Chapter 18 Study Guide Questions #1 1. Who coined the term
advertisement

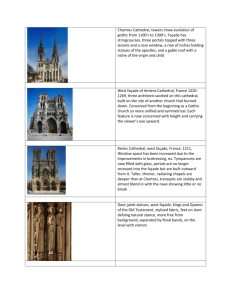
Chapter 18 Study Guide Questions #1 1. Who coined the term Gothic and how did he mean for the term to be used? 2. From what date do art historians date the birth of Gothic style? Aside from that, why is Gothic not a cohesive moment throughout Europe? 3. What sets the Gothic age apart as a time of profound change? 4. Who was Abbot Suger and what role did he play in the beginnings of Gothic architecture (see insert page 481)? 5. Explain the basics of a Gothic rib vault (see insert page 482). What is its major advantage over the Romanesque vault? 6. What does lux nova mean and how is it seen in the new Gothic style cathedrals? 7. From where does the Royal Portal at Chartres gain its name? Why is this part of the cathedral different from the majority of the rest of Chartres? 8. How are the 3 doorways of the Royal Portal united ichnographically and visually? 9. Explain the prominence of Mary in the Royal Portal. 10. How has the interpretation of the Second Coming changed from the Romanesque period? 11. How is the Old and New Testament mixed on the Royal Portal of Chartres? 12. How are the column statues both stylized and naturalistic? 13. What elements at Laon Cathedral are of Romanesque design? In what ways do the designers purposely move away from Romanesque design? 14. Explain the major differences you see in the elevation of an Early Gothic cathedral such as Laon and a High Gothic cathedral such as Amiens. 15. Notre-Dame in Paris has the same 4-story elevation as Laon with a key difference. Explain that difference. 16. Explain the basics of Scholasticism and the work of Peter Abelard and Thomas Aquinas (see insert page 487) 17. How do the flying buttresses work together with the ribbed vaults at Notre-Dame? 18. Which holy relic is said to be held at Chartres cathedral? 19. Which part of the original cathedral was the only feature to survive the fire in 1194 and what did the post-1194 builders do with this feature? 20. Looking at the new plan of Chartres cathedral, what are the essential changes in a High Gothic building from an Early Gothic building? Which essential High Gothic feature was included in the design of Chartres for the first time in history? 21. What changed in regards to the elevation of Chartres? What accounts for the relative darkness of the Chartres nave despite the amount of glass? 22. Compare and contrast the Virgin and Child and angels from Notre Dame de la Bette Verriere at Chartres with the Theotokos and Child from the Hagia Sophia (page 342). 23. Explain the numerical symbolism included on the Rose window at Chartres. 24. How are the jamb statues from the Porch of the Confessors on the south transept of Chartres so different from the Old Testament Kings and Queens from the west façade? 25. What evidence of a “Classical Revolution” do you see in the statue of Saint Theodore from the Porch of the Martyrs on the south transept of Chartres cathedral? 26. How does the design of Amiens draw from but also improved upon the design of Chartres? 27. What are the distinctive features of the west façade of Amiens cathedral? 28. How does the Beau Dieu compare to both previous portal statues (the Old Testament Kings and Queens, and the statues from the Porch of the Confessors) as well as previous depictions of Christ (Christ as the Good Shepherd and the Pantokrator)? 29. What is the major departure on the west façade of Reims cathedral? 30. How was the “Classical Revolution” continued with the Visitation jamb statues of Reims cathedral? 31. For what purpose was Sainte-Chapelle built? Explain why the style associated with Saint Louis is considered “radiant?” 32. Explain the significance of Saint Louis in French culture and history (see insert page 498). 33. How is Virgin of Paris “elegant” in her proportions? Compare Virgin of Paris with Hermes and Dionysus by Praxiteles (page 146).