Computer Essentials
advertisement

Computer
Essentials
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Computer Essentials
1. Computers and Devices
1.1 ICT
1.1.1 Define the term Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) refers to technologies that provide
access to information through telecommunications. It is similar to Information
Technology (IT), but focuses primarily on communication technologies. This includes
the Internet, wireless networks, cell phones, and other communication mediums.
In the past few decades, information and communication
technologies have provided society with a vast array of new
communication capabilities. For example, people can
communicate in real-time with others in different countries
using technologies such as instant messaging, voice over IP
(VoIP), and video-conferencing. Social networking websites
like Facebook allow users from all over the world to remain
in contact and communicate on a regular basis.
Modern information and communication technologies have created a "global village," in
which people can communicate with others across the world as if they were living next
door. For this reason, ICT is often studied in the context of how modern communication
technologies affect society.
1.1.2 Identify different types of ICT services/uses like: Internet services, mobile
technology, office productivity applications
Internet Services
Wi-Fi
Some public places, such as airports and local councils now offer wireless
access to the Internet. Sometimes this service is provided free of charge.
It may also be provided with a charge, or else you may need a username
and password in order to use the service (e.g. in universities)
2
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Cable
The same cable that supplied TV channels can also supply your Internet connections. Often
cable gives you very high speed Internet access
Dial Up
The most common type of Internet connection. Your computer is connected to a modem which
connects to the phone line. You can use dialup or broadband via the phone line.
Satellite
If you live in a very remote area, your only way to connect to the
Internet may be via a satellite link. This may require large satellite
dishes and expensive specialised equipment. The cost of the Internet
connection may also be high
Mobile Technology
Smart phone
A Smartphone is a mobile phone (cell phone) offering
advanced computer-like features. Capabilities and standards vary from
one manufacturer to another.
Most smartphones have some sort of operating system allowing you to
connect to other devices and also to install applications. Most
smartphones allow you to send and receive emails and may even allow
you to browse the Web.
Some have a personal organizer built into them and some sort of
contact management organiser.
Some even have a miniature computer-type keyboard built into them,
while others have a touch screen.
You might even have GPS positioning systems.
Some smartphones allow you to read documents in Microsoft Word or
Adobe PDF format.
3
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Other features can include a built-in camera, the ability to play music, display photos and
video clips, media software for playing music, browsing photos and viewing video clips.
Mobile Phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is used for mobile
communication (including speech, text-messaging, e-mailing and
accessing the web)
Many also allow you to send and receive pictures and video. Most
mobile phones use a signal from a local transmission tower and will
not work when you are out of range or if the signal is blocked by
mountains, or even buildings.
Satellite phones use a signal coming from a satellite. They tend to be
much more expensive to purchase and use. While you should never
be out of range, the satellite signal may be blocked by tall buildings.
Office productivity applications
Word processing applications
A word processing program (such as Microsoft Word) allows you to produce letters,
memos, etc., easily. You can easily mail merge a list of names and addresses to
produce mass mailers, individually addressed to customers or subscribers.
Spreadsheets applications
A spreadsheet program (such as Microsoft Excel) allows you to work out a company’s
income, expenditure and then calculate the balance. It enables you to make 'what if'
type projections of how the company will fair in the future and to forecast how
changes in prices will affect profits.
Database applications
A database program (such as Microsoft Access) allows you to compile information and
then to search this information to extract just the information you require. For
instance, if you have a database of all the equipment housed within an office you can
very simply produce a report listing only the equipment above a certain value.
Presentation applications
A presentation program (such as Microsoft PowerPoint) allows you to produce
professional looking presentations, which can be printed out directly onto slides
for use with an overhead projector. Alternatively, you can display your presentations
directly on a computer screen or via a computerised projector.
4
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
1.2 Hardware
1.2.1 Define the term hardware. Identify the main types of computers like: desktops,
laptops, tablets. Identify the main types of devices like: smart phones, media players,
digital cameras
What is Hardware?
The term hardware refers to the physical
components of your computer such as the system
unit, mouse, keyboard, monitor etc.
5
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Main types of computers:- desktops, laptops, tablets.
Desktops
A desktop computer (or desktop PC) is
a computer that is designed to stay in a single
location. It may be a tower (also known as
a system unit) or an all-in-one machine, such
as an iMac. Unlike laptops and other portable
devices, desktop computers cannot be
powered from an internal battery and
therefore must remain connected to a wall
outlet.
In the early age of computers, desktop computers were the only personal computers
available. Since laptops and tablets did not exist, all home PCs were desktop computers.
Still, the term "desktop computer" was used back then to differentiate between personal
PCs and larger computers, such as mainframes and supercomputers.
Laptops
Laptop computers, as the name implies, are small
portable computers which can run on batteries as
well as mains power. They use special screens,
rather than the traditional bulky VDUs (Visual Display
U nits), which allows for longer battery life as well as
portability. A newer term, “Notebooks”, simply
indicates a VERY small laptop. These are especially
popular with salespersons on the move or people
giving presentations. While they tend to still be more
expensive than an equivalent Desktop computer, they
can now match the power of a Desktop computer.
Tablets
A tablet, or tablet PC, is a portable computer that uses
a touch screen as its primary input device. Most tablets are
slightly smaller and weigh less than the average laptop.
While some tablets include fold out keyboards, others, such
as the Apple iPad and Motorola Xoom, only offer touch
screen input.
6
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Early tablet touch screens were designed to work with light
pens, but most modern tablets support human touch
input. Many tablets now support multitouch input, which
allows you to perform gestures with multiple fingers, such
as pinching an image to zoom out, or spreading your
fingers apart to zoom in. Tablets without physical
keyboards allow you to enter text using a pop-up keyboard
that appears on the screen.
Main types of devices:- smartphones, media players, digital cameras
Smartphone
A Smartphone is a mobile phone (cell phone) offering
advanced computer-like features. Capabilities and standards vary
from one manufacturer to another. Most Smartphone have some
sort of operating system allowing you to connect to other devices
and also to install applications. Most Smartphone allow you to
send and receive emails and may even allow you to browse the
Web. Some have a personal organizer built into them and some
sort of contact management organiser. Some even have a
miniature computer-type keyboard built into them, while others
have a touch screen. You might even have GPS positioning systems. Some Smartphone allow
you to read documents in Microsoft Word or Adobe PDF format. Other features can include
a built-in camera, the ability to play music, display photos and video clips, media software
for playing music, browsing photos and viewing video clips
Media Players
Media players allow you to store digital music and video. A
famous example is the ipod from Apple, which lets you store
your digital music which you can then listen to at your leisure.
Thousands of songs can be stored on these devices. You can
also get devices with a built-in screen which will allow you to
watch films and video clips that you download to these devices.
7
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Digital Cameras
A digital camera can be used in the same way a traditional
camera can, but instead of storing images on rolls of film
which require developing, the images are stored digitally in
memory housed within the camera (or on memory cards).
These pictures can easily be transferred to your computer
and then manipulated within any graphics programs
which you have installed on your computer.
1.2.2 Define the terms processor, Random Access Memory (RAM), storage. Understand
their impact on performance when using computers and devices.
Processor
A processor, or "microprocessor," is a small chip that resides
in computers and other electronic devices. Its basic job is to
receive input and provide the appropriate output. While this may seem
like a simple task, modern processors can handle trillions of calculations
per second. The central processor of a computer is also known as the CPU,
or "central processing unit." This processor handles all the basic system
instructions, such as processing mouse and keyboard input and running
applications.
