises
1.45 2.4 3.5 4.60
DaRy Homework Quiz
1. a=90°,b=58°,c=45° 2. x=6, y=9
Lesson Opener
Allow 10 minutes.
1. a. A b. D,E,F c. B,C 2. a. A,B,F, b. E e. C,D & ~. C,E b. B,D c. A,F
Geometry’ ........... ......... ...........
Ch&pter 10 Resource Book
C0pyright © McDougal Littel[ Inc; ....................
All rights reserved.