Harold's Calculus Notes “Cheat Sheet” AP Calculus AB & BC Limits
advertisement
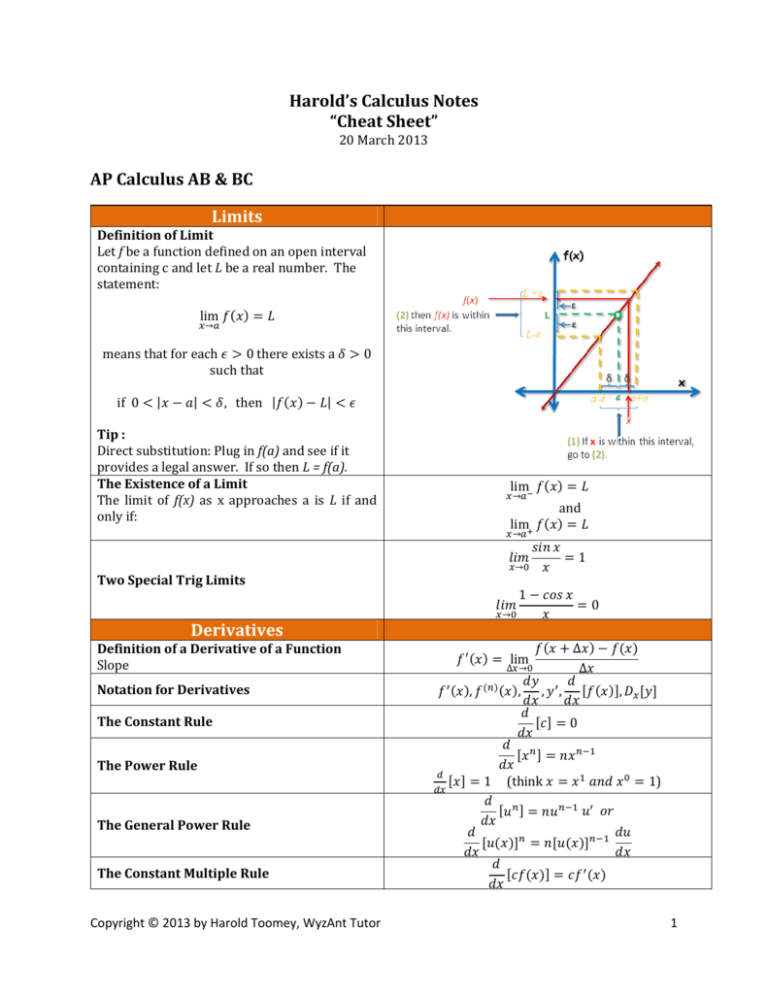
Harold’sCalculusNotes “CheatSheet” 20March2013 APCalculusAB&BC Limits DefinitionofLimit Letfbeafunctiondefinedonanopeninterval containingcandletLbearealnumber.The statement: lim → meansthatforeach 0thereexistsa suchthat | | if0 | ,then| 0 Tip: Directsubstitution:Pluginf(a)andseeifit providesalegalanswer.IfsothenL=f(a). TheExistenceofaLimit The limit of f(x) as x approaches a is L if and onlyif: → and lim → 1 → TwoSpecialTrigLimits 1 0 → Derivatives DefinitionofaDerivativeofaFunction Slope NotationforDerivatives lim , , , TheConstantRule ThePowerRule TheGeneralPowerRule ∆ ∆ lim ∆ → , , 0 1(think TheConstantMultipleRule Copyright © 2013 by Harold Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 1) 1 TheSumandDifferenceRule 1 2 PositionFunction VelocityFunction AccelerationFunction TheProductRule TheQuotientRule , 0 TheChainRule Sine cos Cosine Tangent Secent Cosecent Cotangent ApplicationsofDifferentiation Rolle’sTheorem fiscontinuousontheclosedinterval[a,b],and fisdifferentiableontheopeninterval(a,b). Iff(a)=f(b),thenthereexistsatleastonenumberc in(a,b)suchthatf’(c)=0. MeanValueTheorem IffmeetstheconditionsofRolle’sTheorem, then ′ lim lim → L’Hôpital’sRule → GraphingwithDerivatives → 0 ∞ , , 0 ∗ ∞, 1 , 0 , ∞ , ∞ 0 ∞ lim TestforIncreasingandDecreasing Functions Find‘c’. lim ∞ , 0 lim → → , ⋯ 1. Iff’(x)>0,thenf isincreasing(slopeup) 2.Iff’(x)<0,thenfisdecreasing(slopedown) 3.Iff’(x)=0,thenfisconstant(zeroslope) Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 2 TheFirstDerivativeTest TheSecondDeriviativeTest Letf’(c)=0,andf”(x)exists,then TestforConcavity PointsofInflection Changeinconcavity 1. Iff’(x) changesfrom– to+atc,thenf hasarelative minimumat(c,f(c)) 2.Iff’(x)changesfrom+to‐atc,thenfhasarelative maximumat(c,f(c)) 3.Iff’(x),is+c+or‐c‐,thenf(c)isneither 1. Iff”(x)>0,thenf hasarelativeminimumat(c, f(c)) 2.Iff”(x)<0,thenfhasarelativemaximumat(c, f(c)) 3.Iff’(x)=0,thenthetestfails(See1stderivative test) 1. Iff”(x)>0 forallx,thenthegraphisconcave upward 2.Iff”(x)<0forallx,thenthegraphisconcave downward If(c,f(c)) isapointofinflectionoff,theneither 1.f”(c)=0or 2. f” does not exist at x = c. AnalyzingtheGraphofaFunction x‐Intercepts(ZerosorRoots) y‐Intercept Domain Range Continuity VerticalAsymptotes(VA) HorizontalAsymptotes(HA) InfiniteLimitsatInfinity Differentiability RelativeExtrema Concavity PointsofInflection f(x)=0 f(0)=y Validxvalues Validyvalues Nodivisionby0,nonegativesquareroots x =divisionby0orundefined lim → → andlim → → → ∞andlim → → ∞ lim → Limitfrombothdirectionsarrivesatthe sameslope Createatablewith domains,f(x),f’(x),andf”(x) If ” → ,thencupup∪ → ,thencupdown∩ If ” f”(x)=0 ApproximatingwithDifferentials Newton’sMethod Findszerosoff,orfindsciff(c)=0. TangentLineApproximations FunctionApproximationswithDifferentials ′ ∆ Integration BasicIntegrationRules Integrationisthe“inverse”ofdifferentiation. Differentiationisthe“inverse”ofintegration. 