Go with the Flow - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
advertisement

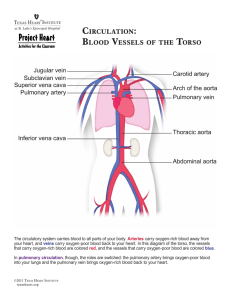
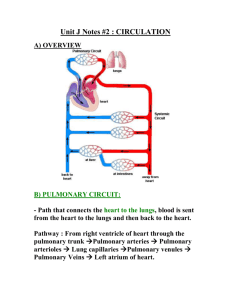
Name: ___________________________ Period: _________ Go with the Flow Objective: Students will name and locate the major areas and structures of the heart and trace the pathway of the blood through the heart, lungs, and body. Question: What is the role of each heart chamber? Materials: copy of heart diagram, red and blue pencils, markers, or crayons Procedure: You will trace the pathway of blood through the heart and lungs by adding arrows to the diagram; you will also color the oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich sides of the heart. Label the number and part of the heart – use the class copy to help guide you along with the step by step instructions. 1. Starting on the left side of the heart, label the right atrium. 2. Locate the two major veins entering the right atrium. Label the upper vein, the superior vena cava 3. Label the lower one the inferior vena cava. The blood returning to the heart is loaded with carbon dioxide. Color the veins blue. Draw arrows in the veins to indicate the direction of flow. 4. Between the right atrium and right ventricle is the tricuspid valve; it prevents the backflow of blood. 5. The next chamber is the right ventricle, (R.V.) Label and color the R.V. blue. Draw in arrow to show the flow of blood from the R.A. through the tricuspid valve to the R.V. 6. The R.V. sends blood into the pulmonary artery, which takes the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. Locate the pulmonary artery and draw in arrows to show the flow of blood and color it blue. This branch goes to the left lung. 7. The pulmonary artery goes to both the left and right lungs, label #6 “ to left lung” and #7 pulmonary artery to right lung. **Blood goes to lungs and receives oxygen (is “oxygenated”) 8. Pulmonary vein carries the oxygenated blood back to the heart and into the left atrium. Label this one “pulmonary veins from left lung” 9. Pulmonary veins from the right lung. Label and color the pulmonary veins red. Add in the arrows to show the direction of the flow of blood. 10. Locate and label the left atrium (L.A.), which receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. Add in the arrows to show the direction of the flow of blood. 11. Between the L.A. and L.V. is the mitral or bicuspid valve; it prevents the backflow of blood. Label it the mitral valve. 12. The next chamber is the left ventricle, (L.V.). The left ventricle is the strongest chamber of the heart. It discharges oxygen-rich blood into the aorta, the largest blood artery in the body. Label and color the L.V. red. Draw in arrows to show the flow of blood from the L.A. through the bicuspid valve to the L.V. to the aorta. 13. Aortic valve opens to let blood flow into the aorta and then closes to stop the blood from flowing back into the heart. 14. Aorta – sends the oxygenated blood to the body. It is the largest artery in the body. Many arteries come off of the aorta to supply blood to various parts of the body. 15. A thick muscular wall, called a septum separates the right and left sides of the heart. The septum prevents the oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood from mixing in the heart. Locate and label the septum. Follow-Up Questions: 1. What do the colors blue and red indicate? 2. What mechanism keeps the blood flow in one direction? 3. Why is the left ventricle the strongest chamber in the heart? 4. Why is the aorta the largest blood vessel/artery in the body? 5. Name the two major veins which bring oxygen-poor blood into the heart? 6. Which chamber receives oxygen-poor blood from the body? 7. Which chamber pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs? 8. Which chamber received oxygen-rich blood from the lungs? 9. Which chamber pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body? Heart Diagram 16 .