CHEM 210 Chapter 1 Review Quiz
advertisement

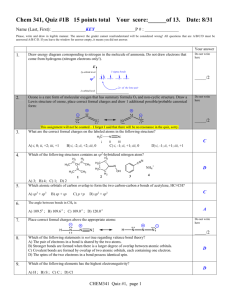
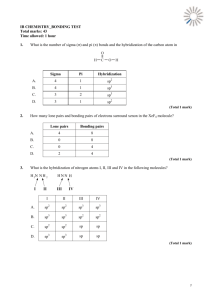
Quiz 1 Name __________________________ CHEM 210 1. What is the proper Lewis structure of HNO3? A) B) C) D) 2. How many lone pairs of electrons will be present in the following molecule? CH3–N=N=N A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 3. In the nitrate ion (NO3-), what is the charge on nitrogen? All electrons are shown. A) No charge B) - 1 C) + 1 D) + 2 4. The best Lewis structure for ethyne (C2H2; commonly called “acetylene”) has A) 2 single bonds, 1 B) 2 double bonds C) 2 single bonds, 1 D) 2 single bonds, 1 triple bond, and 1 and 2 lone pairs triple bond, and no double bond, and 2 lone pair lone pairs lone pairs 5. What is the formal charge (FC) of each atom in the following molecule? NH4+ A) FC Hydrogens: 0 B) FC Hydrogens: 0 C) FC Hydrogens: 0 D) FC Hydrogens: 0 FC Nitrogen: 0 FC Nitrogen: -1 FC Nitrogen: +2 FC Nitrogen: +1 6. What is the formal charge (FC) of each atom in the following molecule? BH4B) FC Boron: 0 C) FC Boron: -2 D) FC Boron: -1 A) FC Boron: 0 FC Hydrogen1: +1 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen2: -1 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 FC Hydrogen4: 0 FC Hydrogen4: 0 FC Hydrogen4: 0 FC Hydrogen4: 0 7. What is the formal charge (FC) of each atom in the following molecule? A) FC Carbon: +1 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 B) FC Carbon: 0 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 C) FC Carbon: -2 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 D) FC Carbon: -1 FC Hydrogen1: 0 FC Hydrogen2: 0 FC Hydrogen3: 0 8. How many total resonance structures can be drawn for the following anion (include those without separation of charge)? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 9. How many resonance structures can be drawn for the following molecule? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 10. How many other major contributing resonance structures are possible for the following heterocycle? A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 11. How many energetically equivalent resonance structures exist for the oxalate dianion? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 12. What is the electron configuration for oxygen? A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 B) 1s2 2s2 2p5 C) 1s2 2s2 2p4 D) 4 D) 1s2 2s2 2p3 13. Which of the following compounds does NOT have an octet around the central atom? A) NH3 B) BH3 C) H3O+ D) NH4+ 14. Which of the following statements about an sp hybridized carbon is FALSE? A) It is divalent B) It forms bonds C) It has two p D) It always forms that are linear. orbitals triple bonds to carbon. 15. A p orbital has what shape? A) an oval B) a sphere C) a wedge of pie D) a dumbbell 16. The hybridization of the central carbon in and the bond angle CCN are 2 A) sp , 180°. B) sp, 180°. C) sp2, 120°. D) sp3, 109°. 17. What are the hybridizations of carbons 1 and 2 respectively in the following structure? A) sp3 and sp2 B) sp2 and sp3 C) sp3 and sp D) sp2 and sp2 18. What are the hybridizations of atoms 1 and 2 respectively in the following structure? A) sp3 and sp2 B) ) sp2 and sp3 C) sp3 and sp D) sp2 and sp2 19. Identify the orbital hybridization at the two indicated carbons in the molecule below. A) C1: sp; C2: sp B) C1: sp2; C2: sp2 C) C1: sp; C2: sp2 D) C1: sp2; C2: sp 20. The geometric shape of acetone, (CH3)2CO, is best described as A) linear. B) trigonal planar C) bent. 21. The correct molecular geometry around oxygen in CH3OCH3 is A) linear. B) bent. C) tetrahedral. D) trigonal planar 22. Which molecule has the largest dipole moment? C) H2S A) HCl B) CCl4 D) CO2 23. Which molecule has the smallest dipole moment? A) CO2 B) CHCl3 C) H2O D) NH3 D) tetrahedral 24. Consider the structure with the electron-pushing arrow: Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The bond B) The products will between the tertiary be a carbon cation carbon and bromine and bromine anion is breaking C) This process is called homolytic cleavage. D) The C–Br bonding electrons become a lone pair on the bromine 25. What is the product of the curved arrow mechanism shown below? A) B) No reaction C) D) 26. In this reaction, HNO3 + H2SO4 → HSO4– + H2NO3+ a curved arrow should point A) from HNO3 to B) from H2SO4 to C) from HSO4– to D) from H2NO3+ to H2SO4 HNO3 H2NO3+. HSO4–. 27. For the protonation of acetone, the correct curved arrow mechanism is B) C) D) A) KEY: 1. A. 2. D. 3. C. 4. C. 5. D. 6. D. 7. D. 8. D. 9. C. 10. B. 11. D. 12. C. 13. B. 14. D. 15. D. 16. B. 17. A. 18. D. 19. D. 20. B. 21. B. 22. A. 23. A. 24. C. 25. D. 26. A. 27. D.