Read only Memory (ROM)
Read Only Memory (ROM) as the name suggests is a special type of
memory chip which holds software which can be read but not written
to. A good example is the ROM-BIOS chip, which contains read-only
software. Often network cards and video cards also contain ROM chips
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the main 'working' memory used by the
computer. When the operating system loads from disk when you first switch
on the computer, it is copied into RAM. The original IBM PC could only use
up to 640 KB of memory (just over half a megabyte), whereas a modern
computer can effectively house as much RAM as you can afford to buy.
Commonly modern computers are supplied with over 128 MB of RAM
(Usually you find computers with 1 or 2 GB or RAM – 1 GB is equivalent to
1024 MB). As a rough rule, a Microsoft Windows based computer will operate faster if you install
more RAM. When adverts refer to a computer having 128 Mbytes of memory, it is this RAM which
they are talking about. Data and programs stored in RAM are volatile (i.e. the information is lost
when you switch off the computer).
8
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Storage
A computer storage device is any type of hardware that stores data. The most common type of
storage device, which nearly all computers have, is a hard drive. The computer's primary hard drive
stores the operating system, applications, and files and folders
for users of the computer.
While the hard drive is the most ubiquitous of all storage
devices, several other types are common as well. Flash memory
devices, such as USB keychain drives and iPod nanos are
popular ways to store data in a small, mobile format. Other
types of flash memory, such as compact flash and SD cards are
popular ways to store images taken by digital cameras.
External hard drives that connect via Fire wire and USB are also common. These types of drives are
often used for backing up internal hard drives, storing video or photo libraries, or for simply adding
extra storage. Finally, tape drives, which use reels of tape to store data, are another type of storage
device and are typically used for backing up data.
1.2.3
Identify the main types of integrated and external equipment like: printers, screens, scanners,
keyboards, mouse/track pad, webcam, speakers, microphone, and docking station.
Printers
Most data is printed once you have created it and there are a vast number of different printers
available to accomplish this. Most common are inkjet and laser printers both of which can now
produce coloured output. There are many different types of printers. In large organisations and
offices, laser printers are most commonly used because they can print very fast and give a very high
quality output. In most organisations, the printers are connected to the computers via a network.
This means that each person with a computer does not require his or her own printer. Each
computer connected to the network can print using a particular shared printer.
Laser Printer
This type of printer is mostly used in offices where high amount of copies is
necessary to be printed, it is more economical and it uses the same system as a
photocopier, these are more common in black and white only, but nowadays
colour laser printers are also being introduced.
Inkjet Printer
The inkjet printer is the most commonly used printer at home. It makes use of
cartridges filled with inks.
9
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Impact Printer
A printer in which a keystroke actually hits the paper, like a typewriter, to
produce hard copy.
Dot Matrix Printer
Used in offices for invoicing purposes. They make use of papers with holes at
the sides, and also have a carbonated paper.
Daisy Wheel and Line Printer
An almost obsolete type of printer. A daisy wheel printer has
a small plastic 'wheel' with spokes running out from its
centre. At the end of each spoke there is a flat part that has a
raised alphanumeric character shape. The way it works is that
the wheel is rotated to bring a character up against an inkribbon. Then a tiny hammer pushes the shape on to the
ribbon causing a letter or number to appear on the paper behind the ribbon. Daisy wheel printers
are noisy and slow compared to modern ink-jet and laser printers.
Plotter
Plotters are used to print or plot large formats such as floor plans and large
photographic posters. Plotters are often used by engineers, designers and
architects to produce large technical drawings (often a metre wide and any
length). The paper is rolled back and forth; while a set of ink pens move side to
side, dropping down onto the paper when required.
Screens
Monitor- (VDU- Visual Display Unit)
VDU stands for Visual Display Unit. In other words, it is the monitor of the
computer. It is used for showing the main output of the computer in way
that humans can understand, since the computer works and calculates only
in binary (1 and 0). Traditional computer monitors are based on the same
sort of technology that is used within a television screen. Recently, the TFT
(Thin Film Transistor) monitors were introduced. These will take less space
on the desk than the traditional CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitors and use
less energy.
Projection devices
Projection devices can be attached to your computer and are
useful for displaying presentations to a group of people. They
are best used in combination with presentation programs, such as Microsoft
PowerPoint. They are used within education and are also very popular for
sales presentations.
10
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Touch Screen
A touch screen is a display that also serves as an input device. Some
touch screens require a proprietary pen for input, though most modern
touch screens detect human touch. Since touch screen devices accept
input directly through the screen, they do not require external input
devices, such as mice and keyboards. This makes touch screens ideal for
computer kiosks, as well as portable devices, such as tablets and smart
phones.
Scanners
A scanner allows you to scan printed material and convert it into
a file format which may be used within the PC. You can scan
pictures and then manipulate these inside the PC using a graphics
application of your choice. In addition, you can scan printed text
and convert this not just to a picture of the text but also to, actual
text which can be manipulated and edited as text within your
word-processor. There are a number of specialist
programs, generically called OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
programs which are specifically designed for converting printed text into editable text within your
applications.
Keyboards
The keyboard allows you to type information into the
computer. It has evolved over the years. The keyboard is
built into laptop computers but is a separate item if used
with a Desktop computer. They can be connected via
cables or may be wireless.
Mouse/trackpad
Mouse
When using an operating system, such as Microsoft Windows, you use the
mouse to select drop down menus, to point and click on items, to select
items and to drag and drop items from one place to another.
Trackpad
A trackpad (also touchpad) is a pointing device consisting of specialized
surface that can translate the motion and position of a user's fingers to a
relative position on screen. They are a common feature of laptop
computers and also used as a substitute for a computer mouse where desk
space is scarce. Touchpads vary in size but are rarely made larger than 40
square centimeters (about 6 square inches). They can also be found on personal digital assistants
(PDAs) and some portable media players.
11
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Webcam
Ever since it was invented, the Web has become increasingly
interactive. You can now use a small digital movie camera (a Webcam)
mounted on the PC monitor to allow two-way communication involving
not just text communication but sound and video communication as well.
While not yet considered a standard piece of PC kit, it is only a matter of
time
Speakers
Most computers are sold with the capability to add a pair of speakers to
your system unit. In fact, in some cases, the computer screen may have
speakers built directly into the unit.
Microphone
Early voice recognition systems offered very poor results, due to the
limitations of the software combined with hardware limitations. It
takes an awful lot of CPU processing power to convert the spoken
word into text which appears on the screen. Things are changing
rapidly however and recent systems allow you to talk to a PC and see
text appear on the screen. Most of these systems require an initial
training period, where you train the software to respond to your
particular voice. Whilst still not perfect this is a key technology of the future.
Docking station.
A docking station, or dock, is a device that connects a laptop to multiple
peripherals. It provides a single connection point that allows a laptop to
use a connected monitor, printer, keyboard, and mouse. This allows a
laptop to function like a desktop computer.
1.2.4
Identify common input/output ports like: USB, HDMI.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Port
You will see one or more USB sockets at the back / front of the system unit,
allowing you to plug in devices designed for the USB. These devices include
printers, scanners and digital cameras. Memory sticks can also be plugged
into a USB port allowing you to copy data to or from your hard disk.
12
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a compact
audio/video interface for transferring uncompressed video data
and compressed/uncompressed digital audio data from a HDMIcompliant device ("the source device") to a compatible computer
monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device.
