Electronic Configuration • Electrons are placed in orbitals based on
advertisement

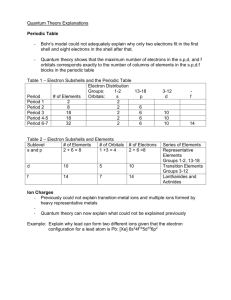
Electronic Configuration • Electrons are placed in orbitals based on the energy of the shell (n ; principal quantum number) • Each subshell contains only two electrons • Arrows indicating spin show the difference of each electron’s energy • This process is the Aufbau Principal Ground state electron configurations • Example: Li • atomic number = 3 • nucleus has 3 protons • neutral atom has 3 electrons • 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 1 electron in 2s orbital 2s 1s 1 Different ways to show electron configuration Box notation Energy level diagram ↑↓ 1s 2s ↑ 2s 1s Spectroscopic notation Li 1s2 2s1 Read this “one s two” not “one s squared” Write the superscript 1. Don’t leave it blank How degenerate orbitals are filled • Definition of degenerate orbitals • have the same energy • are almost always in the same subshell • Electrons prefer to be in different orbitals with the same spin (Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity) • Example: electrons in a p-subshell ↑ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 2 Electron configuration of O • Atomic number of O = 8 so neutral atom has 8 e– Electron configuration of O ↑↓ 1s O 1s2 config. has 2 e– • Atomic number of O = 8 so neutral atom has 8 e– • First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 6 e– left. 3 Electron configuration of O ↑↓ 1s ↑↓ 2s O 1s22s2 config. has 4 e– • Atomic number of O = 8 so neutral atom has 8 e– • First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 6 e– left. • Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. 4 e– left. Electron configuration of O ↑↓ 1s ↑↓ 2s ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 2p O 1s22s22p4 • • • • config. has 8 e– Atomic number of O = 8 so neutral atom has 8 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 6 e– left. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. Last 4 e– go into 2p subshell. 4 Electron configuration of Co • Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ 1s Co 1s2 config. has 2 e– • Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– • First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. 5 Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s Co 1s22s2 config. has 4 e– • Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– • First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. • Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. 23 e– left. Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s Co 1s22s2 config. has 4 e– • Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– • First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. • Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. 23 e– left. 6 Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p Co 1s22s22p6 • • • • config. has 10 e– Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. 23 e– left. Next 6 e– go into 2p subshell. 2p subshell is now full. 17 e– left. Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p 3s Co 1s22s22p63s2 • • • • • config. has 12 e– Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 2p subshell. 2p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 3s orbital. 3s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. 23 e– left. 17 e– left. 15 e– left. 7 Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p Co 1s22s22p63s23p6 • • • • • • config. has 18 e– Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 2p subshell. 2p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 3s orbital. 3s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 3p subshell. 3p subshell is now full. 25 e– left. 23 e– left. 17 e– left. 15 e– left. 9 e– left. Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s Co 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 • • • • • • • config. has 20 e– Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 2p subshell. 2p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 3s orbital. 3s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 3p subshell. 3p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 4s subshell. 4s subshell is now full. 25 e– left. 23 e– left. 17 e– left. 15 e– left. 9 e– left. 7 e– left. 8 Electron configuration of Co ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d Co 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d7 • • • • • • • • ↑ config. has 27 e– Atomic number of Co = 27 so neutral atom has 27 e– First 2 e– go into 1s orbital. 1s subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 2s orbital. 2s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 2p subshell. 2p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 3s orbital. 3s subshell is now full. Next 6 e– go into 3p subshell. 3p subshell is now full. Next 2 e– go into 4s subshell. 4s subshell is now full. Last 7 e– go into 4d subshell. 25 e– left. 23 e– left. 17 e– left. 15 e– left. 9 e– left. 7 e– left. Simplifying electron configurations • Build on the atom’s noble gas core • He 1s2 O 1s22s2sp4 O [He]2s2 ↑↓ 1s ↑↓ 2s ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 2p • Ar 1s22s22p63s23p6 Co 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d7 Co [Ar]4s23d7 ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d ↑ 9 The periodic table trick The last subshell in the electron configuration is one of these (row #) s (row # – 1) d (row #) p (row # – 2) f Electron configuration of Sn • Locate Sn on the periodic table 10 Electron configuration of Sn Sn [Kr] • The noble gas core is Kr Electron configuration of Sn Sn [Kr]5s2 • The noble gas core is Kr • From Kr, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 5th row → 5s2 11 Electron configuration of Sn Sn [Kr]5s24d10 • The noble gas core is Kr • From Kr, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 5th row → 5s2 • Then go 10 spaces across the d-block on the 5th row → 4d10 • note: n = row – 1 = 5 – 1 = 4 Electron configuration of Sn—done Sn [Kr]5s24d105p2 • The noble gas core is Kr • From Kr, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 5th row → 5s2 • Then go 10 spaces across the d-block on the 5th row → 4d10 • note: n = row – 1 = 5 – 1 = 4 • Finally go 2 spaces into the p-block on the 5th row → 5p2 12 Practice • Refer to a periodic table and write the electron configurations of these atoms using spectroscopic notation. Also show box notation for the orbitals not in the noble gas core. • Zn [Ar]4s23d10 ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 4s 3d • I [Kr]5s24d105p5 ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 5s 4d 5p The f-block is inserted into to the d-block 13 Find the electron configuration of Au • Locate Au on the periodic table Find the electron configuration of Au • Au [Xe] • The noble gas core is Xe 14 Find the electron configuration of Au • Au [Xe]6s2 • The noble gas core is Xe • From Xe, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 6th row → 6s2 Find the electron configuration of Au • Au [Xe]6s24f14 • The noble gas core is Xe • From Xe, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 6th row → 6s2 • Then detour to go 14 spaces across the f-block → 4f14 • note: for the f-block, n = row – 2 = 6 – 2 = 4 15 Find the electron configuration of Au • Au [Xe]6s24f145d9 • The noble gas core is Xe • From Xe, go 2 spaces across the s-block in the 6th row → 6s2 • Then detour to go 14 spaces across the f-block → 4f14 • note: for the f-block, n = row – 2 = 6 – 2 = 4 • Finally go 9 spaces into the d-block on the 6th row → 5d9 • note: for the d-block, n = row – 1 = 6 – 1 = 5 The periodic table 16 Electron configurations • Without using a periodic table find the groundstate electron configuration of an atom with • 6 electrons • 12 electrons • 24 electrons 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 5s 5p 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 6f 7s 7p 7d 7f Electron configurations • Without using a periodic table find the groundstate electron configuration of an atom with • 6 electrons 1s 1s22s22p2 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 5s 5p 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 6f 7s 7p 7d 7f • 12 electrons 1s22s22p63s2 • 24 electrons 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4 17 The periodic table trick (row #) (row #) – 1 (row #) (row #) – 2 Using the periodic table trick • Atomic number = 6 C [He]2s22p2 • Atomic number = 12 Mg [Ne]3s2 • Atomic number = 24 Cr [Ar]4s23d4 18 Magnetic susceptibility • C [He]2s22p2 paramagnetic ↑↓ 2s • Mg [Ne]3s2 ↑ diamagnetic ↑↓ 3s • Cr [Ar]4s13d5 ↑ 2p 3p paramagnetic ↑ 4s ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ 3d ↑ 19