Chemistry Review – Answer Key Chemistry Review
advertisement

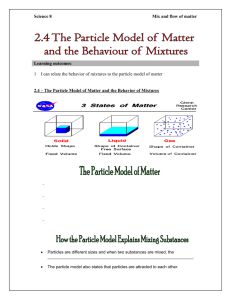
Chemistry Review – Answer Key Chemistry Review 1. Identify and describe intrinsic properties of matter. Include the definition for intrinsic property and at least 2 examples. Intrinsic properties are either physical or chemical properties of a substance. They are properties that do not change even if the size of the substance changes. Examples: Physical – no new substance is formed Chemical – new substances are formed Density Rusting Magnetism Burning Melting/boiling temperature Exploding Solubility (dissolves in water) Reacts with acid to form bubbles Conducts (moves) electricity 2. You have 4 liquids (Red, yellow, blue and green). Red has a density of 2.0, yellow has a density of 0.4, blue has a density of 1.0, and green has a density of 0.8. Sort the liquids according to density. A 5th liquid, “X” has a density of 0.6 than blue, but more dense than yellow. Where would liquid “X” fit? “X” would fit between the yellow and green layers 3. You have 3 liquids: water, glycerin, and oil. Glycerin is more dense than water, and oil is less dense than water. If mixed together, in what order with these liquids be layered in a cylinder? Oil – least dense Water Glycerin – most dense 4. You are given a white mystery substance that you think is either white sand or salt. What property could you use to identify your substance? Explain how you would test this. Solubility (dissolves in water). Salt would dissolve, sand would not. 5. Describe two physical properties that could help you separate substances out of a mixture Property How it could be used Magnetism Something attracted to a magnet could be pulled out with a magnet Solubility Something that dissolves could go into a liquid, go through a filter and other things would be stuck behind Density Some things float and others sink, you could add water 6. What is the difference between an element and a compound? Draw a picture of each. Element: made of one kind of atom Compound: made of one kind of molecule (can be a solid, liquid or gas) (can be a solid, liquid or gas) Continued on next page 7. Describe what particles in solids, liquids and gas are doing. In your answer include the spacing, attraction, motion and energy of each state of matter. Also include a diagram of each state of matter. Describe what happens to make a liquid change to a gas. Spacing Motion Attraction Energy Thermal and kinetic Solid Touching Vibrate in same position VERY attracted Least energy Liquid Very close Slide past each other Attracted enough to stay together Gas Spread apart Moving freely everywhere Weak attraction Most energy As heat is added to a solid, the particles vibrate faster and faster until they break free from the positions they are stuck in and start to move around each other. When that happens, the solid has melted and the particles are doing what liquid particles do. As heat is added to a liquid, the particles move faster and faster until they completely break free from each other and spread out as much as possible. When that happens, the particles are doing what gas particles do. The less energy particles have, the more attracted to each other they are. Continued on next page 8. In a chemical reaction, you start with reactants and end with products. How does the mass before a reaction compare to the mass after a chemical reaction? There are the same number and kinds of atoms in the reactants before a chemical reaction as there are in the products after a chemical reaction. No atoms were created or destroyed, so the mass before and after would be the same. Reactants: Products: 1 Carbon (black) 4 Hydrogen (white) 4 Oxygen (red) 1 Carbon (black) 4 Hydrogen (white) 4 Oxygen (red) 9. Vinegar and baking soda are put together in a sealed plastic bag. At first they are not mixed. Then the bag is tipped and bubbles form as they mix, plus the bag expands. What happens to the mass in the bag? Give evidence to support your answer. Since the bag is sealed, it is a closed system where no atoms or molecules can get in or out so all the atoms before and after the reaction are still there and the mass stays the same, even though the bag expands (has more volume) because the reaction produced carbon dioxide, which is a gas that spreads out as much as possible.