HDMI is a digital replacement for existing analogue
video standards.
There are a number of HDMI-standard cable connectors available, each of which can be used for any
uncompressed TV or PC video format, including standard, enhanced, high definition, and 3D video
signals
1.3 Software and Licensing
1.3.1
Define the term software and distinguish between the main types of software like: operating
systems, applications. Know that software can be installed locally or available online.
Software
Software is the collection of instructions which makes the computer
work. For instance, when you type in words via the keyboard, the
software is responsible for displaying the correct letters, in the correct
place on the screen. Software is held either on your computer’s hard
disk, CD-ROM, DVD or on a diskette (floppy disk) and is loaded (i.e.
copied) from the disk into the computers RAM (Random Access
Memory), as and when required. Software is also available online
There are two types of software:
Systems or Operational Software (Operating System)
Applications Software
Systems Software
System software refers to the files and programs that make up your
computer's operating system. System files include libraries of functions,
system services, drivers for printers and other hardware, system preferences,
and other configuration files. The programs that are part of the system
software include assemblers, compilers, file management tools, system
utilities, and debuggers. The system software is installed on your computer
when you install your operating system.
13
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Applications Software
An application program is the type of program which you use once the operating system has been
loaded.
Examples include:
- Word-processing programs (for producing letters, memos etc)
- Spreadsheets (for doing accounts and working with numbers)
- Databases (for organising large amounts of information)
- Games
Graphics programs (for producing pictures, advertisements,
manuals etc).
It is important that you recognise examples of application programs
covering the following areas:
- Word processing
- Spreadsheets
- Databases
- Presentations
- E-mailing and Web browsing
- Photo editing
- Computer games
1.3.2
Define the term operating system and identify some common operating systems for
computers and devices.
The operating system is a special type of program which loads automatically when you start your
computer. The operating system allows you to use the advanced features of a modern computer
without having to learn all the details of how the
hardware works. There are a number of different types
of operating system in common use. The IBM PC
(Personal Computer) was introduced way back in 1981
and was originally supplied with an operating system
called DOS (Disk Operating System). This operating
system was very basic, and you had to be a bit of a
computer expert just to understand how to use it. It
was NOT user-friendly. Later on, Microsoft introduced Windows and this is the operating system
which is most widely used on PCs today. There are a number of different types of Windows. Most
people are today running Windows XP or Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows 8
Other examples of Operating Systems are:
- Windows 95
- Windows 98
- Windows 2K (or Windows 2000)
- Linux and UNIX
14
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
1.3.3
Identify common examples of applications like: office productivity, communications, social
networking, media, design, mobile applications.
Examples of office productivity software include Microsoft Office, Google Apps For Business,
Libre Office Productivity Suite, Open Office, Zoho, KOffice, MS Publisher, Notepad, WordPad,
Paint, and PhotoFiltre.
Examples of Communications include Skype, Viber, What’s Up
Examples of Social Networking Facebook, Twitter, Linked IN
Examples of Media include Windows Media Player, VLC
Example of Design include Photoshop, Gimp, Kompozer
Example of Mobile Applications such as Play store, Calendar, email
1.3.4
Define the term End-User License Agreement (EULA). Recognise that software must be
licensed before use.
When you purchase a piece of software you don't actually own the software. What you are
buying is a licence to be able to use the software. You are able to load your software onto your
machine at home and use it for as long as you like.
The licence which comes with commercial software is also known as the EULA or End User Licence
Agreement. An End user Licence agreement is a legal contract between a software author or
publisher and the user. Software Copyright is a way to legally protect the ownership of software.
The EULA will appear on the first screen of the installation wizard when you start to install the
product. In order to continue with installation, you must read and agree to the terms set out in the
licence.
1.3.5
Outline the types of software licenses: proprietary, open source, trial version, shareware,
freeware.
Proprietary
Proprietary software or closed source software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal
right of the copyright holder with the intent that the licensee is given the right to use the software
only under certain conditions, and restricted from other uses, such as modification, sharing,
studying, redistribution, or reverse engineering. Usually the source code of proprietary software is
not made available.
Open source software
This type of software licence makes the programming code available to anyone who wishes to
enhance or develop the code. Over the years many companies have complained that Microsoft is
reluctant to share this level of code detail with competitors, which they claim gives Microsoft an
unfair advantage and stifles competition. It is important not to confuse open source software with
free software. Sometimes the source code is made available within the public domain for use by all,
as they see fit. In other cases the source code is made available to particular companies under tight
non - disclosure agreements, to protect commercial sensitivities.
15
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Trial Version
Trial version refers to a version of the product that will be close to full-featured, but with certain
aspects "disabled."
Shareware
This is where you can use software for a free trial period. Sometimes the shareware versions may be
fully functional, but after a time period will either start to display an annoying message, asking
you to register (i.e. pay for) your software, or in some cases it may stop working altogether after the
trial period. This 'try before you buy' method of getting software is becoming increasing popular
with the major software suppliers.
Freeware
This is software which can be copied or downloaded free. It is often fully functional. Examples may
include software developed by organisations such as Universities, where the aim was not to profit
from the software. It is very important not to confuse freeware and shareware.
1.4 Start Up, Shut Down
1.4.1
Start a computer and log on securely using a user name and password.
First check that all cables are plugged securely into the rear of the machine.
Then check that the monitor is turned on.
Locate the power switch on the system unit (tower) and press it once to turn on the
computer.
You may be asked to supply a logon ID and a password.
1.4.2
Log off, shut down, and Restart a computer using an appropriate routine.
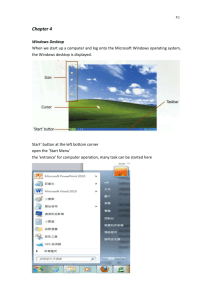
Log off
Click on button that represents Start
Click on the arrow next to shutdown
16
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
And then click Log Off
Shut Down
Click on button that represents Start
Click on the button to shutdown
Restart
Click on button that represents Start
Click on the arrow next to shutdown
And then click Restart
2. 2 Desktop, Icons, Settings
2.1 Desktop and Icons
2.1.1
Outline the purpose of the desktop and the task bar
The Desktop is the first screen you see in your computer after Windows is loaded. And it always
stays there (sometimes underneath other windows) until you shut down your computer. The
Purpose of the Desktop is to provide icons such as Recycle Bin, Shortcuts which you have created
and more
17
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
The purpose of the taskbar is to provide the user with an easy way of opening and managing
programs installed on their computer.
2.1.2
Identify common icons like those representing: files, folders, applications, printers, drives,
and shortcuts/aliases, recycle bin/wastebasket/trash.
18
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
2.1.3
Select and move icons.
Click on the icon to Select it and then drag it to where you need the icon you can also use Cut, Copy
and Paste techniques
2.1.4
Create, rename, move, delete a shortcut/alias.
Creating Desktop Shortcut Icons
Sometimes it might be necessary for you to
create a shortcut on the desktop. Usually the
reason behind this is that you use a particular
file / folder on a regular basis and you want to
be able to open it easily and quickly.
To Create a New Shortcut:
Right click on a file / folder.
Move the pointer to send to.
Click Desktop (Create Shortcut). A
shortcut to that file / folder will be
created on the desktop.
Move a Shortcut to another Location on your Computer
Right click on a file / folder.
Click create shortcut.
The shortcut will be created next to your selected file / folder.
Move the shortcut to the desired location. (Using cut & paste or drag & drop techniques).
