Color & Light
advertisement

Color & Light Notes
Table of Contents
page#
1,2
Light Vocabulary
Electromagnetic
Spectrum
3
The Eye
4
Lenses and Mirrors
5,6
Color
7
Telescopes
8
Light Vocabulary
Photon - "packet of energy" released by an electron when it moves to another energy level in an atom.
Frequency - number of waves produced in a given amount of time.
Amplitude - maximum distance a wave vibrates from the rest position.
Transverse wave - a wave in which the particles of the wave's medium vibrate perpendicular to the
direction the wave is traveling.
Light energy - the energy produced by the vibrating electrically charged particles.
Electromagnetic Spectrum - the entire range of electromagnetic waves.
Radiation - the transfer of energy through matter or space as electromagnetic waves, such as visible
light and infrared waves.
Reflection - the bouncing back of a wave after it strikes a barrier or an object.
Law of reflection - the law that states the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Absorption - the transfer of energy carried by light waves to particles of matter.
Scattering - the release of light energy by particles of matter that have absorbed energy.
Refraction - the bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another.
Diffraction - the bending of waves around a barrier or through an opening.
Interference - a wave interaction that occurs when two or more waves overlap.
Transmission - the passing of light through matter.
Transparent - the term describing matter through which light is easily transmitted.
Translucent - the term describing matter that transmits light but also scatters the light as it passes
through the matter.
Opaque - the term describing matter that does not transmit any light.
Pigment - a material that gives a substance its color by absorbing some colors of light and reflecting
others.
Luminous - the term that describes objects that produce visible light.
Illuminated - the term describing visible objects that are not a light source.
1
Incandescent light -light produced by hot objects.
Fluorescent light - visible light emitted by a phosphor particle when it absorbs energy such as
ultraviolet light.
Neon light -light emitted by atoms certain gases, such as neon, when they absorb and then release
energy.
Vapor light - light produced when atoms combine with gaseous metal atoms.
Plane mirror - a mirror with a flat surface.
lens - a curved transparent object that forms an image by refracting light.
Concave mirror/Iens - a lens or mirror that is thinner in the middle than at the edges.
Focal point - the point on the axis of a mirror or lens through which all incident parallel light rays are
focused.
Convex mirror/Iens - a lens or mirror the is thicker in the middle than at the edges.
Cornea - a transparent membrane that protects the eye and refracts light.
Pupil - the opening to the inside of the eye.
Iris - the colored part of the eye.
Retina - the back surface of the eye.
Laser - a device that produces intense light of only one wavelength and color.
Hologram - a piece of film on which an interference pattern produces a three-dimensional image of an
object.
2
Electromagnetic
Spectrum
SPECTRA:
ABSORPTIOt>J
THE
KYDROOp.l:
ELECTROMAGNETfC
HE1JUM.:
SPECTRUM..
Roy G. Biv
"THESE VAVES TRAVEL lHROUGl-\ Tl'\E
ELEC1ROI"\PtGNETIC FIELD. ll-EY
\JERE ffiRMER!Y CPRRED 13f1'l-\£
AETHER, ""HlG{ IJAS tECCM'\l$lO'£D
IN )9<17 DUE TO SUl:X;ET OJTS.
REO
R1lJlTO
I
Q
uv
A (m)
",'.
,0'
ooo'llo,
f (~,)
•.
'
I
1Hz
10'
IfI
I
I
10'1."
,
17
Q~
IOOH,
roC
.
10"
1tl-
10","
,
I.'
1101>
,
10.
10"
10'
••I;;
ie;;;
IGC••
I"
I
.,....
"7
"I
I
r«lt!<,
•
1'r
,
'0
I
'0'
I
1Ill"
'0°'
I
,
j,o
10••
"""
ID'
I
~1Ilb
",",
1:01'110.
",',
lGl1,
I
,7
on
,0"
i,-
10"
,~
I
.-
,,,.
, ,.",
I~
,
I~'
,,"
Ill<
,01lf,
,
<P
I
e"w1T
""-
-...
,
I
,67
I
10'"
I
tOfiI""
~
I/)~
I
O"MtJR
10"
t
~..,.:;;
10'"
I
1,.Mt
ttl"
d
'c.
lit
I
&&IGoL~;t
to--
IbA~
I
tco"..
Ier;Ie."
tiki!:
I'
10."
j
'tOf ••••
Ir'}'
1
.etA .•• Nrm ~-/tllD
/
I
-2
IO-r1
I
1",",
IZ.
I~n.
_i
'ZIof'h-
I
II'
EM Spectrum
Radio
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible
Ultraviolet
X-Rays
Low Energy
Gamma Rays
High Energy
Low Frequency - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -High Frequency
Long Wavelength ---------------------------------------------------------------
3
Short Wavelength
Parts of the Eye
DIIAGRA.M O'F THE EYE
COiR:NEA
IIRIS-~
OPTIC
NERVE
PUPIL--- .
RmNA
Parts of the eye and their function:
Iris - the part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil- the opening in the eye that light passes through to the inside of the eye.
Lens - a curved transparent object that forms an image by refracting light.
Cornea - a transparent membrane that protects the eye.
Retina - the back surface of the eye where light and images are focused.
Vitreous Humor - clear gelatinous matter that fills the section between the retina and the lens.
Sclera - tough, white, outer layer of the eyeball that covers everything except the cornea.
Optic Nerve - either of two sensory nerves connecting the retinas of the eyes with the brain.
4
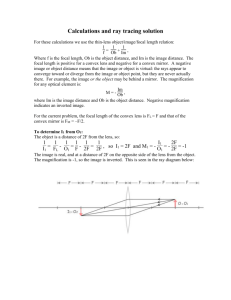
Lenses and Mirrors
'COnca 'lie'
:suJ'fi!ue. /
c: 1Jn;',(!S
itrflNard
Convex .:.ens
o
~;
U!ll't !rays
to' $pf"ead: ~p.!l'rt.j
Causes, L1"gnt
Oii"divcill:e'
otr'c.onv~e
ra.!f$
.
w met:!!'l.,.
Double Convex
Converging lens
F
?~~,.
•.. ~ .•....
" .....•.
Diverging ilens
5
Double Concave
/
)
,.
/
6
,-------------~---_._-----------
Color
Primary colors of light - red, blue, and green
Primary colors of pigments - cyan, magenta, and yellow
Transmission - is the passing of light through matter.
Transparent - matter through which light is easily transmitted.
Translucent - matter through which light passes but is scattered.
Opaque - matter that does not transmit any light. (ie. Solid)
Color Addition - when colors of light combine, more wavelengths of light are present.
Color Subtraction - each pigment absorbs at least one color of light. When you mix more colors of
pigments together, more colors of light are absorbed, or subtracted.
Pigment - a material that gives a substance its color by absorbing some colors of light and reflecting
others.
7
Telescopes
Eye;pieca
Reflecting
Light
G
(b)
a. Refracting Telescope - a refracting telescope uses a pair of convex lenses to gather and focus light.
b. Reflecting Telescope - a reflecting telescope uses a concave mirror, flat mirror, and lens to collect
and focus light.
Parts
F - Double Convex Lens
G - Concave mirror .
H - Plain (flat) mirror
Eyepiece - focus
8