Marine Productivity and Nutrient Cycling Base of the food chain
advertisement

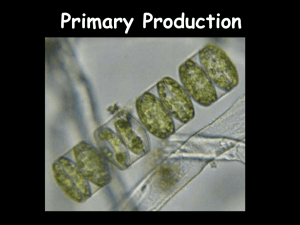
Base of the food chain Marine Productivity and Nutrient Cycling What is at the base of terrestrial food chains? Plants Of Fighting Phytos and Super Zoops In the ocean, microscopic phytoplankton are at the base of many marine food webs Diatoms Thalassiosira Dinoflagellates Diatoms Asterionella Phytoplankton Chaetoceros 1 Dinoflagellates have a tough Ceratium organic wall. They are common in estuaries and shelf waters; many produce cysts which can rest dormant within the sediments Pfiesteria piscicida autotrophic ~250 micrometers long heterotrophic “fish killer” toxic algal blooms Peridinium Diatoms have shells made of opaline silica; their shells accumulate beneath areas of high productivity to form deposits called siliceous ooze. heterotrophic ~50 micrometers long Autotrophs Why are land plants and marine phytoplankton at the base of food chains? Coccolithophores have shells made of calcium carbonate; these shells accumulate on areas of the seafloor above the CCD and form deposits called calcareous ooze. They are autotrophs. Autotrophs produce organic molecules from inorganic substances. Plants & phytoplankton are photosynthetic autotrophs. They utilize the energy of the sun to drive the biochemical reactions of photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + inorganic + solar → C6H12O6 + 6O2 nutrients carbon dioxide water energy nitrates, phosphates, trace elements, & vitamins glucose oxygen (simple sugar) The opposite of this reaction is respiration (what animals do exclusively) 2 Heterotrophs Primary Productivity The production of organic matter by all autotrophs is called primary production. All animals are heterotrophs; animals are dependent on the primary producers either directly or indirectly. stored chemical energy: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats herbivores (“grazers”) feed directly on autotrophs carnivores (“predators”) feed on live herbivores or primary production is measured in gC/m2/day other carnivores grams of Carbon per square meter per day scavengers feed on carrion Most primary production in the ocean is by photosynthesis by microscopic, unicellular phytoplankton; lesser amounts by: Animals acquire energy through respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + organic by-products glucose oxygen (simple sugar) carbon dioxide water photosynthetic bacteria (=cyanobacteria) chemosynthetic bacteria multicellular algae (seaweeds) vascular plants in coastal waters (grasses, mangrove trees) Solar radiation Productivity Basics Primary productivity by photosynthesis requires two essential ingredients: Low Latitudes Mid-Latitudes High Latitudes solar energy and inorganic nutrients if both are not readily available, productivity will be limited dependent on incident radiation, absorption, scattering varies with turbidity (murkiness), latitude, season euphotic zone is the upper part of the photic zone that receives enough light intensity to support net productivity (productivity > respiration). bottom of zone is called the compensation depth at bottom, light intensity = ~1% of surface intensity (in meters) photic zone is from the surface to the depth at which photosynthesis is still possible Water Depth 1. Solar energy (radiation) huge "solar footprint" 0 PHOTIC ZONE 100 (depth of light penetration is schematic only) EUPHOTIC ZONE 200 (sunlit surface waters where net productivity occurs) Angle of solar incidence varies with latitude and season 3 Productivity Basics (cont’d.) Primary productivity by photosynthesis requires two essential ingredients: solar energy and inorganic nutrients if both are not readily available, productivity will be limited 2. Nutrients macronutrients – required in large doses - nitrates (NO3 ) 3 phosphates (PO4 ) 4 silicates (SiO4 ) Note: In ocean waters and in phytoplankton tissues, the ratio of N:P is 16:1 – known as the “Redfield Ratio” so N is the “limiting nutrient” micronutrients – required in small doses trace elements (e.g., Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn, others) vitamins the principal source of nutrients is from the weathering of soils and rocks on land; dissolved nutrients are delivered to the ocean by river runoff so, where would you predict the highest primary productivity? along continental margins, especially in coastal waters 4