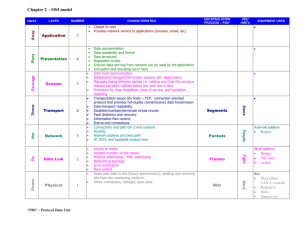
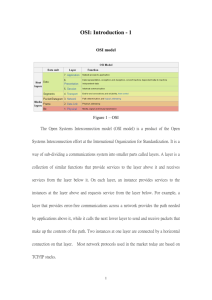
OSI - Department of Computer Engineering
advertisement
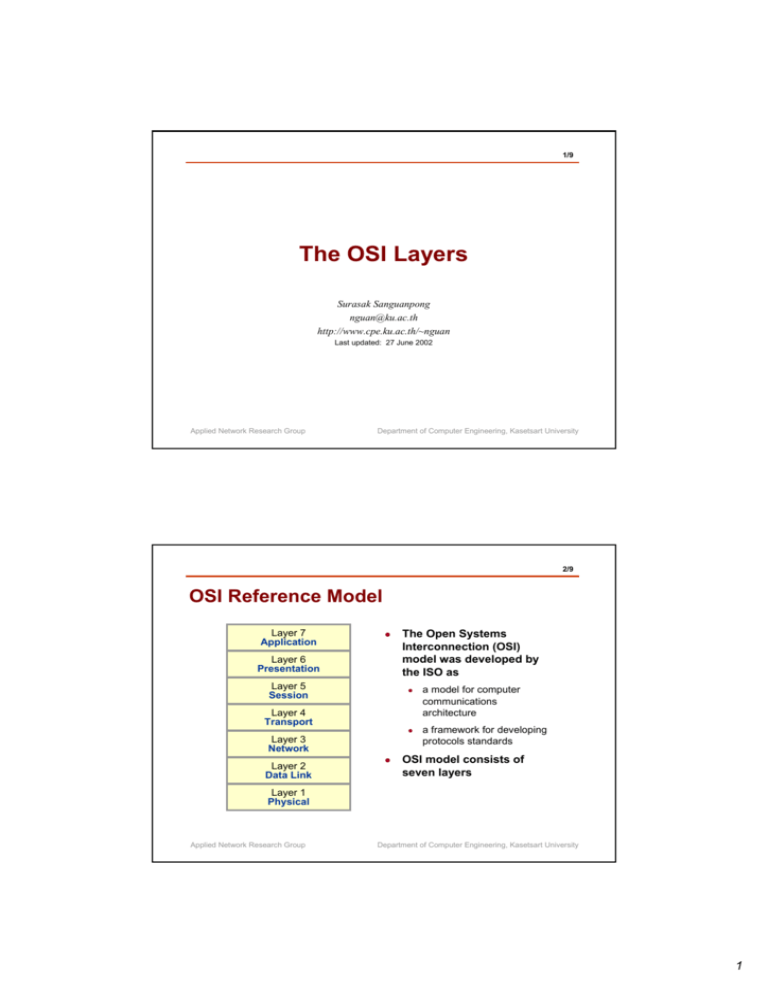
1/9 The OSI Layers Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 27 June 2002 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 2/9 OSI Reference Model Layer 7 Application z Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model was developed by the ISO as z Layer 4 Transport z Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Data Link z a model for computer communications architecture a framework for developing protocols standards OSI model consists of seven layers Layer 1 Physical Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 1 3/9 Layering Application Programs Layer 7 Application User-oriented functions Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session Layer 4 Transport Communications functions Applied Network Research Group Layer 3 Network Packet Layer 2 Data Link Frame Layer 1 Physical Bit Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 4/9 Why Seven Layers? Applications Applications Applications Physical Transport Presentation Need at least Physical and Application layers Network Session Datalink Transport Physical Applications Datalink Physical Datalink concerns all the link independent details for different link technology Applied Network Research Group Both end-to-end and hop-by-hop actions are required Transport layer handles end-to-end functions such as flow control Network layer handles routing in hop-by hop fashion Network Datalink Physical Separate some application functions to Presentation and Session Layers Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 2 5/9 Layer Boundary Service #M Service #3 Service #2 Layer N Service #1 Service Access Point (SAP) z Each layer has its own functionality z When a layer needs functionality of another layer, it must issue a request. z At each layer boundary, there is at least one point of services called SAP Layer N-1 = Service Access Point Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 6/9 Virtual Communications Applications Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Application protocol Presentation protocol Session protocol Transport protocol Network Access Protocol Datalink protocol Physical protocol Applications Presentation Session Transport Network Datalink Physical Physical Media Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 3 7/9 Protocol Data Unit protocol data unit (PDU) = combination of data from the next higher and control information Data Applications Application PDU Presentation Presentation PDU Session Session PDU Transport PDU Transport Network PDU Network Datalink Datalink PDU Physical AH Data Encapsulation PH AH Data SH PH AH Data TH SH PH AH Data NH TH SH PH AH Data DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT Additional of control information to data is referred to encapsulation Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 8/9 Decapsulation Data Decapsulation In each layer, corresponding header/trailer has been removed Applied Network Research Group AH Data Applications PH AH Data Presentation SH PH AH Data TH SH PH AH Data NH TH SH PH AH Data Session Transport Network DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT Datalink DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT Physical Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 4 9/9 OSI and TCP/IP OSI TCP/IP Application Presentation Application Session Transport Transport Network Internet Data Link Network Access Physical Physical Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 5