19
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Rename a shortcut or Delete a Shortcut
Right click on the shortcut.
Click on Rename to change the name of the Shortcut or Delete if you want to remove the
shortcut
2.2 Using Windows
2.2.1
Identify the different parts of a window: title bar, menu bar, toolbar, ribbon, status bar, scroll
bar.
Ribbon
Title Bar
Menu Bar
Status Bar
Tool Bar
Scroll Bar
20
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
2.2.2
Open, collapse, expand, restore down, maximise, resize, move, and close a window.
You need to do other actions with windows, including: collapsing, expanding, restore, resizing,
moving and closing
To MOVE a window, hover over the title bar.
Then click the left mouse button and drag the
window to the position you want.
To COLLAPSE
the window,
click the
minimize
icon
To Expand
the window,
click the
maximize
icon
To CLOSE the
window, click the
close icon
To Open a File. Click Once and a
Window will open. Choose the file
you want to open and click Open
2.2.3
To RESIZE a window, move the mouse over the
edges of the window until you see a doubleended arrow. You then need to click the left
mouse button and drag the window to the right
size.
Switch between open windows.
If you have windows open, but they are minimized, you can restore them quickly and easily. All you
need to do is click on the window that you want to open, displayed in the taskbar.
If you want to switch between two
open windows i.e. if you have one
open but want to view another that is
minimized, simply click on the
application icon and then choose from
the files you have opened
21
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
2.3 Tools and Settings
2.3.1
Use available help functions.
Click on button that represents Start
Then Click on Help and Support
A window will load up. In Search Help box write what you need to
search example how to rename files and click on the magnifier glass
Click on the category you need the information about example rename
a file and then all the information about renaming a file will occur
2.3.2
View the computer's basic system information: operating system name and version number
installed RAM.
Click Start
Control Panel
22
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Click on System and Security and then click on System
The following window will be displayed:
Operating system
Version Number
CPU Speed
RAM – Random Access Memory
Note: You can also display the computer’s basic system information, by right clicking on the
computer from the menu Start and selecting Properties.
2.3.3
Change desktop configuration settings: date and time, volume settings, background,
resolution.
Change Date and Time
From the Control Panel Click on Clock, Language and Region
Click on Date and Time
23
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Change the date, Month and year from the calendar given and the time from the arrows
facing up and down
Volume Settings
From the Control Panel Click on Hardware and Sound
Click on Sound
Then double click on speakers
24
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Click on the tab Levels and change the volume of the speakers accordingly
Background
From the Control Panel Click on Appearance and Personalization
Click on Personalization
Click on Desktop Background
From Picture location choose whether you need solid Colours, a picture from library or Top
Rated Photos. In case it’s a picture saved in your documents click on browse and search for
the desired picture
After you have chose the picture choose how the picture should be positioned ex fit to
screen, tile etc
25
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Resolution
From the Control Panel Click on Appearance and Personalization
Click on Display
Click Adjust Resolution from the left
2.3.4
Change, add, and remove keyboard language. Change default language.
Change/Add keyboard Language
From the Control Panel Click on Clock, Language and Region
26
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Click on Region and Language
Then Click on the tab Keyboards and Language
Click on Change Keyboard
Click on Add and select a Country
Remove Keyboard Language
Click on the Language you want to remove from the installed Service and Click Remove
Change Default Language
Click on the arrow to change the default Language
27
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
2.3.5
Shut down a non-responding application
Sometimes a program / application fail to respond i.e. the program ‘hangs’. Typically non-responsive
cannot be closed in the normal way. In such case, you need to follow these steps in order to shut
down (close) the program:
Press Ctrl, Alt and Delete on your keyboard
A window will occur. You will see a list of things which you can choose from. It’s important
that you click on Start Task Manager. You will see a list of programs. Click on the program
that is not responding and click End Task
The End Program dialog box will be displayed.
Click End Now button
1
3
2
2.3.6
Install, uninstall an application.
To install an application put the CD that you bought in the CD Drive. Open the computer from the
Start Button and double click on the Application Icon. Then follow step by step by its wizard
To uninstall an application:
From the Control Panel Click on Programs
Click on Programs and Features
28
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
2.3.7
Choose Software from the list below that you wish to Remove and Click on Uninstall
Connect a device (USB flash drive, digital camera, media player) to a computer. Disconnect a
device using an appropriate routine.
Connect a USB Flash Drive
Put the pendrive in a USB port and automatically the Computer will install it
Connect a Digital Camera and Media Player
Attach appropriate end of cable to the camera and the other end to the USB port found either on
the front or on the back of your tower.
Connect to
camera
Connect to
USB port
29
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Disconnect a device using an appropriate routine.
2.3.8
Click on the arrow facing upwards in the system tray
Click on the icon that shows a USB wire and click Eject. When the Text Safe to Remove
Hardware appears on the screen pull out the pendrive
Capture a full screen, active window.
Locate the print screen button on your keyboard and press it once. This will take a picture of
the current screen.
Click Paste.
If you only need to capture a copy of the active window, press Alt from your keyboard and
press the print screen button, whilst holding the Alt key.
When you click Paste in an application, you will see that only the active
window will be pasted and not the whole screen
30
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
3. 3 Outputs
3.1 Working with Text
3.1.1
Open, close a word processing application. Open, close files.
Opening a Word Processing Application
Click on the Start Button
Click All Programs
Select Microsoft Office
Click on Microsoft Office Word
To close a Document / Microsoft Word
Click the Microsoft Office Button
and click close, Close. OR
Otherwise click on the small ‘x’ button
Opening an Existing Document
3.1.2
Click the Microsoft Office Button
and Click Open, or Press CTRL+O (Depress the CTRL key
while pressing the ―O‖) on the keyboard
Choose the location where the file is Saved
Click on the file and Click Open
Enter text into a document.
Flashing insertion point indicates where the next character you type will appear. Simply start typing
to enter text. If you make any mistakes, use the Backspace key to delete unwanted characters.
3.1.3
Copy, move text within a document, between open documents. Paste a screen capture into a
document
Select the text that you wish to copy.
Click on the Home tab and select Copy
Click at the position within the document where you wish to paste the copied text. If you
wish to paste it in another document, click on the document window on the taskbar.
Click on the Home Tab again and Select Paste.
Move text within a document or between open documents.
Select the text that you wish to move.
Click on the Home tab and select Cut
Click at the position within the document where you wish to paste the
copied text. If you wish to paste it in another document, click
on the document window on the taskbar.
Click on the Home Tab again and Select Paste.
31
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Paste a screen capture into a document
3.1.4
Locate the print screen button on your keyboard and press it
once. This will take a picture of the
current screen.
Click Paste.
If you only need to capture a copy of the active window, press Alt from your keyboard and
press the print screen button, whilst holding the Alt key.
When you click Paste in an application, you will see that only the active
window will be pasted and not the whole screen
Save and name a document.
Click the Microsoft Office Button
Click Save or Save As
OR
Press CTRL+S (Depress the CTRL key while pressing the ―S‖) on the keyboard,
OR
Click the Save icon on the Quick Access Toolbar
32
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Write the name of the document in the file name field then click Save
3.2 Printing
3.2.1
Install, uninstall a printer. Print a test page.
Install a Printer
Click Start button.
Click Control Panel.
Click on Hardware and Sound
33
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Click on Devices and Printers
Double-click Add Printer to start the Add Printer Wizard, and then click next.
