Hope and Mindset: Transforming Chaffey's Future
advertisement

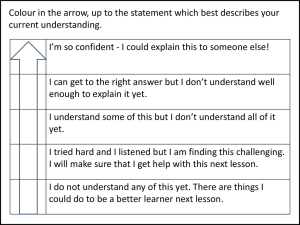
Hope and Mindset: Transforming Chaffey’s Future Dr. Sherrie Guerrero Jim Fillpot Lisa Bailey Laura Hope Why Hope? Research regarding the influence of hope on behavior and thinking “Actionability” Translation of these strategies in the entire culture Timeliness What is Hope? HOPE = willpower + “waypower” AGENCY + PATHWAYS in order to achieve a GOAL Hope Scale – Management/Confidential Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Entire Scale) Number of Respondents 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 mean = 58.4; median = 59.0; standard deviation = 4.04 Hope Scale – Management/Confidential Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Agency Sub-Scale) Number of Respondents 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 mean = 29.3; median = 30.0; standard deviation = 2.36 Hope Scale – Management/Confidential Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Pathway Sub-Scale) Number of Respondents 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 mean = 29.0; median = 29.0; standard deviation = 2.38 Comparison of Students & Management/Confidential on Total, Agency, & Pathway Hope Scales 60 54.0 58.4 Students Management/Confidential 50 Score 40 30 27.1 29.3 26.9 29.0 20 10 0 ES = .80 ES = .69 ES = .70 TOTAL Hope Scale Agency Hope Scale Pathway Hope Scale Hope Scale – Preliminary Student Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Entire Scale) 50 Low Hope Number of Students 45 40 Average High Hope Hope 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 mean = 54.0; median = 55.0; standard deviation = 6.46 Hope Scale – Preliminary Student Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Agency Sub-Scale) 90 Low Hope Number of Students 80 70 Average Hope High Hope 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 mean = 27.1; median = 28.0; standard deviation = 3.80 Hope Scale – Preliminary Student Data HOPE SCALE SCORE (Pathway Sub-Scale) 90 Low Hope Number of Students 80 70 Average Hope High Hope 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 mean = 26.9; median = 27.0; standard deviation = 3.59 Success Rate Differences by Level of Hope TOTAL Hope Scale 100 90 Success Rate 80 70 79.6% 67.8% 70.1% 60 50 ES = .22 40 30 20 ES = .27 10 0 Low Hope Students Average Hope Students High Hope Students Success Rate Differences by Level of Hope AGENCY Hope Scale 100 90 80 70 66.7% 72.3% 76.3% 60 50 40 30 20 ES = .21 10 0 Low Hope Students Average Hope Students High Hope Students Success Rate Differences by Level by Hope PATHWAY Hope Scale 100 90 80 70 71.6% 70.4% Low Hope Students Average Hope Students 74.4% 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 High Hope Students Other Observed Differences Success Rates by Course Characteristics (TOTAL) Transfer Status High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Transferable 79.8 69.7 75.0 Not Transferable 78.3 74.1 61.2 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope CTE Courses 80.0 70.0 78.9 Not CTE Courses 79.3 70.9 69.4 Foundation High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Foundation 78.8 75.4 65.6 Not Foundation 79.5 70.1 72.9 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Full-Time 78.4 63.4 69.5 Part-Time 80.1 75.8 73.2 CTE Status Teaching Arr. Other Observed Differences Success Rates by Course Characteristics (Agency) Transfer Status High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Transferable 76.6 70.5 73.4 Not Transferable 78.7 74.6 58.0 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope CTE Courses 74.0 72.2 74.5 Not CTE Courses 78.0 71.3 68.6 Foundation High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Foundation 76.9 75.0 67.9 Not Foundation 77.0 71.0 70.3 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Full-Time 71.9 65.9 63.3 Part-Time 80.3 75.4 74.4 CTE Status Teaching Arr. Other Observed Differences Success Rates by Course Characteristics (Pathway) Transfer Status High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Transferable 74.7 69.8 80.3 Not Transferable 80.8 73.2 67.2 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope CTE Courses 77.8 71.3 76.0 Not CTE Courses 75.5 70.4 77.2 Foundation High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Foundation 83.3 71.6 76.6 Not Foundation 75.2 70.5 77.0 High Hope Average Hope Low Hope Full-Time 73.9 63.2 76.5 Part-Time 77.4 75.8 77.2 CTE Status Teaching Arr. Measuring Hope in Everyone What does the research say about hope? What do our “hope scores” reveal? What can we learn from the research? Connecting the Hope Initiative to the Strategic Plan Strategic Plan Completion Framework What it looks like Introduction: Connecting students to necessary resources and pre-enrollment processes Senior Early Assessment ME First Systemic changes What it looks like Connection: Establishing Students’ Relationship With the College Contact students if they drop a class Offer intervention Advancement: Providing Intrusive Academic Support in Key Areas Contact undecided students and invite them to a workshop What it looks like Advancement: Requiring Students to Define Academic and Career Goals Reconsider the ways students identify goals at intake/application Advancement: Developing Sustained Engagement Strategies Tie enrollment priorities to successful progress on goal What it looks like