Post-Tour - Memorial Art Gallery
advertisement

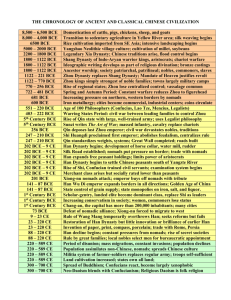
Memorial Art Gallery Passport to the Past Arts of the Ancient World, the Middle East, Asia, Africa, and Europe, from the collections of the Memorial Art Gallery Where in the World . . . ? The Eastern Hemisphere Indian Ocean When . . . ? A Memorial Art Gallery Timeline What do “BCE” and “CE” mean? BCE (Before the Common Era) and CE (Common Era) refer to the same time periods as the more traditional BC (Before Christ) and AD (Anno Domini, which means “The Year of our Lord”). The Ancient Middle East Askos in the Form of a Ram Persian, 999—700 BCE, Terracotta; 67.39 Cuneiform Tablet with Case Sumerian, Ur III, 2049 BCE, Clay; 54.58.4.1-2 Drachm of King Shapur I Sassanian, 241—272 CE Silver; 95.24 Horse Bit with Cheekpieces in the Form of Winged Sphinxes , Iranian, 1100—700 BCE Bronze; 48.39 Master of Animals Finial Iranian, 799—700 BCE, Bronze; 2007.35 Pyxis , Syrian, 899—700 BCE, Porphyry; 49.14 Worshipper Bearing an Animal Offering Mesopotamian, ca. 1800s BCE, Clay; 45.60 Tribute Bearer from Persepolis Persian, ca. 358—338 BCE, Limestone; 44.1 Belt Claps with Horse and Goat, Georgian; from Transcaucasia, 1 – 200 CE Bronze; 2007.34 How do you think these objects were used? What do they tell us about the cultures that made and used them? What tools or methods did the artists use to make these objects? Ancient Egypt A Canopic Jars (set of 4), 664—332 BCE Limestone; 3-6.81L B The God Osiris as a Mummified Man, 1069—332 BCE, Bronze; 51.116 Inner Coffin of Pa-debehu-Aset, 332—30 BCE, Wood, gesso, pigments, gilding; 2000.11.2 The God Horus as a Falcon, 664—525 BCE Bronze; 53.44 B New Year’s Bottle, 664—525 BCE, Terracotta, glaze; 51.200 Sphinx , 332—30 BCE, Granite; 51.307 Black-topped Red Ware Vessel, ca. 5300—3000 BCE Terracotta; 28.106 What do these pairs of objects have in common? In what ways are they different? What do they tell us about ancient Egyptian culture? King Ny-user-ra, 2390—2360 BCE, Red granite; 42.54 China Dragon, 220—580 CE, Bronze; 58.31 Ceremonial Food Vessel, Type Gui, 1000s—early 900s BCE, Bronze; 42.15 Horse, 600s—900s CE, Terracotta, glaze; 30.26 Tomb Tile with Tiger, Winged Horses, and Phoenixes, 1—299 CE Clay and pigments; 42.16 Court Musicians from a Tomb 600s—early 700s CE, Terracotta, pigments; 31.2 A Bearer of Good Wishes: Fragment of a Taoist Wall Painting, 1600—1644 CE, Ink and pigments on clay; 86.117 Bodhisattva Guanyin on Mt. Potola, early 1200s, Wood, pigments; 42.21 Stele with Taoist Deity, 960—1279 CE, Stone; 36.51 Can you match each object with the area’s religious beliefs or traditions? What evidence did you use? Many new ideas came into China by sea or the Silk Road; can you find examples of outside cultural influences in these objects? India & Southeast Asia The God Ganesa Thai,1300s, Bronze; 81.10 The God Surya, Indian, 600 CE Buff sandstone; 61.12 A Royal Couple on a Terrace, Indian, 1800—1850, Gouache on ivory; 2007.20 Shadow Puppet (Wayang Kulit) of Puntadéwa Javanese, late 1700s, Buffalo hide and horn; 37.16 Head of the Bodhisattva Avalokitesvara, Cambodian, 1000s—1100s Stone; 36.4 Tara, Indian, 