Follow the on-screen instructions to finish the wizard.
Uninstall a printer
Click Start button.
Click Control Panel.
Click on Hardware and Sound
Click on Devices and Printers
Click on Remove Device and Click Yes
34
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Print a test page
3.2.2
Open Printers by clicking the Start button Picture of the Start button,
Then click Control Panel
Click Hardware and Sound,
And then click devices and Printers.
Right-click the printer that you want to test, and then click Properties.
On the General tab in the Printer Properties dialog box, click Print Test Page.
Set the default printer from an installed printer list.
Normally in a computer network environment, there will be several printers.
Users will therefore need to send their documents to a specific printer – probably to the printer
closest to their computer system. Such users will set this printer as the default printer. The default
printer is the printer to which a computer sends documents when you select the Print command
without first specifying which printer you want to use with a program. You can have only one default
printer; it should be the printer you use most often.
To set a printer as the default printer:
Click Start button.
Click Control Panel.
Click on Hardware and Sound
Click on Devices and Printers
35
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
3.2.3
The Printers window appears, showing a list of printers connected to
the network will be displayed.
Right-click the name of the printer to set as a default printer.
Click Set as Default Printer. The icon of selected printer will display a
checkmark on the top right corner.
Print a document from a word processing application.
Click on the Office Button.
Point to Print, and then click on Print from the sub-menu
The Print dialog box will be displayed as illustrated below.
In the Page range section choose whether you wish to print all the pages in the document, the
current page only, selected pages, or a particular selection.
In the Copies section specify how many copies of the same document you wish to print.
36
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
You can choose to print all the pages in the range specified, or else you can choose to only print
the odd or the even pages.
Finally, click OK.
3.2.4
View, pause, restart, cancel a print job.
View a Print Job
Once you have started printing you can view a print job’s process.
Double click on the printer icon displayed at the bottom-right of your screen.
This will display a dialog
box showing the progress
of your print jobs.
Otherwise, from the
Control Panel, click on
Printers, then doubleclick on the printer in
use.
Pause, Restart or Cancel a Print Job
Open to View the Print Job Progress
Right click on the file you want to cancel, pause or Restart and choose
From the Menu given
4 File Management
4.1 Introducing Files and Folders
4.1.1
Understand how an operating system organises drives, folders, files in a hierarchical
structure. Navigate between drives, folders, sub-folders, files.
What are Drives, Folders and Files?
When accessing a drive on your computer, Windows uses a system of drive letters to serve as logical
pointers to the different physical drives you have access to. From each drive letter it is possible to
access all of your files stored on that particular physical drive. For instance, the Hard Disk drive letter
is usually ‘C’. On some computers, you will find two hard disks, one of which will be the C drive and
the other will be the D drive. The Floppy Disk is referred to as drive A. Pen drives are referred to as
37
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Removable Disks and they may be assigned different letters, depending on the number of disks
installed on your computer.
To help organise your files it is possible to create folders (also referred to as directories) to help
divide and even sub-divide the files stored within the various logical drives available. A system of
hierarchical folders within folders which represent your hard disk are often referred to as the folder
(directory) tree, in the same way the very top of the file system is known as the root folder
(directory). Finally, at the very end of this structure are the various files which we use. Each file
name can be up to 255 characters in length.
4.1.2
4.1.3
Display file, folder properties like: name, size, location.
Right click on the folder.
Click Properties.
Change view to display files and folders like: tiles, icons, list, and details.
Open the Folder and click on the View tab on the right hand side of the screen and choose between
tiles, icons, list and details
38
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.1.4
Identify common file types like: word processing, spreadsheet, presentation, portable
document format (pdf), image, audio, video, compressed, executable files.
Within the Windows Explorer window each file will be marked with a small icon, as illustrated. In the
example shown, the first file displays an icon representing Microsoft Word, and if you look along the
line of information about this file, it clearly states (assuming that you are using the details mode to
view the files) that the file is indeed a Microsoft Word Document. The second file is marked as a
Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation file in the same way.
File extensions
File names usually end with a 3 character extension. A period (.) separates the filename from the file
extension. Some of the common file extensions are listed below:
39
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.1.5
Open a file, folder, drive.
To open a File, folder or drive, double click on it.
4.1.6
Recognise good practice in folder, file naming: use meaningful names for folders and files to
help with searching and organisation.
Create file names that are logical, meaningful to all users, simple to read and relevant.
Use lowercase when naming files.
Do not use the following characters: &, ( ) % # ‘ â€oe / \ - { } [ ] < > @
When numbering similar types of files or sequences try to anticipate maximum
numbers
Files should not be located in directory structures with more than six levels, as this can
create difficulties when accessing and archiving files.
40
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.1.7
4.1.8
4.1.9
Create a folder.
Identify the area where you will create your new folder, e.g. Desktop or My Documents.
Right click in an empty space, point to New, and then click Folder.
A new folder will be created and you can use the keyboard to type a name for the folder.
Press Enter
Rename a file, folder.
Right click on the folder / file.
Click Rename.
Type in a new name.
Press Enter
Search for files by properties: all or part of file name using wildcards if necessary, content,
date modified.
To open the Search dialog box, click on the Start button, and write the file/folder where you have
Start Search and click on See more results. Automatically it will start searching but f you need more
options click on the Search Box. This will show the Add Search filter window. Options you can search
for files and folders by date modified, kind, type size etc. Click on the one you need to Search with
41
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
To search for a file using wildcards instead of the full name. In the previous example, we knew the
full name of the file or folder for which we were searching. In some cases we may only know part of
the name, in which case we can use wildcards.
For example:
To search for all files whose names start with z
o Type: z*
To search for all files whose names start with za
o Type: za*
To search for all files whose names start with za and contain 5 characters
o Type: za???
To search for all Microsoft Excel files whose names start with za and contain 5 characters
o Type: za???.xls
4.1.10 View list of recently used files.
Click on the Start icon (bottom-left of your screen), and from the popup menu displayed
select Recent Items
A submenu will display a list of recently used documents.
Clicking on one of these document files will load the document into the relevant program.
4.2 Organising Files and Folders
4.2.1
Select individual, adjacent, nonadjacent files, folders.
To select an individual file / folder simply click once on the file / folder. The file / folder will
be highlighted in blue.
To select a number of adjacent files / folders. Click on the first file / folder in the block you
wish to select, then press Shift and keep holding the key whilst clicking on the last file /
folder in the block.
42
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.2.2
To select a number of non-adjacent files / folders. Click on the first file / folder that you wish
to select. Then press and hold the Ctrl key, whilst clicking on the other files / folders that you
wish to select.
Sort files in ascending, descending order by name, size, type, date modified.
The files displayed in My Computer window can be sorted by name, size, file type and the date/time
last modified:
Click View, Details.
Click the appropriate header:
Note: To reverse the sort order, re-click the appropriate header.
Counting the Number of Files of a particular type in a Folder
Let’s say you have a folder that contains files of different types and you want to know the
number of files that are of the type .txt (text files). Follow these steps:
43
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Set the view to Details.
Sort the files by type.
Click on the first text file in the list. Press and hold the Shift button, while clicking on the last
text file in the list.
Right click on one of the files in the list and click
Properties. You will see the following window:
This means that in the folder we have 10 files which
are of the type ‘.txt’.
44
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.2.3
4.2.4
Copy, move files, folders between folders, drives.
Select the files / folders that you wish to duplicate / move.
