Rational Numbers - Southgate Schools
advertisement

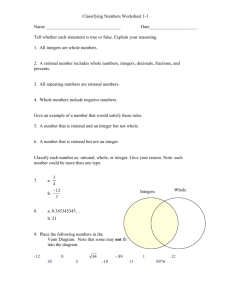
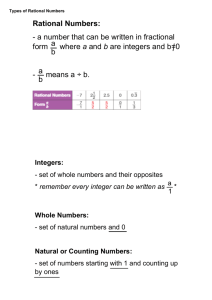
National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards 7.NS.2 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. 7.NS.2b Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; this estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation. Mathematical Practices 1, 3, and 4 are aspects of mathematical thinking that are emphasized in every lesson. Students are given opportunities to be persistent in their problem solving, to express their reasoning, and apply mathematics to realworld situations. Exercises 11 and 15 focus on Mathematical Practice 4 Model with mathematics. Exercises 12 and 14 focus on Mathematical Practice 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Exercise 13 focuses on Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 1 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers 1 Launch the Lesson Focus narrowing the scope Objective Compare and order rational numbers. 7.NS.2, 7.NS.2b, 7.EE.3 Coherence connecting within and across grades Previous Now Next Students wrote rational numbers Students compare and order Students will add and subtract as decimals and fractions. rational numbers by writing them fractions with like denominators. in the same form. Rigor pursuing concepts, fluency, and applications See the Levels of Complexity chart in the Practice and Apply section. Lesson Vocabulary rational number common denominator least common denominator As students enter the classroom, have them complete the Common Core Quick Check to review and assess the skills presented in the previous lesson. Engage Explore Explain Elaborate Evaluate Ideas for Use You may wish to launch the lesson using a whole group, small group, think-pair-share activity, or independent activity. Think-Pair-Share Give students one minute to think through their responses to the Launch the Lesson: Vocabulary activity. Have them share their responses with a partner. Then have each partner share their response with the whole group. 1, 6, 7 Alternate Strategy Have students generate their own rational numbers that can be placed into each category of the Venn diagram. For each number they generate, have them explain why that number can be placed into that category. 1, 3, 7 Resources Common Core Quick Check: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 2 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers 2 Teach the Concept Focus: Mathematical Background Rational numbers can be written as the ratio of two integers (the second integer cannot be 0). Decimals that neither terminate nor repeat are not rational. Fraction-Decimal Equivalents When students are memorizing common fraction-decimal equivalents, it is useful to use coin equivalents. Quarter: = 0.25, Dime: = 0.10, = 0.50, = 0.30, = 0.75 = 0.90 One dollar can be divided equally into fifths, so = 0.20, = 0.40, and = 0.60. The McGraw-Hill Professional Development Video Library provides short videos that support Glencoe Math. The featured videos for mathematical content in this lesson are: Compare and Order Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Percents Rational and Irrational Numbers Simplifying Fractions and Expressions For classroom presentation, use the Step-by-Step Examples to demonstrate the examples from the Student Edition. Engage Explore Explain Elaborate Evaluate Ask the scaffolded questions for each example to differentiate instruction. 1. Compare rational numbers. What is the difference between the two mixed numbers? The numerators of each fraction are different. Between which integers does each mixed number lie? -1 and -2 Explain how even though 5 > 1, the mixed number < . Sample answer: The mixed numbers are negative, and as you move to the left on the number line, values decrease. Explain how you could compare the numbers without locating them on a number line. Sample answer: Both mixed numbers have the same whole number part. By comparing the numerators, farther left than is . Need Another Example? Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 3 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Fill in the with <, >, or = to make a true sentence. > 2. Compare rational numbers. Can we simply compare the numerators 7 and 8 to determine which fraction is greater? Explain. no; The denominators are different. What is the LCD of 12 and 18? 36 Explain how to rewrite each fraction using the LCD. Multiply How do you know that is equivalent to by ; multiply ? We multiplied by by . , which is the same as multiplying by 1. Would your result be different if you simplified prior to comparing the numbers? Explain. no; Sample answer: The result is the same because of equivalent fractions. Need Another Example? Fill in the with <, >, or = to make a true sentence. < 3. Compare rational numbers. What are you trying to determine? the class that owns more roller shoes What are the two numbers we need to compare? 20% and 5 out of 29 What will you have to do to compare these values? Sample answer: Express each number as a decimal. How do you determine that 5/29 0.1724? Divide the numerator by the denominator. How could you use estimation to compare? = and > Need Another Example? In a football game, the quarterback completed 11 out of 19 passes. The next week, he completed 60% of his passes. During which game did he complete the greater fraction of his passes? the second game 4. Order a set of rational numbers. In what form could we compare these numbers? Sample answer: decimal form Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 4 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Will annexing zeros change the value of a decimal? No, you can annex as many zeros as needed. Why should you extend each decimal place to the thousandths? because each pair has the same tenths and hundredths values How do you know just by looking at the numbers 3.44 and 3.4 which one is greater? Sample answer: 3.4 repeats the digit 4 forever. Even if it just repeated the digit to the thousandths place, 3.444 > 3.44. Is a terminating decimal, repeating decimal, or neither? Explain. Neither; is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal. Need Another Example? Order the set from least to greatest. 