0 0 Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 3 TheConstantMultipleRule TheSumandDifferenceRule ThePowerRule If , 1 1 1then ln| | If , then TheGeneralPowerRule , 1 1 1 2 SummationFormulas 1 2 6 1 1 4 ∆ , ReimannSum ‖∆‖ DefinitionofaDefiniteIntegral Areaundercurve lim ‖∆‖→ ∆ ∆ SwapBounds AdditiveIntervalProperty TheFundamentalTheoremofCalculus (SeeHarold’sFundamentalTheoremofCalculus “CheatSheet”) TheSecondFundamentalTheoremof Calculus ′ (SeeHarold’sFundamentalTheoremofCalculus “CheatSheet”) Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 4 MeanValueTheoremforIntegrals Find‘c’. 1 TheAverageValueforaFunction IntegrationMethods 1.Memorized See1‐pager ofcommonintegrals Set , then 2.U‐Substitution _____ _____ ____v _____ _____ _____ Pick‘ ’usingtheLIATERule: L‐Logarithmicfunctions:ln , log , . I‐Inversetrig.functions:tan , sec , A‐Algebraicfunctions: , 3 , . T‐Trigonometricfunctions:sin , tan , . E‐Exponentialfunctions: , 19 , . 3.IntegrationbyParts where arepolynomials Substutution: Identity:1 Substutution: 1 Identity: 7.TrigSubstitutionfor 8.TableofIntegrals sin 6.TrigSubstitutionfor√ . Case1:Ifdegreeof thendolongdivisionfirst Case2:Ifdegreeof thendopartialfractionexpansion 4.PartialFractions 5.TrigSubstitutionfor√ sec Substutution: tan Identity:1 CRCStandardMathematicalTables book Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 5 TI–NspireCASiPadapp TI‐89Titaniumcalculator RiemannSum MidpointRule TrapezoidalRule Simpson’sRule Googleofmathematics.Showssteps. Free. www.wolframalpha.com WolframAlphaiPhone/iPadapp 9.ComputerAlgebraSystems(CAS) 10.NumericalMethods 11.WolframAlpha PartialFractions Condition CaseI:Simplelinear( where arepolynomials anddegreeof degree) CaseII:Multipledegreelinear( CaseIII:Simplequadratic( degree) degree) CaseIV:Multipledegreequadratic( degree) TypicalSolutionforCasesI&II | TypicalSolutionforCasesIII&IV NumericalMethods | ∗ lim ‖ ‖→ RiemannSum ⋯ and∆ and‖ ‖ ∆ Types:LeftSum,MiddleSum,RightSum where ̅ ∆ MidpointRule ∆ ∆ ̅ ̅ where∆ ̅ ⋯ ̅ and ̅ ErrorBounds:| Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor | , 6 TrapezoidalRule ∆ 2 2 2 ⋯ 2 where∆ and ErrorBounds:| ∆ | ∆ 3 4 2 4 4 2 Whereniseven and∆ ∆ and Simpson’sRule ErrorBounds:| InfiniteSequencesandSeries | lim → Example:( 2.GeometricSeriesTest 3.p‐SeriesTest 4.AlternatingSeriesTest 5.IntegralTest 6.RatioTest 7.RootTest 8.DirectComparisonTest 9.LimitComparisonTest ⋯ ⋯ 1 1 1 → 1 1 onlyif| | 1 where istheradiusorintervalofconvergence lim ⋯ Similartoanarithmeticseries ConvergenceTests TermTest ⋯ GeometricSeries(finite) 1. (Limit) , , …) , ArithmeticSeries(infinite) PartialSum Sequence GeometricSeries(infinite) ⋯ (SeeHarold’sSeriesConvergenceTests “Cheat Sheet”) ” ” ” ” ” ” ” ” Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor 7 TaylorSeries PowerSeries ⋯ PowerSeriesAboutZero ⋯ 0 MaclaurinSeries Taylorseriesaboutzero ! TaylorSeries ! ! TaylorSerieswithRemainder ∗ 1 ! where andlim → BinomialSeries 1 1 1 CommonSeries ! 1 ln 1 1 sin cos sinh 1 1 ! 2 ! 1 2 1 1 1 ! 2 2 1 2 2 ∗ 0 2 … ! 2! 3! 4! 1 ! | | 1 1 Euler’sEquation Copyright © 2013 by Harold A. Toomey, WyzAnt Tutor ⋯ ⋯ 1 | | 2 1 cosh arctan 1 1 | | 1 2 3 4 5 3! 5! 7! 9! 2! 4! 6! 8! 3! 5! 7! 9! 2! 4! 6! 8! 3 5 7 9 1 cos 0 sin ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ 8