Geol. 1100 0 Physical Geology Study Guide 3 – Fall 2015 Relative

Geol. 1100 0 Physical Geology Study Guide 3 – Fall 2015
Relative Dating: stratigraphy’ Steno’s principles of superposition, original horizontality and lateral continuity; Hutton’s principle of cross-cutting relationships; unconformities
(nonconformity, angular unconformity, disconformity, paraconformity); Geologic Time
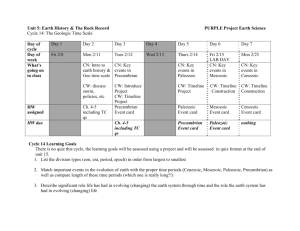
Scale: developed for economic reasons; William Smith’s principle of faunal succession; mass extinctions break out eras and periods; Charles Lyell found minor extinctions in the
Cenozoic Era; Know the Eras (Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic); Know the Periods (COSDCPP, TJC, PN) and when the breaks are between the Eras (540 Ma,
248 Ma, 66 Ma).
Radiometric Dating: What is an isotope?; atomic number vs. atomic mass; unstable isotope vs. stable isotope; radiometric decay; stochastic process; definition of half life and understand it; parent atom vs. daughter atom; mass spectrometer.
Geologic History: Rocks : Early Precambrian – protocontinent, craton, continental accretion; Late Precambrian – Rodinia, Snowball Earth hypothesis; Paleozoic – rifting of
Rodinia, continental accretion by collisions of volcanic arcs and continents, Pangea,
Ancestral Rockies Orogeny; Mesozoic – subduction beneath western U.S. (formed the
Sierra Nevada), Sevier and Laramide Orogeny (fold and thrust belts); Cenozoic – extension (stretching) of western North America, Basin and Range, San Andreas Fault,
Yellowstone Hotspot. Life : Early Precambrian – single cell life; Late Precambrian – complex, multicellular life, Ediacaran Fauna (around time of Snowball Earth); Paleozoic
– Cambrian Revolution (hard parts), Ordovician (land plants), Silurian (fish); Late
Paleozoic (amphibian and then reptiles and then early mammals); Mesozoic – age of dinosaurs; Cenozoic – age of mammals.
Landscapes – erosional vs. depositional landscapes; how landforms look is a function of
(rock types, structural geology, climate, uplift rates, erosional/depositional process (e.g. glaciers) and time); glacial features – moraines, till; Hydrologic cycle – evaporation, advection, precipitation, runoff, infiltration.
Mass movements – forces at work on particles sitting on slope (shear stress, gravity, normal stress, friction, slope angle; critical angle (aka angle of repose) (where τ = σ x coefficient of friction); role of water (surface tension vs. liquefaction); cohesion (by roots or rock type); shear resistance = C+( σ n
– P pore
) x (1/tan α ) (don’t memorize this, but understand it); slump; what types of things leads to mass movements taking place.
Rivers – tributary vs. distributary pattern; meandering streams (and how they work) vs. braided streams; channel belt vs. floodplain; cut bank vs. point bar; shear stress moves particles in a river; levee formation; hydrograph
Oceans – atmosphere/ocean coupling; insolation; Coriolis Force; Hadley Cell; gyre; thermohaline current; North Atlantic deepwater; how tides work; ocean waves and how they work; Tsunamis (how they form and how they grow towards shorelines).