1100s, Black chlorite; 61.13 Head of a Buddha, Thai, 1350—1757, Bronze; 30.33 Calligraphic Frieze with Inscription from the Qur’an , North Indian, 1400s CE, Red sandstone; 2009.8 Some of these objects have something important in common – What is it? How many different ways can you sort these objects? Can you guess how cultural ideas spread from one area to another? THE GREEK WORLD Kraters with Chariot Procession, Mycenaean, 1275—1225 BCE, Terracotta; 51.203-204 Corinthian Helmet, late 600s BCE, Bronze; 2008.70 Protome, 450—425 BCE, Terracotta, pigments; 88.5 Grave Stele, 300s BCE, Pentelic marble; 36.54 Black Figure Kylix with Dionysian Revelers, 500s BCE, Terracotta; 29.90 Piriform Jar, Minoan, ca. 1250—1150 BCE, Terracotta; 2006.76 Red Figure Pelike, 400s BCE Terracotta; 29.89 Wreath of Oak Leaves, ca. 300 BCE, Gold; 99.57 What do these objects have in common? How many different ways could they be categorized? What do they tell us about ancient Greek culture? Figure of a Woman (Tanagra Type), 323—90 BCE, Terracotta, pigments; 66.14 Other Mediterranean Cultures Cinerary Urn, Carthaginian, 700s BCE, Terracotta; 25.42 Askos in the Form of a Horse, Carthaginian, before 146 BCE, Terracotta; 25.41 The God Mars as a Warrior Etruscan, , 400s BCE Bronze; 53.41 Oinochoe (Pitcher), Etruscan, 400—301 BCE, Terracotta; 51.179 Cinerary Urn with Reclining Figure, Etruscan, 200—100 BCE Terracotta; 44.49a-b Oil Lamp, Carthaginian, before 146 BCE Terracotta; 20.73 Oil Lamp, Carthaginian, before 146 BCE, Terracotta; 20.75 Bombylios (Baby Feeder), Carthaginian, before 146 BCE, Terracotta; 25.51 Hercules, Etruscan, 400s BCE, Bronze; 73.18 Votive Head of a Woman, Etruscan, 300—1 BCE, Terracotta; 47.14 Kylix, Etruscan, 560—450 BCE, Terracotta; 5 1.180 These objects are grouped by culture – what are the two cultures? Where are they located? What other categories could you use to group these objects? North Africa Jar in the Shape of a Human Head Egyptian, n.d., Terracotta; 28.497 Sgraffito Ware Vessel Sharif Al-Abwami, Egyptian, 1300s CE Glazed ceramic; 51.350 Grotesque Head (Theater Character) Ptolemaic Egyptian, 200s BCE Clay; 28.84.7 Cinerary Urn Carthaginian, 700s BCE, Terracotta; 25.42 Figure of a Goddess of the Dancer Type Predynastic Egyptian, before 3400 BCE, Terracotta; 28.376 Askos in the Form of a Horse Carthaginian, before 146 BCE, Terracotta; 25.41 Standing Female Figure Coptic Egyptian, 799—700 CE, Terracotta, pigments; 28.264 Vase with Acanthus Design Roman Egyptian, 1—99 CE, Terracotta, glaze; 51.198 Where in North Africa were these objects created? What tools and skills did the artists use? How do you think the objects were used? Many objects were exported to other places – do these remind you of any other objects you have seen? THE ROMAN WORLD Double-headed Perfume Flasks, ca. 200—400 CE, Blown glass; 28.68.1-2 Tyche, Patron Deity of a Municipality, Roman, 1—199 CE (copy of Greek original) Marble, 49.73 Wall Fragment with Cupid Holding a Mask, from Pompeii, before 79 CE, Fresco; 28.75 Portrait Head of an Old Man with a Beard, 100s CE, Commemorative Coin of the Marble; 46.39 Emperor Constantine, 307—334 CE, Bronze; 95.25 Togatus, 1—99 