MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 PSYCHOLOGY WEEK 11
advertisement
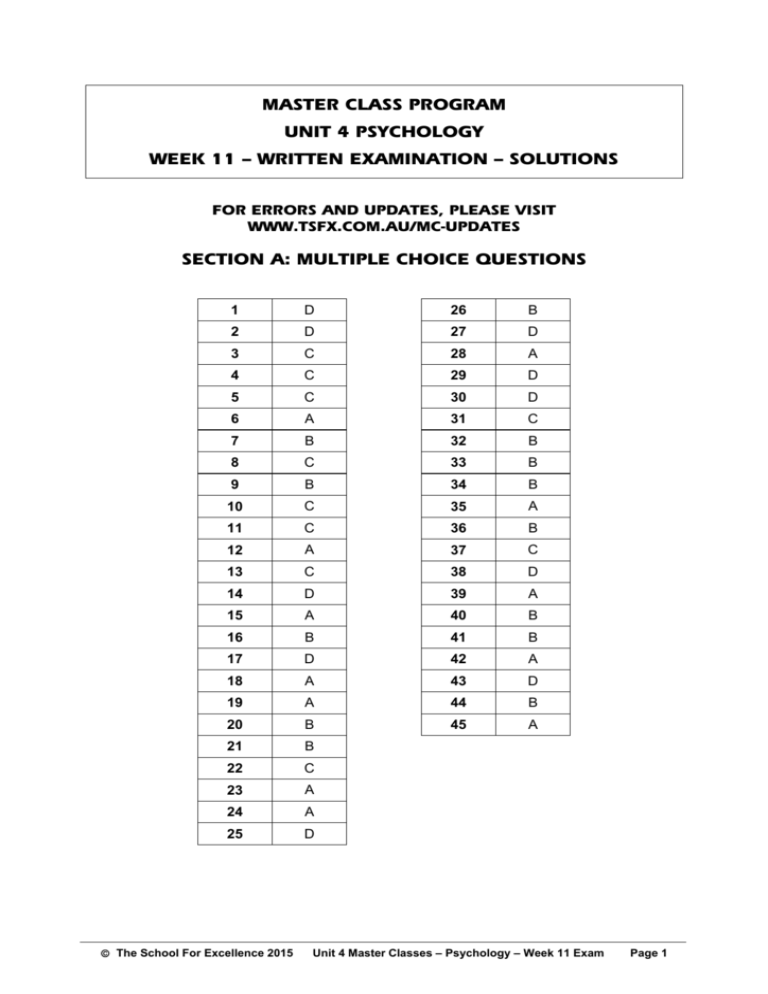
MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 PSYCHOLOGY WEEK 11 — WRITTEN EXAMINATION — SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1 D 26 B 2 D 27 D 3 C 28 A 4 C 29 D 5 C 30 D 6 A 31 C 7 B 32 B 8 C 33 B 9 B 34 B 10 C 35 A 11 C 36 B 12 A 37 C 13 C 38 D 14 D 39 A 15 A 40 B 16 B 41 B 17 D 42 A 18 A 43 D 19 A 44 B 20 B 45 A 21 B 22 C 23 A 24 A 25 D The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 1 SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER SECTION ANSWERS QUESTION 1 A fixed action pattern is a complex sequence of behaviour that occurs when appropriately stimulated, that is identical amongst a species or gender-specific amongst a species (1 mark) e.g. male weaver birds tying a grass knot to hold next together to attract their mate (1 mark) QUESTION 2 Unconditioned stimulus Unconditioned response Conditioned stimulus Conditioned response being stung by ants (ant sting) nauseous vomiting due to ant sting sight of an ant nauseous response due to sight of ant (4 marks: all 4 correct = 1 mark for each correct response) QUESTION 3 Discriminative stimulus: Shopping at Coles or Woolworths (1 mark) Behaviour: Spend over $30 on groceries (1 mark) Consequence: Receive a 4c discount voucher (1 mark) QUESTION 4 ATTENTION: Jenny must ensure her daughter Josephine is paying attention to and concentrating on her demonstrating the ironing (which Josephine is likely to do because she looks up to her mother) (1 mark) RETENTION: Josephine must store the demonstration from Jenny in her memory as a mental representation of the behaviour so that she can access the information later. (1 mark) Students must name the stage and apply it to the scenario of Jenny ironing. QUESTION 5 (a) Differentiate between synaptogenesis and synaptive pruning. Synaptic pruning is the ridding/elimination of excessive or unused synapses (1 mark) whereas synaptogenesis is the formation/creation of new synaptic connections between neurons (1 mark) (b) Explain the processes of adaptive plasticity in development. 1 mark for any below. • • • Brain changes and develops as a result of new experiences or to compensate for lost functioning Enables older brains to change by experience or learning Diminishes with age The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 2 QUESTION 6 (a) Both Punishment and Response Cost are acceptable answer for one mark. (b) Any two of the following or other appropriate but only one mark if both reasons imply ‘attention seeking’: • • • • • • • Not harsh/severe enough to weaken the response No alternative (positive) behaviours provided ‘Attention’ from the punisher may positively reinforce/reward the bad behaviour May lead to fear or dislike of the punisher May lead to ‘avoidance of getting caught’ behaviour Not administered soon enough after the response May lead to more aggressive behaviour QUESTION 7 Extinction is the gradual decrease in the rate of a conditioned response. This occurs when the conditioned stimulus is presented alone without the unconditioned stimulus. E.g. If the bell (CS) in Pavlov’s experiment is presented alone without food (UCS) for a number of trials, after a while the bell will not cause the dog to salivate significantly (CR). Spontaneous recovery occurs following extinction of a condition response and after a rest period (24hrs) when the Conditioned Stimulus is again presented alone to elicit the Conditioned Response (e.g. dogs in Pavlov’s study will show significant salivation (that had been previously extinguished) to the bell when it is presented alone, following a rest period). E.g. 1. 2. 3. Extinction takes place (dog no longer salivates to bell or CS) Rest period where bell (CS) is not presented Bell (CS) again presented and dog again salivates (CR) QUESTION 8 (3 marks) (a) Dimensional Advantages (1 of the following): • • • Takes into account the severity of symptoms Takes into account individual uniqueness/differences in the diagnosis Likely to result in less stigma than a categorical approach because a specific label is not attached. (Note: ‘Less stigma’ not ‘no stigma’.) Dimensional Disadvantages (1 of the following): • • • (b) Is a more subjective approach than categorical Lower inter-rater reliability as grading symptoms can be subjective (Note: Lower inter-rater reliability than the categorical. The categorical is also sometimes inconsistent) DSM-IV-TR or DSM-V or ICD-10 (1 mark) The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 3 QUESTION 9 (4 marks) (a) Any two of: • • • • HPA axis immune system cardiovascular system sympathetic nervous system (2 marks) (b) The process of achieving stability through physiological or behavioural change which enables the body to meet internal and external demands. (1 mark) (c) Allostatic load refers to the cumulative cost to the body of allostasis. This can result in decreased efficiency in the initiation and termination of the allostatic response potentially influencing a variety of physical disorders including, e.g. cardiovascular diseases and obesity, or mental disorders, e.g. depression. QUESTION 10 (4 marks) (a) Any one of: • • • • It considers cognitive approaches (unlike the fight-flight response which focuses on the involuntary physiological responses). It is a dynamic model (rather than a static model) which examines the individual’s interaction with their environment in terms of their appraisal of a situation and reappraisal, and thus considers their ability to adjust their responses. It caters for individual differences to be focusing on variations in how stressors are perceived and dealt with. It identifies different methods for managing psychological responses to stressors. 