5. Order a set of rational numbers. In what form can we compare these numbers? Sample answer: decimal form Could you use another form to compare? If so, which form? yes; Sample answer: percent What are the fractional values for each number? decimal values? percentage values? , , , ; 0.67, 0.64, 0.60, 0.69; 67%, 64%, 60%, 69% Which form do you prefer to use to compare the numbers? See students’ preferences. Need Another Example? Maddie is a guard on the basketball team. She made 70% of her field goals in the first game. She made 0.62, , and 66% of her field goals in the next three games. List Maddie’s made field goal statistics from least to greatest. 0.62, 66%, 70%, Alternate Teaching Strategy If students have trouble finding the LCD of the fractions, Then use one of these reteach options: 1. Quick Review Math Handbook, pp. 153-155 2. Problem-Based Learning Book 2, Unit B: Rational Numbers, Investigation 2: Order and Compare Rational Numbers 3. Have students write equivalent fractions for each fraction until they find fractions with a common Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 5 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 3. Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers denominator. For example, to compare and , , , the comparison. . Since and and and , students would write , , , , have a common denominator, they can be used for . , so . Formative Assessment Use these exercises to assess students' understanding of the concepts in this lesson. If some of your students are not ready for assignments, use the differentiated activities below. Pairs Discussion Have students work together to complete Exercises 1-4. Give them blank number lines for Exercises 3 and 4. Students should place values on a decimal or fraction number line. 1, 5 Numbered Heads Together Provide a list of varying fraction, decimal, and percentage values. Have students work in groups generate equivalent values of remaining forms for each given value. Call on one group member to share the group’s responses. 1, 7 Tips for New Teachers Rational Numbers Help students remember the definition of rational numbers by pointing out that rational numbers can be written as a ratio of integers (provided the second integer is not 0). You may also wish to remind students that terminating decimals can be written as fractions. Teach with Tech Interactive WhiteBoard Draw a number line on the IWB to compare and order rational numbers. Have students use the highlighter tool to show the placement of various rational numbers as suggested by other students in the class. Have students decide on the order of value of the rational numbers. Repeat with different sets of rational numbers. Podcast Have students write a song, rap, or poem about rational numbers, integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. Included should be what type of number is in each set and how the different sets of numbers relate to each other. Have students record the result using software and share it by way of a podcast. Resources Virtual Manipulatives Fractions as Decimals Fractions as Decimals Mixed Numbers as Decimals Write a Fraction as a Decimal Using Division Write a Fraction as a Decimal Using Division Write a Fraction as a Repeating Decimal Real-World Example: Write a Decimal as a Fraction Compare Rational Numbers Compare Rational Numbers Order Rational Numbers Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 6 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Real-World Example: Order Rational Numbers eToolkit Problem-Based Learning Book 2, Unit B, Student Edition: Rational Numbers Problem-Based Learning Book 2, Unit B, Teacher Edition: Rational Numbers Hot Topic 2-9: Fraction, Decimal, and Percent Relationships Compare and Order Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Percents Simplifying Fractions and Expressions Manipulative Masters: Number Lines Compare with Percents Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 7 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers 3 Practice & Apply Engage Explore Explain Elaborate Evaluate Independent Practice and Extra Practice The Independent Practice pages are meant to be used as the homework assignment. The Extra Practice page can be used for additional reinforcement or as a second-day assignment. Levels of Complexity The levels of the exercises progress from 1 to 3, with Level 1 indicating the lowest level of complexity. Suggested Assignments You can use the table below that includes exercises of all complexity levels to select appropriate exercises for your students' needs. Differentiated Homework Options Approaching Level 1–9, 11, 12, 14, 15, 24, 25 On Level 1–7 odd, 9–12, 14, 15, 24, 25 Beyond Level 9–15, 24, 25 can provide additional remediation support with personalized instruction and practice. Create Your Own Homework Online eSolutionsManual™ can be used to create worksheets for the suggested assignments above, or to create your own worksheets for differentiated homework or review. The following worksheets are also available for additional homework practice: The Skills Practice editable worksheet provides students with additional practice in the skills taught in this lesson. The Homework Practice editable worksheet helps students practice skills in this lesson and use those skills to solve problems. The Problem-Solving Practice editable worksheet helps students become better problem solvers by providing frequent opportunities to solve real-world problems. The Extra Practice worksheet provides additional practice for the skills taught in this lesson. The Step-by-Step Solutions provide a worked out solution for selected exercises from the Independent Practice in the Student Edition. Common Error Students may have trouble comparing fractions with unlike denominators because they Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 8 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers may only compare