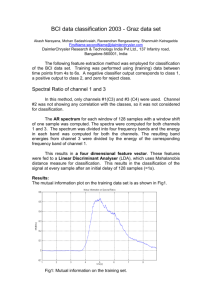
Brain Computer Interface
advertisement

Brain Computer Interface Mina Mikhail minamohebn@gmail.com Introduction • Ways for controlling computers – Keyboard – Mouse – Voice – Gestures • Ways for communicating with people – Talking – Writing – Gestures Problem • Shortage of the current ways of interaction – Require muscle movements • Disabled people – Totally paralyzed people are estimated to be 2 cases per 100,000 each year – Amyotrohic lateral sclerosis (ALS) • This raises the need of a new way of communication Brain Computer Interface • Direct Neural Interface or Brain-Machine interface • An interface between the human brain and computers • A New communication Channel BCI Misconceptions • Cannot read thoughts • Cannot write to the brain • Cannot repair injured areas • Cannot operate without your will Human Brain • The Ultimate Parallel Machine ! • Billions of neurons require a lot of energy. – 15% of the cardiac output – 20% of total body oxygen consumption – 25% of total body glucose utilization. • Energy consumption for the brain to simply survive is 0.1 calories per minute … and … • 1.5 calories per minute during crossword puzzle Brain Regions Parietal Frontal lobe Occipital • Frontal Lobe Temporal – Primary motor cortex, Frontal Eye, – information processing, • Parietal – Sensory information, taste, pressure, sound, temp.. • Occipital – Visual processing center • Temporal – Auditory processing Human Brain • Whenever a neuron is active, its voltage changes Human Brain • Million of neurons fire together • Each mental state produces a distinct pattern of electrical activity Measuring Brain Activity Measuring Brain Activity • Positron emission tomography – A radio Active isotope is injected into the subject’s blood – Isotopes emits positrons • Advantages – High spatial resolution • Disadvantages – Expensive – Low time resolution – Not portable Functional Magnetic Resonance • FMRI depends on blood flow • It measures the magnetic properties of the hoemoglobin • Active neurons consume oxygen carried by hemoglobin • Advantages – High spatial resolution • Disadvantages – Expensive – Low time resolution – Not portable EEG • Measures the electrical activity of the neurons. • Advantages – High time resolution – Cheaper – portable • Disadvantages – Low spatial resolution – Still not user friendly EEG Montage • 10-20 system – An international system that describes and applies the location of the electrodes Rhythmic Activity • Delta Band – < 3 Hz – Deep sleep • Theta Band – 4-7 Hz – Drowsiness and meditation • Alpha Band – 8-12 Hz – Awake • Beta Band – 13-30 Hz – Concentration and thinking BCI Categories BCI Categories BCI Categories Differences • Electrode placements • Number of electrodes • Number of trial before taking a decision General Approach Signal Acquisition • • • • • • EEG CAP Bioamplifier Electrodes Active electrodes Conductive gel Impedance Checker Signal Preprocessing • Artifacts – Technical Artifacts • Line noise • Electrode Artifacts Signal Preprocessing • Physiological Artifacts – Eye Blinking artifacts – Eye movement Artifacts – Muscle Activity artifact Signal Preprocessing Methods for Artifact Rejection • • • • Filters Artifact Rejection Artifact Subtraction (using EMG sensors) Blind Source Separation – Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Feature Extraction (frequency domain) • Frequency Domain Features – FFT, wavelets, finite impulse response – EEG Frequency Band Power • most of the times a measure of event related desynchronization (ERD) is used Feature Extraction (Time domain) • Spatial Domain Feautres – Hjorth parameters • Three parameters are used to characterize the EEG – Activity (mean power) – Mobility (mean frequency) – Complexity Classification • Bayes Classifiers • Support Vector Machines • Artifical Neural Networks Application • • • • Wheel Chair Controlling Cursor Controlling OS Word Processing Research Labs • • • • • Graz Brain Computer Interface BCI Research at Alberta University BCI Research at Oxford University Berlin Brain Computer Interface Computer Vision and Multimedia Laboratory Geneva University BCI Systems