GRADE 9 BIOLOGY– Level Descriptors B1 Influences on life
advertisement

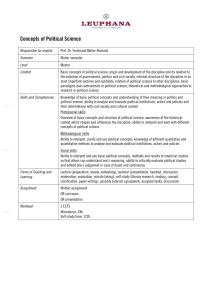
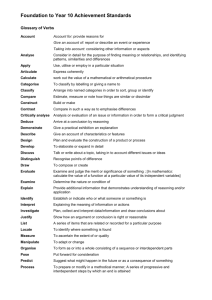
GRADE 9 BIOLOGY– Level Descriptors B1 Influences on life Topic 1 - Classification, variation &inheritance A* (90- 100) A ( 80-89) B (70-79) C (60-69) D (50-59) Explain how scientists place vertebrates into five groups based on oxygen absorption method, reproduction, thermoregulation. Compare the characteristics of five kingdom& chordates. Describe the main characteristics of the five kingdom& chordates . Realize why scientists do not classify virus into any of the five kingdom Identify the hierarchy of classification, five kingdoms of life &five chordate groups . Explain why binomial classification is needed to identify study and conserve species. Describe how accurate classification may be complicated eg: hybridization in ducks and ring species. Discuss why the definition for species as organism for producing fertile offspring is limited. Demonstrate an understanding of the problems in assigning organisms into a specific group eg: duckbilled platypus, Axolotl. Define the term hybrid and ring species and give examples of each. Explain how organisms are adapted to survive extreme environment- deep hydrothermal vents and polar regions. Describe the adaptive features of organisms surviving in extreme environment. Discuss the key factors contributing to evolution by natural selection. Construct and use keys to identify organisms. Know that naming of an organism binomially includes genus and species name. Interpret data on types of variation, bar chart & normal distribution curve. Describe the causes of variation- genetic & environmental. Calculation of mean height/weight and construction of graphs bar chart/histogram/ normal distribution curve. Define continuous & discontinuous variation. Identify types of variation in organisms with examples. Explain new evidence from DNA research and emergence of resistant organisms to support Darwins theory. Evaluate the role of scientific community in validating new evidence – use of scientific journals peer review process& scientific conferences. Describe how speciation occurs as a result of geographical isolation. Differentiate the terms gene and alleles. Define the terms genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant & recessive Analyse & interpret patterns of monohybrid inheritance using genetic diagram, Punnetsquare and family pedigrees. Describe the symptoms of genetic disorderscystic fibrosis and sickle cell anaemia. Calculate outcomes of monohybrid cross using probabilities, percentages& ratios. Identify the causes Define a genetic of genetic diseases disorder/disease with – cystic fibrosis and examples. sickle cell anaemia. Give examples of Suggest the cure genetic disorders. for cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anaemia. Evaluate the outcomes of pedigree analysis for genetic diseases. Identify genes found on chromosomes in the nucleus. Topic 2 - Responses to a changing environment A* (90- 100) A ( 80-89) B (70-79) C (60-69) D (50-59) Interpret negative feedback mechanism involved in thermoregulation. Explain how thermoregulation takes place on a hot day and cold day. Describe the role of the various parts of the skin in thermoregulatio n-hair erector muscle, sweat glands and blood capillaries. Differentiate thermoregulation and osmoregulation. Define homeostasis. Differentiate type1 diabetes with type2 diabetes. Suggest the role of various endocrine organs of human bodypituitary , pancreas, thyroid, adrenal, ovary and testis. Explain how blood glucose level is regulated by insulin and glucagon by negative feedback mechanism. Describe how diet, physicl activity and insulin injection control diabetes. Label the various parts of human skin. Discuss the importance of homeostasis in organisms. Know that hormones are produced by endocrine organs and transported to target organs by blood. Evaluate correlation between obesity and type 2 diabetes. Use data to analyze the relationship between obesity and type 2 diabetes. Explain the commercial uses of plant hormonesweedkiller, rooting powder, seedless fruits and ethene . Explain the structure of a typical neuron in conducting nerve impulse- cyton, dendrite, axon and nerve ending. Analyse & interpret data on plant hormone experiments. Analyse &interpret data related to human responses to external stimulus. Describe the role of auxins in phototropism and geotropism Calculate BMI and categorize people as underweight, normal, overweight and obese. Suggest the Plan investigations to advantages prove tropism tropism in plants. shown by shoot tips and roots. Identify the role of various plant hormones- auxin, cytokinin, ethene and gibberellin. Describe how stimulation of receptors sends impulse to CNS by nerve impulses. Compare hormone action with nervous coordination in humans. Suggest the role of receptors in coordination. Know that CNS consists of brain and spinal cord. Describe how impulses are transmitted in a reflex arc in sequence to bring about reflex action Differentiate sensory, motor and relay neuron in structure and function. Draw and label a simple reflex arc. Suggest importance of reflex action. Compare reflex action to involuntary action. Define synapse and reflex arc. Recognize types of tropisms in plants with examples. Give examples of reflexes. Topic 3 - Problems of & solutions to a changing environment A* (90- 100) A ( 80-89) B (70-79) C (60-69) D (50-59) Analyse and interpret data linked with use of drugs. Evaluate data relating to correlation of smoking and negative effects on health. Describe the short term and long term effects of stimulants and depressants. Suggest the general effects of painkillers, stimulants, depressants and hallucinogens. Realize that a drug leads to tolerance, addiction and withdrawal symptoms. Define drug. Discuss the ethics of organ transplant. Give examples of legal and illegal drugs. Evaluate that misuse of antibiotics can lead to development of resistance in organisms. Analyse and interpret data related to energy transfer, food chain , food web and ecological pyramids. Analyse , interpret and evaluate data on global population change . Explain various stages of carbon cycle - feeding, absorption, decomposition, sedimentation, fossilization and weathering. Evaluate how recycling can reduce the demand for resources and problems of waste disposal Explain how pathogens can be prevented by physical and chemical barriers of human body. Plan investigations to prove antimicrobial effects of antiseptics, antibiotics and plant extracts. Describe how some energy is transferred as less useful forms at each trophic level that limits the length of food chains. Describe how pathogens are spread through air, food, water, by vectors, body fluids and contact. Describe the role of antiseptics and antibiotics in controlling infection Identify the antimicrobial effect of plant extracts eg. mint leaves and garlic. Define pathogens. Differentiate pyramid of numbers, biomass and energy. Calculate energy transfer between trophic levels. Draw and label simple food chains & ecological pyramids. Know that interdependence is a dynamic relationship between living organisms . Define the term food chain, food web & biomass. Explain how survival of organisms involve parasitism and mutualism . Give examples of pathogens and diseases in humans. Describe the role of Significance of various parasites parasitism and and mutualists. mutualism in maintaining living interactions. Describe the role of Draw and label the Differentiate various bacteria various components natural and involved in of carbon and artificial nitrogen cycle. nitrogen cycle. recycling. . Define parasites and mutualists. Give examples of parasites and mutualists. Describe how eutrophication happens in a polluted river. Analyse and interpret data related to nonliving indicators of pollution (global temperature, rainfall and incidence of skin cancer). Define indicator species. Suggest the causes of air and water pollution and problems linked with eutrophication in an ecosystem. Plan investigations to find the effects of pollutants on germination and plant growth. Understand the use of indicator species in determining level of pollution Define biogeo chemical cycle. Suggest the importance of carbon and nitrogen cycle. Give examples of pollution indicators.