CE, Marble; 73.146 Sarcophagus with Portrait Medallion, 250—274 CE, 49.72 Mosaic Floor Panel with Head of Tethys, Made in Antioch, Syria, 200s CE, Stone and glass; 42.2 How many different materials have been used to make these objects? What can these objects tell us about how the Romans lived? How do the objects compare with those we use today? A Medieval Europe A A B Madonna and Child, ca. 1300-1350 French; Made in Île-de-France Limestone, polychromy, gilding; 28.466 Châsse (Reliquary) with Scenes from the Life of St. Stephen, French, 1220—1230, Enamel, gilded copper; 49.20 Mourner’s Niche from the Tomb of Philip the Bold, Jean de Marville, Netherlandish (active 1366 - 1389); Marble, 49.51 Crucifixion with God the Father, Giovanni del Biondo, Italian (active 1356—1399, 51.26 Console with Doubting Thomas French, early 1200s, Limestone, paint; 49.76 Madonna and Child with Saints Francis of Assisi, John the Baptist, Peter and Dominic, Nardo di Cione, Italian (active 1343 - d. 1365/66 ) Tempera on panel; 57.4 What do these pairs of objects have in common? How are they different? What do they tell us about Medieval European culture? The Islamic World Calligraphic Frieze with Inscription from the Qur’an, North Indian, 1400s CE, Red sandstone; 2009.8 Bowl with Acanthus Design Iranian, 1200s CE Glazed terracotta; 51.317 Kubachi Ware Tile Iranian, 1500s CE, Glazed terracotta; 21.2 Sgraffito Ware Vessel Sharif Al-Abwami, Egyptian, 1300s CE Glazed ceramic; 51.350 Plate, Turkish, 1500s CE, Glazed terracotta; 79.91 Section of a Qur’an endowed by Sultan Qansuh al-Ghawri Egyptian, Mamluk Dynasty, 1ate 1400s CE Ink and gold on parchment; 2008.69 Ghiordes Prayer Rug Turkish, 28.459 Lusterware Bowl with Seated Figures, Iranian, 1200s 52.11 Leaf from a Manuscript of Poetry, Iranian, 1600s CE Ink and gold on parchment; 28.317 How have the artists decorated these objects? How many different countries are these objects from? What does that say about them? How do you think the objects were used? The Renaissance in Europe Adoration of the Magi Master of the Holy Blood , Flemish (active early 1500s), 80.43 Saint James, French, late 1400s, Limestone, paint; 94.49 Saint Elizabeth German, ca. 1500, Wood; 57.7 Marriage Chest (Minnekastchen) German, late 1400s, 2008.2 Portrait of a Boy of the Bracciforte Family of Piacenza, 1540 Girolamo Mazzola Bedoli, Italian (ca. 1505 - ca. 1569); 76.13 Madonna and Child Enthroned with Angels Master of the St. Ursula Legend, Flemish (active 1470-95), before 1483; 48.11 Partial Armor made for the Dukes of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Brunswick Armory, German, ca. 1562 Etched steel, leather; 2006.57 Conversion of Saint Paul, Francesco Ubertini, Italian (1494?