WORD ROOTS AND COMBINING FORMS
advertisement

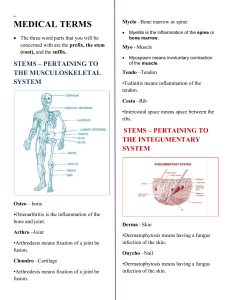
Schultz WORD ROOTS AND COMBINING FORMS Many medical terms are “compound” words. That is, they are made up of more than one root of combining form. Example of such compound words are leucocytes (white blood cell) and chemotherapy (treatment of disease by administering chemicals). The following list includes some of the most commonly used word roots, prefixes, suffixes and combining forms of used in making medical terms. Alg-, Algia- pain Neuralgia (nyoo-RAL-ja), pain along the course of a nerve. Angio- vessel Angiocarditis (an-ge-O-kard-i-tis), inflammation of blood vessels in the heart. Arthr-, Arthro- joint Arthropathy (ar-THROP-a-the), disease of a joint. Brachi- arm Brachialis (bra-ke-AL-is), muscle for flexing the forearm. Bronch- trachea, windpipe Bronchoscopy (bron-KOS-ko-pe), direct visual examination of the bronchi. Cardi-, Cardia-, Cardio- heart Cardiogram (KARD-e-o-gram), a recording of the force and the form of the heart’s movements Cephal- head Hydrocephalus (hi-dro-SEF-a-lus), enlargement of the head due to an abnormal accumulation of fluid Cerebro- brain Cerbrospinal fluid(se-re-bro-SPIN-al), fluid contained within the cranium and spinal canal. Chondr-, Chondri-, Chondrio- cartilage Chondrocyte (KON-dro-sit), a cartilage cell. Cost- rib Intercostal (in-ter-kos-tal ), in between the ribs Crani- skull Crainotomy (kra-ne-OT-o-me), surgical opening of the skull. Cyt-, Cyto-, Cyte- cell Cytology (si-TOL-o-je), the study of cells. Derma-, Dermato- skin Dermatosis (derm-ma-TO-sis), any skin disease. Entero- intestine Enteritis (ent-e-RIT-is), inflammationof the intestine. Gastr- stomach Gastrointestinal (gas-tro-in-TES-tin-al), pertaining to the stomach and intestine. Hem-, Hemat- blood Hematoma (he-ma-TO-ma), blood beneath the skin. Hepar-, Hepato- liver Hepatitis (hep-a-TIT-is), inflammation of the liver. Hist-, Histio- tissue Histology (his-TOL-o-je), the study of tissues Mast- breast Mastitis (ma-STIT-is), inflammation of the mammary gland. Meningo- membrane Meningitis (men-in-JIT-is), inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. Morpho- form, shape Morphology (mor-FOL-o-je), study of the form and structure of things. Myo- muscle Myocardium (mi-o-KARD-e-um), heart muscle. Nephro- kidney Nephrosis (ne-FRO-sis), degeneration of kidney tissue. Neuro- nerve Neuroblastoma (ner-o-blas-TO-ma), a malignant tumor of the nervous system composed of embryonic nerve cells. Oculu- eye Binocular (bi-NOK-yoo-lar), pertaining to the two eyes. Osteo- bone Osteoblast (os –te-o-blast ), bone producing cell. Patho- disease Pathogenic (path-o-JEN-ik), giving origin to disease. Pyo- pus Pyuria (pi-YOOR-e-a), pus in the urine. Scler-, Sclero- hard Arteriosclerosis (ar-ter-e-o-skle-RO-sis), hardining of the arteries. Soma-, Somato- body Somatotrophic (so-mat-o-TRO-fik), having a stimulating effect of body growth. Viscer- organ Visceral (VIS-e-ral), pertaining to the abdominal organs. Prefixes (2) A-, An- without, lack of, deficient Aseptic (a-SEP-tik), without infection; Anesthesia (an-es-THE-zha), without sensation. (1) Ab- away from, from Abnormal (ab-NOR-mal), away from normal. (2) Ad- to, near, toward Adduction (a-DUK-shun), movement of an extremity toward the axis of the body. (1) Dis- separation, apart, away from Disarticulate (dis-ar-TIK-yoo-lat), to separate at joint. (2) Dys- painful, difficult Dyspnea (disp-NE-a), difficult breathing. (1) End-, Endo- inside Endocardium (en-do-KARD-e-um), membrane lining the inner surface of the heart. (2) Epi- upon, on, above Epidermis (ep-i-DER-mis), outermost layer of skin. (2) Ex-, Exo- out, away from Exocrine (EK-so-krin), excreting outwardly or away from. (2) Hyper- beyond, excessive Hyperglycemia (hi-per-gli-SE-me-a), excessive amount of sugar in the blood. Schultz (2) Hypo- under, below, deficient Hypodermic (hi-po-DER-mik), below the skin or dermis. (2) Inter- among, between Intercostal (int-er-KOS-tal), between the ribs. (1) Intra- within, inside Intracellular (in-tra-SEL-yoo-lar), inside the cell. (2) Para- near, beyond, apart from, beside Paranasal (par-a-NA-zal), near the nose. (1) Peri- around Pericardium (per-i-KARD-e-um), membrane or sac around the heart. (2) Retro- backward, located behind Retroperitoneal (re-tro-per-it-on-E-al), located behind the peritoneum. Suffixes -ac, -al pertaining to Cardiac (KARD-e-ak) (cardial), pertaining to the heart. -ary connected with Ciliary (SIL-e-ar-e), resembling any hairlike structure. -asis, -asia, -esis, -osis condition or state of Hemostasis (he-mo-STA-iss), stopping of bleeding or circulation. (2) -cel, -cele swelling, an enlarged space or cavity Meningocele (men-IN-go-sel), enlargement of the meninges. (2) -ectasia, -ectasis stretching, dilation Bronchiectasis (bron-ke-EK-ta-sis), dilatation of a bronchus or bronchi. (2) -ectomize, -ectomy cutting out, excision of, removal of Thyroidectomy (thi-royd-EK-to-me), surgical removal of thyroid gland. -emia condition of blood Lipemia (lip-E-me-a), abnormally high concentration of fat in the blood. -gen an agent that produces or originates Pathogen (PATH-o-jen), a microorganism or substance capable of producing a disease. -gram a record, that which is recorded Electrocardiogram (e-lek-tro-KARD-e-o-gram), a record of heart action. -graph an instrument for recording Electroencephalograph (e-lek-tro-en-SEF-a-lo-graph), an instrument for recording electrical activity of the brain. -ia a state or condition Hypemetropia (hi-per-me-TRO-pe-a), condition of farsightedness. -iatrics, iatry medical practice or specialities Pediatrics (ped-e-A-triks), medical science relating to care of children and treatment of their diseases. -ism condition of, state Rheumatism (ROO-ma-tiz-am), inflammation, especially of muscles and joints. -itis inflammation Neuritis (nyoo-RIT-is), inflammation of a nerve or nerves. -oma tumor Fibroma (fi-BRO-ma), a tumor comosed mostly of fibrous tissue. -pathy disease Neuropathy (nyoo-ROP-a-the), disease of the peripheral nervous system. -penia deficiency Thrombocytopenia (throm-bo-sit-o-PE-ne-a), deficiency of thrombocytes in the blood. (2) -plegia, -plexy stroke, paralysis Apoplexy (AP-o-plex-se), sudden loss of consciouness, and paralysis. -poiesis formation of Hematopoisis (he-mat-a-poy-E-sis), formation and developement of red blood cells. -rrhea flow, discharge Diarrhea (di-a-RE-a), abnormal frequency of bowel evacuation, the stools with a more or less fluid consistency. -stomy creation of a mouth or artificial opening Tracheostomy (tra-ke-OST-o-me), creation of an opening in the trachea. -tomy cutting into, incision into Ureterotomy (u-re-ter-OT-o-me), incision of a ureter. (3) –tropic, trophic turning toward, influencing, changing Gonadotrophic (go-nad-a-TRO-fic), influencing the gonads. -uria urine Polyuria (pol-e-YOOR-e-a), excessive secretion of urine.