to view the slides
advertisement
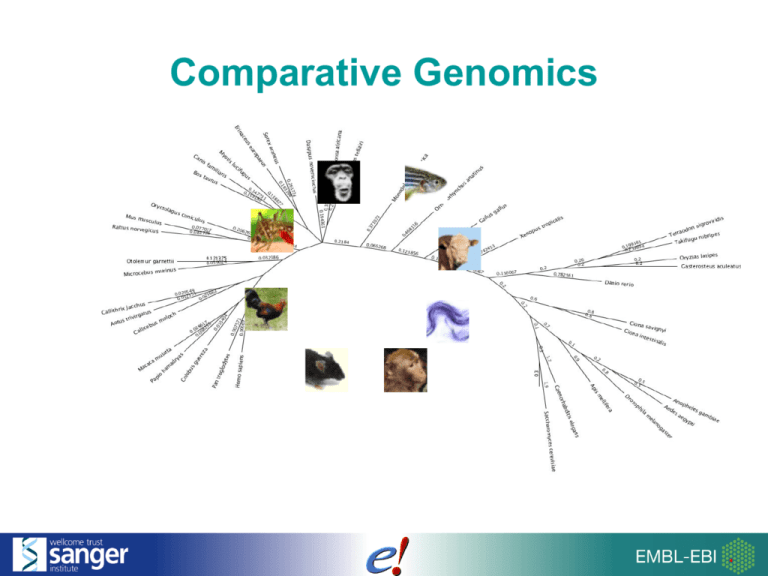
Comparative Genomics How does Ensembl compare species? • Proteins: Homologs & Families • Genomes: Sequence Alignments 2/24 Ensembl Homologues e70: 73 genomes (61 fully supported, 12 on Pre!) 3/24 Types of Homologues • Orthologues : a homologue where the ancestor node is a speciation event • Paralogues : a homologue where the ancestor node is a duplication event 4/24 Orthologues are between species, paralogues are within a species EnsemblCompara GeneTrees: Analysis of complete, duplication aware phylogenetic trees in vertebrates. Vilella AJ, Severin J, Ureta-Vidal A, Durbin R, Heng L, Birney E. Genome Res. 2008 Nov 24. 5/26 The Gene Tree for INS (insulin precursor) A blue square is a speciation event (Orthologues) A red square is a duplication event (Paralogues) 6/24 Gene Trees Amino Acid alignments Tree with ancestor nodes Expanded nodes: Aligned Amino Acid Gap Collapsed (triangle) nodes: >66% Consensus 33-66% Consensus Orthologue Types What is ‘1 to 1’? What is ‘1 to many’? 8/24 Quick exercise MYO6 is a myosin that has been shown (when mutated) to be associated with deafness. 1. Does human MYO6 have a homologue in mouse? 2. If so, in what location (chromosome and base pairs) is the mouse homologue found? 3. Can you find the cDNA alignment between the human and mouse homologues? www.ensemblgenomes.org 10/24 Pan-taxonomic compara Anolis carolinensis Ciona savignyi Danio rerio Equus caballus Gallus gallus Homo sapiens Macaca mulatta Monodelphis domestica Mus musculus Ornithorhynchus anatinus Pan troglodytes Pongo pygmaeus Xenopus tropicalis Anopheles gambiae Caenorhabditis elegans Drosophila melanogaster Dictyostelium discoideum Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Arabidopsis thaliana Oryza sativa Vitis vinifera B_aphidicola_Tokyo_1998 B_burgdorferi_DSM_4680 B_subtilis E_coli_K12 M_tuberculosis_H37Rv N_meningitidis_A P_horikoshii S_aureus_N315 S_pneumoniae_TIGR4 S_pyogenes_SF370 W_pipientis_wMel Aspergillus nidulans Neurospora crassa Saccharomyces cerevisiae Schizosaccharomyces pombe 11/24 Protein Families • How: Cluster proteins for every isoform in every species + UniProt proteins. • BLASTP comparison of: – all Ensembl ENSP… – all metazoan (animal) proteins in UniProt 12/24 How does Ensembl compare species? • Proteins: Homologs & Families • Genomes: Sequence Alignments 13/24 Whole Genome Alignments Pairwise (two species) • Nucleotide alignment: BLASTZ/LASTZ-net closer species e.g. human – mouse • Amino acid alignment: Translated BLAT more distant species, e.g. human – zebrafish Multi-species (more than two species) • Nucleotide alignments: EPO/PECAN selected sets (primates, fish, birds, mammals, vertebrates) 14/26 Within an alignment … 36 mammals are aligned Human genome 15/24 Scoring the nucleotides High score goes to conserved nucleotides atgccgt acgcgat acgtctt GERP scoring of every nucleotide in the alignment (Cooper GM et al., Genome Res., 2005; 15:901-913) 16/24 High scoring blocks High scoring nucleotides make up the ‘constrained elements’ acgcgat acgcgat acgcgat … 17/24 Exercise Go to the Location tab for the human Myo6 gene. 1) Compare the mouse, cow, and human genomes in this region. 2) Do all species in the 13 eutherian mammal alignment have a gene in this locus? Conservation in Alignments Now turn on the following tracks: • Conservation score for 36 eutherian mammals • Constrained elements for 36 eutherian mammals Q) Are the Myo6 exons in regions of high sequence conservation? Non-Coding Regions • “Phylogenetic Footprinting” – conserved noncoding regions can be functional • Regulatory regions discovered in this way for genes: Hoxb-1, Hoxb4, PAX6, SOX9 20/24 Regulatory Features of the PDX1 gene Region in Detail shows conservation of sequence in regions involved in PDX1 transcriptional regulation (1.6-2.8 kb upstream of the gene). 21/24 Syntenic regions Syntenic regions Blastz/ Lastz 22/24 Synteny 23/24 Acknowledgements • • • • • • Javier Herrero Kathryn Beal Stephen Fitzgerald Leo Gordon Matthieu Muffato Miguel Pignatelli 24/24