Right click on the file or folder to Copy (to duplicate) OR Cut (to move).
Open the folder where you want to paste the files / folders and Right click, Paste.
Delete files, folders to the recycle bin/wastebasket/trash and restore to original location.
Deleting Files
To delete a file, simply right click on it and click Delete. The
same procedure applies for a folder.
Files and folders that you delete are placed in the recycle bin,
from where you can permanently delete a file or restore it.
45
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
To permanently delete a file / folder:
In the Recycle Bin right click on the file / folder that
you wish to remove permanently, then click on
delete
Restore from Recycle Bin:
Double click on the Recycle bin to open it.
Right Click on the file or folder you want to Restore
Click Restore
OR
In case you want to restore all of them:
Double click on the Recycle bin to open it.
Click Restore all
4.2.5
Empty the recycle bin/wastebasket/trash.
To empty the Recycle Bin:
Double click on the Recycle bin to open it.
Click, Empty Recycle Bin.
4.3 Storage and Compression
4.3.1
Identify the main types of storage media like: internal hard disk, external hard disk, network
drive, CD, DVD, Bluray Disc, USB flash drive, memory card, online file storage.
Internal Hard Disk: All PCs are supplied with an internal hard disk. This is
where the operating system (such as Windows) is stored. It is also were you
store your data. When you install new applications, they are copied from CD
or DVD to your internal hard disk.
External hard drives: As the name suggests these are secondary hard disks
that you can plug into your computer. They are normally connected via a USB cable. They are
available in a range of speeds and storage capacities and are an ideal way to backup your data, such
as photos or movies.
Network Drives and online file storage: Within an office it is normal that the
computers are connected together via a network. This allows you to store
your data centrally, on a network server. This network server should be
backed-up by the IT support staff on a daily basis. This means that your data
is safely backed up for you. Alternatively you may create and store your data
46
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
on your own PC or laptop and periodically copy it across the network to be stored safely on a
central network server. In many companies network software automatically backs up selected
folder on each computer to the central server.
CD: Most computers are now supplied with a CD- ROM (Compact Disc - Read
Only Memory) drive. CD-ROM discs look exactly like music CDs but contain
computer data instead of music. The advantage of a CD-ROM is that it can
hold a vast amount of data (equivalent to the storage capacity of over 450
floppy disks). The other big advantage of CD-ROMs is that they are
interchangeable. This means that you can own a range of different CD-ROM s
and choose which one to insert into your CD-ROM drive.
DVD: Short for "Digital Versatile Disk”. Similar to CD-ROM drives but allows you
to use DVD disks, which contain vastly more information than a traditional CD ROM disk. These also transfer the data from the disk to the computer far faster,
allowing you to watch movies on your computer screen. A CD-ROM can store
650 – 700 MB of data, while a single-layer; single-sided DVD can store 4.7 GB of
data.
Blue-ray is an optical disc format such as CD and DVD. It was developed for
recording and playing back high-definition (HD) video and for storing large
amounts of data. While a CD can hold 700 MB of data and a basic DVD can hold
4.7 GB of data, a single Blu-ray disc can hold up to 25 GB of data.
USB flash drive: Flash drives plug into the USB port and when viewed via the
Windows Explorer, look just like any other drive. They are supplied in a range of
sizes with the 1 GB devices being a very cheap way of transferring relatively small
amounts of data between computers.
Memory Card: A memory card (also called a flash memory card) is a card
containing memory chips that is often used in devices such as digital cameras,
mobile phones, music players, video game consoles, GPS system and similar
devices where there is a need to store data in a compact from, often using a
battery power source. There are a number of different types of memory cards
with different storage capacities. Many new PCs have built-in slots for different ty
pes of memory cards.
4.3.2
Identify file size, folder size, storage capacity measurements like: KB, MB, GB, and TB.
KB: Kilobyte represents 1,024 bytes,
MB: Megabyte represents 1,048,576 bytes,
GB: Gigabyte represents 1,073,741,824 bytes
TB: Terabyte represents 1,099,511,627,776 bytes
47
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.3.3
4.3.4
View available space on a storage device.
Go to Computer from the Start Button
Right Click on The drive which you need to check the available space
Click on Properties
Understand the purpose of file, folder compression.
File compression allows you to compress files so that the file size becomes smaller. This allows you
to save disk space. It is useful when sending files over the Internet (especially when you have a slow
connection).
4.3.5
Compress files, folders.
Right click on the
folder,
From the popup menu
displayed, select Send to,
Then click Compressed
(zipped) Folder.
48
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
4.3.6
Extract compressed files, folders to a location on a drive.
Right click on the zipped folder that contains the files that you wish to open.
Click Extract All
This will display a Window and click Extract
49
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
5 Networks
5.1 Network Concepts
5.1.1
Define the term network. Outline the purpose of a network: to share, access data and
devices securely.
Network is when you have two or more computers connected to
each other, you have a network. The purpose of a network is to
enable the sharing of files and information between multiple
systems and also access data and devices securely by a Username
and Password the Internet could be described as a global network
of networks. Computer networks can be connected through
cables, such as Ethernet cables or phone lines, or wirelessly, using
wireless networking cards that send and receive data through the
air.
5.1.2
Define the term Internet. Identify some of its main uses like: World Wide Web (WWW), VoIP,
e-mail, IM.
Internet
A collection of networks started by and for the US military to enable them to
'survive' a nuclear war. Later adopted by the educational system, and now
exploited by the commercial world. The Internet is a global network of
interconnected networks. The unique thing about the Internet is the sheer
amount of information which you can access from it. Whatever your
interest, you can search for and find information on the most obscure topics.
The Internet is an incredibly valuable tool, which can be used for research,
communication, marketing and business, amongst other things.
World Wide Web (WWW) vs. the Internet
The World Wide Web (WWW) is just a small part of the Internet as a whole. The Internet relates to
all the hardware and software involved, as well as the WWW. It also includes FTP (File Transfer
Protocol), email and newsgroups. The WWW is basically the text and pictures which you can view
using your web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer, or Netscape Navigator.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Voice over Internet Protocol, is a technology that allows you to talk with
other people via the Internet. You can talk at no extra cost to other people
using VoIP on their computers. You can even make calls to real telephones
at a much cheaper rate than normal.
This system is ideal when you need to make a lot of long distance
of international calls. You can use VoIP by just installing a microphone and headset, or you can
purchase a special VoIP compatible phone, which will normally plug into one of the USB sockets on
50
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
your computer. A well known VoIP product supplier is Skype, who produce a range of excellent
phones.
Electronic mail (e-mail)
Email allows you to send a message to another person almost instantly, anywhere
in the world. It requires both computers to be connected to the Internet. As well
as sending a text message, files can be sent as email attachments.
Instant messaging (IM)
Instant messaging (IM) provides a mechanism for real-time communication
between two or more people sending text messages via their computers. This
is different from sending an email which once sent may be read sometime later
by the person you sent the email to.
Some types of instant messaging software let you speak rather than having to
type your messages. You can use your web cam so that you can see the person you are talking to.
5.1.3
Define the terms intranet, virtual private network (VPN) and identify their main uses.
Intranet is a smaller, closed version of the Internet, which can only be
accessed by authorized members of an organisation. Intranets
are becoming an increasingly popular way to share information within a
company or other organisation. An Intranet uses Internet technologies to
allow users to access company documents, search databases, schedule
meetings and of course send emails. The Intranet can only be accessed by
employees working within a particular firm, using a specific username and
password.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a network that uses a public
telecommunication infrastructure, such as the Internet, to provide
remote offices or individual users with secure access to their
organization's network. A virtual private network can be
contrasted with an expensive system of owned or leased lines that
can only be used by one organization. The goal of a VPN is to
provide the organization with the same capabilities, but at a much
lower cost.