Completion: Monitoring Progress on Goals With Intrusive Action During Key Momentum Points Notification of 15- and 30-unit milestones Connecting to the Entire Community Summer Institute and Faculty Success Center sessions Classified professionals introduction Management Retreat Future training Connecting Hope and Mindset Hope is a continuum of responses in different contexts Mindset is an “actionable” condition Hope and Mindset Low Hope/Fixed Mindset Sets easy goals Overcome by obstacles Fears challenge and failure Shrinks from feedback Blames others for failures Threatened by others’ success High Hope/Growth Mindset Sets challenging goals—takes risks Views obstacles as opportunity Uses failure and feedback Assumes responsibility for failure Celebrates others and their contribution What Creates Low Hope/Fixed Mindset? “Perfect is the enemy of the good” (Voltaire) Fear of rejection or judgment The belief that achievement is equated with ease: “effortless perfection” Change the behavior to change the thinking Encouraging Hope and Growth Mindset Continuum High Hope Growth Mindset of Hope and Mindset “Stuck” Low Hope Fixed Mindset Strategies for High Hope People Praise behavior and performance – not the person Provide constructive feedback Help them set challenging goals Provide support as needed despite the willingness to take responsibility and initiative Help them understand others when they display low hope/fixed mindsets Introduce opportunities for growth Strategies for “Stuck” People Assure when needed about your confidence in their capacity to learn and grow Teach the relationship between challenge and success Give them increasingly challenging tasks Demonstrate your own process when challenged Praise behavior and performance Give them opportunities to express concerns Teach them how to fail successfully Be a role model and provide other models Strategies for Discouraged People Provide increased feedback and discuss the purpose of feedback Set the growth mindset as an expectation Share your own challenges Provide low risk opportunities to try new skills or strategies Coach through dilemmas Encourage discussion about the process of taking risks Praise performance and behavior Call out fixed mindset thinking and encourage reframing Let’s Practice Each group has three employee profiles. Identify and discuss the strategies that you would use to help this person be the best contributor possible. Debriefing about Strategies Trevor Sam Sheila When New Employees Arrive: They use words like… Honored Excited Skilled Well Prepared Willing to do whatever is asked of them They use hopeful words and demonstrate hopeful behaviors. They have high hopes about their manager. Summary of Best Companies: Survey Findings from Glassdoor.com® 2011 BEST COMPANIES (as evaluated by employees) Allow Autonomy Reward Performance Encourage Growth Act Friendly Are Respectful Hire Great People Provide Good Training Cultivate Positive Culture Pay Well WORST COMPANIES (as evaluated by employees) Micromanage Employees Use Favoritism Promote Under-Qualified Managers Do Not Recognize Achievement Provide Poor Pay/Benefits Provide No or Poor Training Are Unethical/Dishonest Reward Problem Employees Problem Solving Through Hope and Mindset ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS: Forward Thinking Autonomy Risk/Reward Continuous Improvement Culture of “How Can We Do This Better?” Mindset of Continuous Improvement According to Jeff Jarvis’ book, What Would Google Do?” by using an online “anti-fan” club, Dell transformed itself from the worst to the first in the area of customer control. Jarvis asks, “Why not apply this same principle to employees?” How Can We Do Better? Case Study: We can improve the experience for students by providing cleaner restrooms Dr. Shannon was given this feedback when he arrived in 2007. How did the College use willpower and waypower? WHAT: CLEAN AND GREEN HOW: EXPECT AND INSPECT: Assessing, Training, Inviting Input, Encouraging Autonomy, Providing Positive Interaction and Friendly Feedback, Rewarding Culture of Critique Hope implies challenges/opportunities lie ahead. Quietly think and reflect: How can your area improve? Pick one process/service and one personnel matter: What challenges are you facing now in your department/division? What opportunities do you see? How do other colleges/organizations do this better? SET THIS ASIDE. DO NOT PROBLEM SOLVE! How Can We Do Better? Break into your groups. On the paper provided, your group is to identify at least three (3) areas we can improve as a College. Use your personal notes, use the strategic plan, etc. All members should express their thoughts. Do NOT problem solve, yet. Report Out. How Can We Do Better? Return to Your Group. Select One of the Areas for Improvement. What Are Some Pathways for Improvement? People Policies Contracts Technology Processes Communication How Can I Do Better? Look at your own list. What can I do today? I can honestly assess myself and the services my department provides I can use hopeful strategies with my staff I can give my colleagues respectful feedback and thoughtful ideas I can keep my norms, goals and objectives on display at all times How Can We Apply These Strategies to Ourselves? Remember that struggle and growth are partners Incorporate growth language within your unit Be a model for a growth mindset Trust in partners to support your growth