the numerators. Have students circle the denominators and remind them to rewrite the fractions using the LCD. Then compare the numerators. Resources Step by Step Solutions: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Skills Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Skills Practice Answers: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Homework Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Homework Practice Answers: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Problem-Solving Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Problem-Solving Practice Answers: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Extra Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Extra Practice Answers, Chapter 4 Homework Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Problem-Solving Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Skills Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Extra Practice: Compare and Order Rational Numbers eSolutions, Glencoe Math Course 2 Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 9 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Additional Activities for Differentiated Instruction Differentiated Instruction activities for Approaching Level, On Level, and Beyond Level Learners can also be found at point-of-use in the Launch the Lesson and Teach the Concept sections. The following are additional activities that can be used with this lesson. The Reteach Worksheet provides additional examples and practice for students who may have difficulty in grasping the math concepts in this lesson. The Enrich Worksheet provides students with valuable opportunities for extending this lesson. Resources Reteach: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Reteach Answers: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Enrich: Intersection and Union of Sets Enrich Answers: Intersection and Union of Sets Reteach: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Enrich: Intersection and Union of Sets Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 10 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Additional Activities for English Learners Differentiated Instruction activities for English Learners can also be found at point-of-use in the Launch the Lesson and Teach the Concept sections. The following are additional activities that can be used with this lesson. Option 1: Use Chapter 4, Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers from the Interactive Guide for English Learners. Option 2: Kinesthetic Learners Place students in groups of four. Give each group twelve cards, each of which shows a fraction or a decimal. Each member of the group draws one card. Then have students order the cards from least to greatest. Repeat the activity several times. Option 3: Verbal/Linguistic Learners Create a word wall with examples of GCF, LCM, and LCD. Explain what each term is, how it is used, and whether the terms are related in any way. Be sure to give examples of all three. Word Wall Printable English/Spanish Word Wall cards are available for the following vocabulary words in this lesson: common denominator least common denominator rational number Resources Word Wall Cards Interactive Guide for English Learners, Student Edition, Course 2, Lesson 4-2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Interactive Guide for English Learners, Teacher Edition, Course 2, Lesson 4-2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Interactive Guide for English Learners, Course 2, Teacher Edition Interactive Guide for English Learners, Course 2, Student Edition Visual Kinesthetic Vocabulary, Course 2, Student Edition Visual Kinesthetic Vocabulary, Course 2, Teacher Edition Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 11 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Assessment Formative Assessment Use this activity as a closing formative assessment before dismissing students from your class. Write the following on the board: and ; and and . Have each student explain out loud to a partner how they would compare each pair of rational numbers. Then have them summarize the process by writing it on a piece of paper to hand in at the end of class. See students' work. The online Self-Check Quiz for this lesson allows students to review concepts from each lesson. Exercises 24 and 25 prepare students for more rigorous thinking needed when taking the CCSS assessment. 24. This test item requires students to explain and apply mathematical concepts and solve problems with precision, while making use of structure. Depth of Knowledge DOK2 CCSS Content Standard 7.EE.3 Mathematical Practices MP1 Online Experience Students will be required to type their responses in the boxes. Scoring Rubric 2 points Students correctly order 4 counties, list the sales tax rate for each, and determine the county with the lowest sales tax. 1 point Students correctly order 4 counties, list the sales tax for each, but fail to determine the county with the lowest sales tax OR students correctly order the counties, but fail to list the correct sales tax rate for each and may or may not identify the county with the lowest sales tax. 25. This test item requires students to reason abstractly and quantitatively when problem solving. Depth of Knowledge DOK1 CCSS Content Standard 7.EE.3 Mathematical Practices MP1 Online Experience Students will be required to click on the bubbles to select all answers that are correct. Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 12 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Scoring Rubric 1 point Students correctly answer each part of the question. Quick Check Are students continuing to struggle with comparing and ordering rational numbers? If Yes Reteach Worksheet If No Skills Practice Worksheet Enrich Worksheet Resources Self-Check Quiz: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 13 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM National Glencoe Math, Course 2, © 2015 Chapter 4: Rational Numbers Lesson 2: Compare and Order Rational Numbers Printed by: Nicole Sladich Page 14 of 14 Printed on 11/04/2014 10:13 PM