51
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
5.1.4
Understand what transfer rate means. Understand how it is measured: bits per second (bps),
kilobits per second (kbps), megabits per second (mbps), and gigabits per second (gbps).
Transfer rate is commonly used to measure how fast data is transferred from one location to
another. For example, a hard drive may have a maximum data transfer rate of 480 Mbps, while your
ISP may offer an Internet connection with a maximum data transfer rate of only 1.5 Mbps.
When you download or upload data the speed of the data transfer is measured by the amount of
data that is transferred per second.
Common transfer rate units are:
5.1.5
Bits per second (bps). (Very slow connections will be quoted in bits per second).
Kilobits per second (kbps).
Megabits per second (mbps). (High speed data transfer is measured in megabits bits per
second.)
Gigabits per second (gbps)
Understand the concepts of downloading from, uploading to a network.
You can ‘download’ data from a network, for instance you can download a file from a web site.
Another example of downloading would be copying a file from another computer on your Local Area
Network to the hard disk on your computer. Uploading refers to copying data from your computer
to another computer, either on your local area network or on your company website.
5.2 Network Access
5.2.1
Identify the different options for connecting to the Internet like: phone line, mobile phone,
cable, wi-fi, wi-max, satellite.
Phone line
The most common type of Internet connection. Your computer is connected to a modem which
connects to the phone line. You can use dialup or broadband via the phone line.
Cable
The same cable that supplied TV channels can also supply your Internet connections. Often cable
gives you very high speed Internet access. Mobile phone: This is often very expensive. The
connection is established via special, Internet compatible mobile phones.
Wi-Fi
Some public places, such as airports and local councils now offer wireless access to the Internet.
Sometimes this service is provided free of charge. It may also be provided with a charge, or else you
may need a username and password in order to use the service (e.g. in universities)
52
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Wi-Max
WiMAX systems are expected to deliver broadband access services to residential and enterprise
customers in an economical way.
Loosely, WiMax is a standardized wireless version of Ethernet intended primarily as an alternative to
wire technologies ( such as Cable Modems, DSL and T1/E1 links ) to provide broadband access to
customer premises.
WiMAX would operate similar to WiFi but at higher speeds, over greater distances and for a greater
number of users. WiMAX has the ability to provide service even in areas that are difficult for wired
infrastructure to reach and the ability to overcome the physical limitations of traditional wired
infrastructure.
Satellite
If you live in a very remote area, your only way to connect to the Internet may be via a satellite link.
This may require large satellite dishes and expensive specialised equipment. The cost of the Internet
connection may also be high.
5.2.2
Define the term Internet Service Provider (ISP). Identify important considerations when
selecting an internet subscription option like: upload speed, download speed and quota,
cost.
ISP stands for Internet Service Provider – If you want to connect to the internet you need to
subscribe via an Internet Service Provider. The ISP gives you a connection to the internet either via
your telephone line, cable connection or via a special digital high-speed line (ADSL).
It’s important to consider these options when selecting an internet subscription:Upload speed – It t determines how quickly your computer/LAN can transmit data to other locations.
In media streaming, its function is to send the initial request for web pages and files to the server.
Download speed – It reflects how much data can be transmitted to your computer/LAN at one time.
This affects the speed of web page loading, file downloading, video/audio streaming, etc
A quota – it is the limit example of downloading from Internet
Cost – It depends on the service and what it consist of.
5.2.3
Recognise the status of a wireless network: protected/secure, open.
Click Networks Icon
. Available networks are displayed in the system tray
In the Wireless Network Connection Hover your cursor over a network name to view a popup that lists the security type.
o If the security type is something such as WEP or WPA2, your network is secured.
53
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
o
o
5.2.4
If the security type is something such as Unsecured or No authentication (open),
your network is not secured.
If you notice an exclamation on the network icon that means also that it is not
secures
Connect to a wireless network.
Click on Start
Then click on Control Panel
Then click on Network and Internet
Click on Network and Sharing
Then click Connect to a Network
And choose which wireless you would like to connect to.
Note: Those wireless networks that are for free you will notice that they will have an exclamation
mark on top of them the others you would need a password
6 Security and Well-Being
6.1 Protecting Data and Devices
6.1.1 Recognise good password policies like: create with adequate length, adequate
character mix, do not share, change regularly.
54
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Password policies refer to guidelines or requirements on the structure and use of passwords. They
can be required for access to a computer system or a group of files or a single file. The following are
some guidelines for password policies:
They should never be blank.
They should not be the names of family members or pets or anything else that would be easy for an
intruder to try out.
Ideally they should never be words, especially words like administrator, admin or root.
They should never be less than five characters and preferably
longer. Short passwords can easily be determined by a brute
force password cracker. This is a piece of software that
repeatedly feeds in all combinations of letters and numbers
until accessed is gained. With short passwords this can be
done in seconds.
A good policy is to use a meaningless combination of letters
and numbers that is seven or eight characters long. What
some users do is to take a meaningful word such as looking and replace the o with the number 0 and
the letter i with the number 1 so that the password becomes l00k1ng. You could also make a less
obvious change, for example replace k with 3 and g with 9 so that the password becomes loo3in9.
Passwords should be changed on a regular basis. Administrators can set a policy that automatically
causes passwords to expire after a certain period of time, for example 7 days.
6.1.2 Define the term firewall and outline its purpose.
A firewall consists of software and hardware protection against invasion via the internet. In
larger companies any connection to the internet automatically goes through a firewall that
would have been installed and customized by the company‘s technical IT team.
The importance of including a firewall in your security strategy is apparent; however, firewalls
do have the following limitations:
A firewall cannot prevent users or attackers with modems from dialling in to or out of
the internal network, thus bypassing the firewall and its protection completely.
Firewalls cannot enforce your
password policy or prevent
misuse of passwords. Your
password policy is crucial in
this area because it outlines
acceptable conduct and sets
the ramifications of
noncompliance.
Firewalls are ineffective
against nontechnical security risks such as social engineering, as discussed in Chapter 1,
“There Be Hackers Here.”
55
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Firewalls cannot stop internal users from accessing websites with malicious code,
making user education critical.
Firewalls cannot protect you from poor decisions.
Firewalls cannot protect you when your security policy is too lax.
6.1.3 Understand the purpose of regularly backing up data to a remote location.
It’s important to take regular backups as your files can be lost or destroyed accidentally; the hard
disk may also develop problems. Thus, backups have to be made not only on the hard disk but also
on an external device such as CDs, DVDs, external hard disks or tape drives. This data should also be
protected from fire or flood disasters.
6.1.4 Recognise the importance of regularly updating software like: anti-virus, application,
operating system software.
No computer software is perfect, just as no human is perfect. This is why, over time, the software
matures as a result of important updates released by their developers. Upon the first release of a
computer program, there will be numerous unforeseen problems and issues experienced by the
initial user base, most of which the developer could not have discovered without the feedback from
users. Hence, the developers release updates.
Basically, updates are additions to software that can help prevent or fix problems, or enhance and
improve how your computer works.
With this in mind, it is important to remember to regularly check for updates to your software
(including Windows, Microsoft Office) for a variety of
reasons.
