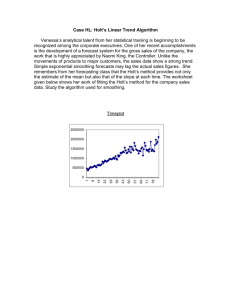
Lesson
Menu
Print
NAME ______________________________________ DATE _______________ CLASS ____________________
Holt Physics
Problem 1A
METRIC PREFIXES
PROBLEM
In Hindu chronology, the longest time measure is a para. One para equals
311 040 000 000 000 years. Calculate this value in megahours and in
nanoseconds. Write your answers in scientific notation.
SOLUTION
Given:
1 para = 311 040 000 000 000 years
Unknown:
1 para = ? Mh
1 para = ? ns
Express the time in years in terms of scientific notation. Then build conversion
factors from the relationships given in Table 1-3.
1 para = 3.1104 × 1014 years
24 h
1 Mh
365.25 days
× ×
1 day 1 × 106 h
1 year
24 h
1 ns
365.25 days
3600 s
× × ×
1 day
1 × 10−9s
1 year
1h
HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this book.
Convert from years to megahours by multiplying the time by the first conversion
expression.
1 Mh
365.25 days 24 h
1 para = 3.1104 × 1014 years × × ×
1 day 1 × 106 h
1 year
= 2.7266 × 1012 Mh
Convert from years to nanoseconds by multiplying the time by the second conversion expression.
1 ns
365.25 days 24 h
3600 s
1 para = 3.1104 × 1014 years × × × ×
1 year
1 day
1h
1 × 10−9 s
= 9.8157 × 1030 ns
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
1. One light-year is the distance light travels in one year. This distance is
equal to 9.461 × 1015 m. After the sun, the star nearest to Earth is Alpha
Centauri, which is about 4.35 light-years from Earth. Express this distance in
a. megameters.
b. picometers.
Problem 1A
1
Menu
Lesson
Print
NAME ______________________________________ DATE _______________ CLASS ____________________
2. It is estimated that the sun will exhaust all of its energy in about ten
billion years. By that time, it will have radiated about 1.2 × 1044 J (joules)
of energy. Express this amount of energy in
a. kilojoules.
b. nanojoules.
3. The smallest living organism discovered so far is called a mycoplasm. Its
mass is estimated as 1.0 × 10–16 g. Express this mass in
a. petagrams.
b. femtograms.
c. attograms.
4. The “extreme” prefixes that are officially recognized are yocto, which indicates a fraction equal to 10–24, and yotta, which indicates a factor equal
to 1024. The maximum distance from Earth to the sun is 152 100 000 km.
Using scientific notation, express this distance in
a. yoctometers (ym).
b. yottameters (Ym).
5. In 1993, the total production of nuclear energy in the world was
2.1 × 1015 watt-hours, where a watt is equal to one joule (J) per second.
Express this number in
6. In Einstein’s special theory of relativity, mass and energy are equivalent.
An expression of this equivalence can be made in terms of electron volts
(units of energy) and kilograms, with one electron volt (eV) being equal
to 1.78 × 10–36 kg. Using this ratio, express the mass of the heaviest
mammal on earth, the blue whale, which has an average mass of
1.90 × 105 kg, in
a. mega electron volts.
b. tera electron volts.
7. The most massive star yet discovered in our galaxy is one of the stars
in the Carina Nebula, which can be seen from Earth’s Southern
Hemisphere and from the tropical latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
The star, designated as Eta Carinae, is believed to be 200 times as massive
as the sun, which has a mass of nearly 2 × 1030 kg. Find the mass of Eta
Carinae in
a. milligrams.
b. exagrams.
8. The Pacific Ocean has a surface area of about 166 241 700 km2 and an
average depth of 3940 m. Estimate the volume of the Pacific Ocean in
a. cubic centimeters.
b. cubic millimeters.
2
Holt Physics Problem Workbook
HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this book.
a. joules.
b. gigajoules.
Menu
Lesson
Print
The Science of Physics
Chapter
1
Additional Practice 1A
Givens
1. distance = 4.35 light years
Solutions
9.461 × 1015 m
distance = 4.35 light years × = 4.12 × 1016 m
1 light year
1 Mm
a. distance = 4.12 × 1016 m × 6 = 4.12 × 1010 Mm
10 m
1 pm
= 4.12 × 1028 pm
b. distance = 4.12 × 1016 m ×
10−12 m
2. energy = 1.2 × 1044 J
1 kJ
a. energy = 1.2 × 1044 J ×
= 1.2 × 1041 kJ
103 J
II
1 nJ
b. energy = 1.2 × 1044 J × −
= 1.2 × 1053 nJ
10 9 J
3. m = 1.0 × 10−16 g
1 Pg
a. m = 1.0 × 10−16 g × 1
= 1.0 × 10−31 Pg
10 5 g
1 fg
b. m = 1.0 × 10−16 g × −1
= 0.10 fg
10 5 g
1 ag
c. m = 1.0 × 10−16 g × −1
= 1.0 × 102 ag
10 8 g
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
4. distance = 152 100 000 km
1000 m
1 ym
= 1.521 × 1035 ym
a. distance = 152 100 000 km × ×
1 km
10−24 m
1000 m
1 Ym
b. distance = 152 100 000 km × × 24 = 1.521 × 10−13 Ym
1 km
10 m
5. energy = 2.1 × 1015 W • h
1 J/s 3600 s
a. energy = 2.1 × 1015 W • h × × = 7.6 × 1018 J
1W
1h
1 GJ
b. energy = 7.6 × 1018 J ×
= 7.6 × 109 GJ
109 J
6. m = 1.90 × 105 kg
1 eV
m = 1.90 × 105 kg ×
= 1.07 × 1041 eV
1.78 × 10−36 kg
1 MeV
a. m = 1.07 × 1041 eV × 6 = 1.07 × 1035 MeV
10 eV
1 TeV
= 1.07 × 1029 TeV
b. m = 1.07 × 1041 eV ×
1012 eV
Section Two — Problem Workbook Solutions
II Ch. 1–1
Menu
Lesson
Print
Givens
Solutions
7. m = (200)(2 × 1030 kg) =
4 × 1032 kg
103 g 103mg
a. m = 4 × 1032 kg × × = 4 × 1038 mg
1 kg
1g
1 Eg
103 g
b. m = 4 × 1032 kg × × 1
= 4 × 1017 Eg
10 8 g
1 kg
8. area = 166 241 700 km2
depth = 3940 m
V = volume = area × depth
17
2
1000 m
V = (166 241 700 km2)(3940 m) ×
1 km
3
V = 6.55 × 10 m
106 cm3
a. V = 6.55 × 1017 m3 ×
= 6.55 × 1023 cm3
1 m3
109 mm3
b. V = 6.55 × 1017 m3 ×
= 6.55 × 1026 mm3
1 m3
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
II
II Ch. 1–2
Holt Physics Solution Manual