1 mark for any one of the above points. (1 mark) (b) Primary appraisal stage: Julia will recognise, evaluate and judge the situation. She will most likely assess the situation as stressful. (1 mark) Secondary appraisal stage: Julia will consider the options and resources available to deal with the stressor. Julia may ask her teacher to complete a re-sit test, study harder for next test – get a tutor (any possible problem solving technique) or emotion –focused – using her emotions such as denial to deal with the situation. (1 mark) (c) Coping mechanisms are found in the secondary appraisal of the Transactional model of Stress and Coping (1 mark) The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 4 QUESTION 11 (4 marks) (a) Any two of: • • • • • • (b) Exercise promotes psychological well-being via production of beta-endorphins. It enhances psychological health. It diverts attention away from stressors. It uses up the stress hormones produced by the sympathetic nervous system and HPA axis when stressed. It reduces muscle tension. Enhances social interaction (2 marks) Biofeedback is a technique used to receive information (feedback) about the state of a bodily processes to help detect higher physiological responses relating to stress. (1) E.g. a heart rate monitor could be used and alert a person when HR is high so that the person can actively do something to reduce it like lie down and meditate. (1) or any relevant example. (2 marks) SECTION C: EXTENDED ANSWER QUESTION SECTION C: EXTENDED RESPONSE This section was marked on the basis of a rubric type score with responses marked unique between students due to the open-endedness of relevant responses. At VCAA we mark to a rubric such as: Criteria 1 Criteria 2 Criteria 3 Criteria 4 Criteria 5 NS: 0 VL: 1 – 2 (10 mark) 1 – 3 (15 mark) L: 3 – 4 (10 mark) 4 – 6 (15 mark) M: 5 – 6 (10 mark) 7 – 9 (15 mark) H: 7 – 8 (10 mark) 10 – 12 (15 mark) VH: 9 – 10 (10 mark) 13 – 15 (15 mark) Identify and describe the key terms/theories/issues Explain the relevant terms/theories/issues & make connections between psychological concepts & data & research Use appropriate examples and evidence to support the extended response Interpret and analyse the issues/data/information Evaluate issues/data/information to draw appropriate conclusions and generalisations No attempt or incorrect information for Criteria 1 Criteria 1 addressed only Criteria 1 + 2 addressed Criteria 1 + 2 + 3 addressed Criteria 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 addressed All criteria addressed The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 5 An example of a very high response could be: Introduction: Background info looking at brain plasticity of young children (vs adolescents, adults). Developmental plasticity discussion of synaptogenesis in early childhood vs synaptic pruning in older age…etc. Aim: To determine whether the optimum age of learning a second language is during early childhood. Research hypothesis: That young children will learn to speak Italian significantly faster than adults. Operationalised IV: Age of learning operationalised as young children below the age of 6 or adults over the age of 25. Operationalised DV: Language comprehension, operationalised as score on verbal conversation test of common Italian words and phrases. Participants: 20 children under 6 and 20 adults over the age of 25 were conveniently sampled using advertisement in local paper and asking for volunteers. An independent groups design will be applied, whereby the children will be taught verbal Italian words and phrases for 2 months, and the adults will be taught in the same way. Probably cannot match participants up due to differing ages and repeated measures would not work either. Limitations: Sampling size and technique was biased. Could potentially use random sampling (equal chance of selection from population of research interest) This means all children under 6 and all adults over 25 from Melbourne metropolitan region should have equal chance of selection. Bigger sample – to represent population of research interest. Extraneous Variables: Anything relevant such as: learning ability, teaching methods, teacher characteristics, time of day of learning and testing, past experience of different languages (particularly in the adults), etc. Improvements: More participants, better sampling technique, use of imaging techniques and any improvements linked to student’s limitations or extraneous variables mentioned would be good. The School For Excellence 2015 Unit 4 Master Classes – Psychology – Week 11 Exam Page 6