Improved security is the most important reason why
you should make sure to update your software.
Security updates are designed to protect your software
(and computer) from harmful programs, viruses, and
exploits. You wouldn’t want your software to leave a back door open on your computer and give
intruders access to your personal information.
New features are released over time for software as the creators continue to develop and mature it.
Some features may improve the functionality of the program, or allow you to easily perform that
one task you could never do before.
Enhanced overall performance of the software and the computer is also often a good reason to keep
up-to-date with updates to your PC programs. At initial creation developers may only envision one
way of writing code and using computer resources to accomplish the necessary task. Then, down the
road, the software developer may discover a less resource-intensive way to complete the same task,
or a simpler way to write the code, either of which could help improve load times of software and inuse performance.
56
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
6.2 Malware
6.2.1 Understand the term malware. Identify different types of malware like: virus, worm,
Trojan, spyware.
Malware is short for “malicious software” - computer programs designed to infiltrate and damage
computers without the users consent. “Malware” is the general term covering all the different types
of threats to your computer safety such as viruses, spyware, worms, trojans, rootkits and so on
Virus
These are malicious programs that are intended to make sabotage.
They can destroy some or all your files stored on your computer or
even the computer itself. An anti-virus program is a must to be
installed on your computer system to be protected. It is important
that you update the antivirus on a regular basis. Computer Viruses
can easily copy themselves once downloaded on your computer;
sometimes they can also send themselves to recipients in your email
address book.
Worm
A worm is a virus that does not infect other programs. It makes copies of
itself, and infects additional computers (typically by making use of
network connections) but does not attach itself to additional programs;
however a worm might alter, install, or destroy files and programs
57
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
Trojan
Trojan is a malware attack that disguises itself as something innocent, such as a computer game, or a
YouTube search results page. An example of a devastating Trojan horse used an email with a link
that supposedly connected the reader to a video
of the Saddam Hussein hanging, but instead just
infected them with malware. Once installed on a
computer, the 'Saddam' Trojan horse then
downloaded and installed a key logger onto the
infected computer. This key logger was used to
record every keystroke by a computer‘s user, thus
stealing financial account information and
passwords.
Trojans are particularly dangerous because they
all appear so harmless on the surface. Often
Trojans are found on a particular website (usually adult, gaming, or gambling), hide in downloaded
free software, or, as in the "Saddam" Trojan horse, a person might be infected by clicking on a
link sent to them in an email.
Spyware
As the name implies, this is software that "spies" on your computer.
Nobody likes to be spied on, and your computer doesn't like it
either. Spyware can capture information like Web browsing habits,
e-mail messages, usernames and passwords, and credit card
information. If left unchecked, the software can transmit this data
to another person's computer over the Internet.
So how does spyware get on your computer? Just like viruses,
spyware can be installed when you open an e-mail attachment
containing the malicious software. It can also be installed when you
install another program that has a spyware installer attached to it.
6.2.2 Be aware how malware can infect a computer or device
Once a computer has been compromised by malware, cyber criminals can attempt to access your
personal information by logging your keystrokes or monitoring your computer’s activity. Your
computer could also be controlled to visit websites or perform other actions without your
knowledge. The effects of malware range from brief annoyance to computer crashes and identity
theft.
58
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
6.2.3 Use anti-virus software to scan a computer.
Antivirus software is a type of utility used for scanning and removing
viruses from your computer. While many types of antivirus (or "antivirus") programs exist, their primary purpose is to protect computers
from viruses and remove any viruses that are found.
An anti-virus program is a must to be installed on your computer system
to be protected. It is important that you update the antivirus on a
regular basis. Updating an antivirus program ensures that you have as
many samples of virus definitions in your system as possible. This
ensures that your computer is completely protected from latest virus
definitions, which are created every day.
6.3 Health and Green IT
6.3.1 Recognise ways to help ensure a user’s well-being while using a computer or device
like: take regular breaks, ensure appropriate lighting and posture.
If you do any physical activity for a long time without a break you risk straining or injuring yourself.
Using a keyboard or a mouse for a prolonged period can lead to the computer user’s equivalent of
tennis elbow. It can affect the fingers, hands, wrists, elbows, or even the back.
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
RSI stands for Repetitive Strain Injury. This mean damage to nerves, muscles and other soft body
tissues resulting from repeated physical movement. To avoid this one needs to take regular breaks
Eyesight
Extended periods of staring at PC screen can lead to fatigue and
ultimately to eyestrain. Make sure that your work area is adequately lit
and ventilated.
Posture
The hardware of your pc should be arranged in the best possible way in
order to provide comfort for the user.
The Desk
The desk should not be very high or very low. When you are using the keyboard, your arms should
rest horizontally.
The Chair
The height and seat depth of the chair should be adjustable.
59
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
The Screen
The top of the screen should rest at eye level. It is advisable that the user stays 40 – 60 cms away
from the screen.
The Keyboard
You may wish to use a wrist pad to relieve pressure on your wrists.
Other Factors
The area where you are using the computer should be adequately lit. Make sure that no light reflects
on the monitor. Take frequent breaks when using the computer. Also, make sure you never have any
trailing cables around your computers, as these can result in accidents.
6.3.2 Recognise computer and device energy saving practices: turning off, adjusting
automatic shutdown, backlight, and sleep mode settings.
People are becoming more aware and more concerned about how our modern lifestyle is having an
impact on the environment.
Here are some of the things that you, as a computer user, can do to help reduce the impact on our
environment:
Use a monitor that consumes less power whilst the computer is inactive.
If you are not going to be using your computer for a period of time, switch it off and don't
just leave it on standby.
Apply Automatic Shutdown to the Computer
60
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
6.3.3 Recognise that computers, devices, batteries, printer cartridges and paper should be
recycled.
We can also help to reduce the impact on our environment
by:
Recycle paper for printing. If you are printing out non
essential documents, print on the back of old paper. If the
paper can no longer be used put it into a recycling bin.
Don't print unless absolutely necessary. Read your documents
on the screen. Pass them onto others in an electronic format
Recycle your old printer ink cartridges and toners.
Recycle your computer - Just because you want a new
computer doesn't mean to say that your old one is worthless.
You can pass your computer onto someone else.
6.3.4 Identify some options available for enhancing accessibility like: voice recognition
software, screen reader, screen magnifier, on-screen keyboard, high contrast.
There are a range of options to improve computer accessibility.
These cover:
Voice recognition software
Screen reader software
Screen magnifier software
On-screen keyboard
High Contrast
Voice recognition software
Voice recognition software lets you talk to a computer and use simple
commands or sentences. These systems are easily confused by regional
accents and background noise, but are getting better each year as the
software improves.
Screen reader software
Screen reader software is designed for the visually impaired and tries to interpret the contents of
the computer screen and then communicate that information in different formats, such as speech
output, sound icons or as Braille output.
Screen magnifier software
This type of software magnifies the screen contents, making it
easier to read. Microsoft Windows has basic screen magnifier
software included.
61
©TCTC
ECDL NOTES – Computer Essentials
On-screen keyboard
An on-screen keyboard is a representation of the physical keyboard on the screen. It is designed
for use by individuals who are not able to use a physical keyboard. Window s has a basic onscreen keyboard option located within the Accessories group.
High Contrast
Make the screen easier to read with a High Contrast colour scheme. You can heighten screen
contrast with an alternative colour combination or change the font sizes for greater legibility.
62
©TCTC