—1557), 1530--35, Oil on panel, 54.2 Portrait of a Caesar, Circle of Gregorio di Lorenzo, Italian (active 1461—1473), Marble; 65.8 Wedding Cutlery Set with Case in the Form of a Fish French, ca. 1550 Ivory, steel, leather, wood; 2010.9 How many ways can these objects be sorted? How do you think the objects in each group were used? Look closely at each object—what skills and tools did the artists use? Japan Fabric Stencil (Katagami), 1800s, Mulberry paper; 84.15.4 Tsuba (sword guard), 1500s—1700s, Bronze; 66.9.38 Lacquered Incense Box (Ko-Dansu), 1600s—1800s, Wood lacquered in gold and red; 77.98 Bodhisattva Kannon, 1100s, Wood, polychromy; 74.83 Screen: Court Ladies, 1700s, Watercolor and ink on paper; 57.6 Sokuhi, 1616 –1671 Sho Calligraphy Ink on paper; 65.10 Sake Bottle Ceramic; 65.45 Four-Tiered Imari Ware Food Container, 1600s—1800s, Porcelain; 81.37 How do you think each of these objects was used? Describe some of the detailed decoration you see. What skills or tools did the artists use? Sub-Saharan Africa Yaka Culture, D. R. Congo Crest Mask, Wood, fibers, pigment; 72.54 Bamana Culture, Mali Crest Mask: Antelope (Chi Wara), Wood, fibers, metal, shells; Male- 69.107, Female and Baby- 93.14 Yaoure or Baule Culture, Côte d'Ivoire Spoon, Wood; 64.102 Yoruba Culture, Nigeria Twin Figures (Ere Ibeji), Wood, pigment, beads, cowrie shells, fiber, sacrificial materials; 65.9.1-2 Asante Culture, Ghana Goldweight: Man w/ Pipe, Brass; 53.76.1 Mende Culture, Sierra Leone Helmet Mask (Sowei), Wood; 72.52 Senufo Culture, Côte d’Ivoire Champion-Cultivator Staff Wood, fiber, shells; 71.64 Western Pende Culture, D.R. Congo Ivory Pendant Amulet (Ikhoko), 51.114 What different materials have been used to make these objects? Makonde Culture, Mozambique Crest Mask (Lipiko), ca. 1950--60 Wood, human hair, pigments; 2006.71 How are these objects used? How can you tell? Can you find all of these modern countries on a map? Fur Culture, Sudan Ivory Bracelet, 67.64 Oceania Kayan-Borbor Culture, Papua New Guinea, Slit Gong Drum, ca. 1940 Wood, paint; 79.19 Abelam Culture, Papua New Guinea Yam Mask, Grass, pigment; 74.78 Arambak Culture, Papua New Guinea Hook Figure (Yipwon), Wood, shell; 70.82 Waresi Culture, Papua New Guinea Spirit Figure (Mindja), Wood, paint; 74.76 Era River Region, Papua New Guinea Spirit Board (Gope), Wood, paint; 87.84 Iatmul Culture, Papua New Guinea Mask, Wood, shells, hair, pigment; 77.158 Middle Sepik River Region, Papua New Guinea Body Mask, Cane fibers, shells, feathers; 73.138 What materials have been used to make these objects? What can they tell us about these people and their culture? Describe the decorations. Can you guess what might have inspired the artists? Details of Works of Art from the Collection of the Memorial Art Gallery Sumerian Cuneiform Tablet with Case, 54.48.17a Roman; made in Antioch, Syria Mosaic with the Head of Tethys, 42.2 Roman Glass Vessel, 51.136 Egyptian, Inner Coffin of Pa-debehu-Aset, 2001.11.2 Etruscan, Oinochoe, 51.179 Thai, Head of Buddha, 30.33 Japanese Four Tier Imari Ware Container, 81.37 Iranian Leaf from a Manuscript of Poetry, 28.317 Chinese A Bearer of Good Wishes; Fragment from a Taoist Wall Painting, 30.26 Roman,. Togatus, 73.146 Yoruba Culture, Nigeria Twin Figure (Ere Ibeji), 65.9.2 Raffaello del Garbo, Italian Madonna and Child with Angel, 47.30 Abelam Culture, Papua New Guinea Yam Mask, 74.78 Chinese Ceremonial Food Vessel Type Gui, 42.15 Chinese, Mongolian Harness Ornament with Ibexes, 73.66 French, Saint James, 94.49 Indian Return to Ayodhya, 83.55 Paul Vredeman de Vries. Flemish Interior of a Gothic Cathedral, 98.19