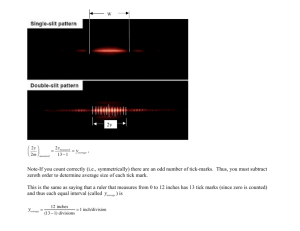
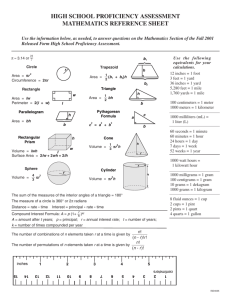
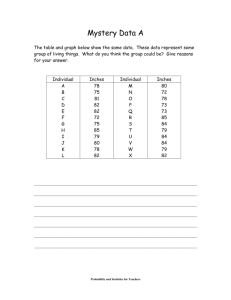
Practical Data for Metallurgists
advertisement

For more information on Timken® steel and other value-added services or products, contact your local Timken Alloy Steel representative. Call 1-866-284-6536 (U.S.A.), +44-1530-512680 (International), fax 330-471-7032 (U.S.A.), or visit our Web site at www.timken.com/products/alloysteel. Practical Data for Metallurgists Practical Data for Metallurgists Engineered Steel Solutions for: Aerospace • Automotive • Bearings • Defense • Distribution • Energy • Industrial www.timken.com Timken ® is the registered trademark of The Timken Company. © 2009 The Timken Company Printed in U.S.A. 2.5M 03-09-09 Order No. 4023 Practical Data for Metallurgists Sixteenth Edition Welcome to the Practical Data for Metallurgists, the guide that technical experts, operations managers and engineering personnel have turned to for more than 50 years for the latest metallurgical information. Our guide—which conforms with information published by AISI and SAE—includes an updated listing of standard steels and their chemical compositions, hardening abilities and tolerances. At Timken, we use a combination of materials science, application engineering and processing capabilities to add value and improve the performance of our customers. Providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your alloy steel needs is just one way we help you reach your fullest potential. 1 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Steel Chemistries Chemical Compositions, etc. Page Number 4-35 Miscellaneous Steel Properties Relative Tool Steel Properties Hardenability Band Data Restricted Hardenability Band Data Jominy Correlation with Round Bars Combined Hardenability Charts Martensite Percent vs. Carbon Content and Hardness Relationship of Fatigue Strength to Tensile Strength Carburizing Rates of Carbon and Alloy Steels Critical Transformation Temperatures and Ms/Mf Points Hot Working Temperatures 36-39 40-50 51-53 54-57 58-71 72 73 74-78 79-81 82-83 Tubing General Tolerances Length Tolerances Straightness Tolerances Seamless Steel Tubing Shapes Tube Size Calculations OD Cleanups Formulas for Calculating Surface Cleanup Formulas for Calculating Camber (Straightness) Cleanup 84-88 89 90-91 92-93 94-97 98 99 99 Bar General Tolerances Straightness Tolerances Weight Table - Rounds and Squares Reduction Ratios for Round and Square Bars 100 101 102-105 106 Miscellaneous Information Iron Carbon Phase Diagram Statistical Process Control (SPC) Information Handy Physical Constants Engineering Conversion Factors Metric-English Stress Conversion Tables Work-Energy Conversion Tables Decimal Equivalent Chart Temperature Conversion Tables Hardness Conversion Tables Useful Equations for Hardenable Alloy Steels Glossary of Metallurgical Terms 107 108-109 110 111-113 114 115 116-117 118-119 120-121 122 123-128 3 STANDARD CARBON STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn P Max S Max 1005 1006 1008 .06 max .08 max .10 max .35 max .25/.40 .30/.50 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 1010 1011 1012 1013 1015 1016 1017 1018 .08/.13 .08/.14 .10/.15 .11/.16 .13/.18 .13/.18 .15/.20 .15/.20 .30/.60 .60/.90 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .60/.90 .30/.60 .60/.90 .040 .040 .040 .030 .040 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 1020 1021 1022 1023 1025 1026 1029 .18/.23 .18/.23 .18/.23 .20/.25 .22/.28 .22/.28 .25/.31 .30/.60 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .30/.60 .30/.60 .60/.90 .60/.90 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 1030 1035 1038 1039 .28/.34 .32/.38 .35/.42 .37/.44 .60/.90 .60/.90 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .040 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 1040 1042 1043 1044 1045 1046 1049 .37/.44 .40/.47 .40/.47 .43/.50 .43/.50 .43/.50 .46/.53 .60/.90 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .30/.60 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .60/.90 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 1050 1053 1055 .48/.55 .48/.55 .50/.60 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .60/.90 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 1060 1065 .55/.65 .60/.70 .60/.90 .60/.90 .040 .040 .050 .050 1070 1074 1078 .65/.75 .70/.80 .72/.85 .60/.90 .50/.80 .30/.60 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 1080 1086 .75/.88 .80/.93 .60/.90 .30/.50 .040 .040 .050 .050 1090 1095 .85/.98 .90/1.03 .60/.90 .30/.50 .040 .040 .050 .050 4 FREE CUTTING RESULPHURIZED STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn P Max S 1117 1118 1126 1132 1137 1138 1140 1141 1144 1146 1151 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .24/.33 .08/.13 .08/.13 .14/.20 .14/.20 .23/.29 .27/.34 .32/.39 .34/.40 .37/.44 .37/.45 .40/.48 .42/.49 .48/.55 1.00/1.30 1.30/1.60 .70/1.00 1.35/1.65 1.35/1.65 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 1.35/1.65 1.35/1.65 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 FREE CUTTING REPHOSPHORIZED AND RESULPHURIZED STEEL Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn P S 1212 1213 1215 .13 max .13 max .09 max .70/1.00 .70/1.00 .75/1.05 .07/.12 .07/.12 .04/.09 .16/.23 .24/.33 .26/.35 NOTE: 12XX grades are customarily furnished without specified silicon content because of adverse effect on machinability. HIGH MANGANESE CARBON STEEL Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn P Max S Max 1522 1524 1526 1527 1541 1547 1548 1552 1566 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .18/.24 .19/.25 .22/.29 .22/.29 .36/.44 .43/.51 .44/.52 .47/.55 .60/.71 1.10/1.40 1.35/1.65 1.10/1.40 1.20/1.50 1.35/1.65 1.35/1.65 1.10/1.40 1.20/1.50 .85/1.15 5 STANDARD ALLOY STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn Cr 1330 1335 1340 .28/.33 .33/.38 .38/.43 1.60/1.80 1.60/1.90 1.60/1.90 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. ............. ............. ............. 4023 4027 4037 4047 .20/.25 .25/.30 .35/.40 .45/.50 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 ............. ............. ............. ............. 4118 4120a 4130 4137 4140 4142 4145 4150 .18/.23 .18/.23 .28/.33 .35/.40 .38/.43 .40/.45 .43/.48 .48/.53 .70/.90 .90/1.20 .40/.60 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.60 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .08/.15 .13/.20 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 4320 4340 E4340 .17/.22 .38/.43 .38/.43 .45/ .65 .60/.80 .65/.85 .40/.60 .70/.90 .70/.90 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 ............. ............. ............. 4620 .17/.22 .45/.65 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 ............. 4820 3.25/3.75 .20/.30 Ni Mo Other .18/.23 .50/.70 .............. 50B46§ .44/.49 .75/1.00 .20/.35 .............. .............. ............. 5120 5130 5132 5140 5150 5160 51B60§ .70/.90 .70/.90 .60/.80 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .80/1.10 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 51100 .98/1.10 .25/.45 .90/1.15 ............. ............ E52100 .98/1.10 .25/.45 1.30/1.60 ............. ............ 52100 .93/1.05 .25/.45 1.35/1.60 ............. ............ ............. P 5 .025 S 5 .025 P 5 .025 S 5 .015 .17/.22 .28/.33 .30/.35 .38/.43 .48/.53 .56/.64 .56/.64 6 ............. STANDARD ALLOY STEELS – continued SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo 6150 .48/.53 .70/.90 .80/1.10 ............. ............ Other V .15 min 8615 8617 8620 8622 8630 8640 8645 .13/.18 .15/.20 .18/.23 .20/.25 .28/.33 .38/.43 .43/.48 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. 8720 .18/.23 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 ............. 8822 .20/.25 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .30/.40 ............. Si 9259 .56/.64 .75/1.00 .45/.65 ............. ............. .70/1.10 9260 .56/.64 .75/1.00 ............. ............. ............. 1.80/2.20 § B 5 .0005/.003 a Formerly PS 15 Unless specified: Si 5 .15/.35, P 5 .035 max (SAE J1268), S 5 .040 max, Ni 5 .25 max, Cr 5 .20 max, Mo 5 .06 max These standard grades can have modifications in chemistry when agreed upon by user and supplier. 7 PS GRADES (Formerly EX Grades) Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits PS No. C 10 .19/.24 16 .20/.25 17 .23/.28 18 .25/.30 19 .18/.23 20 .13/.18 21 .15/.20 31 .15/.20 32 .18/.23 33 .17/.24 34 .28/.33 36 .38/.43 38 .43/.48 39 .48/.53 40 .51/.59 54 .19/.25 55 .15/.20 56 .08/.13 57† .08 max 58 .16/.21 59 .18/.23 61 .23/.28 63 .31/.38 64 .16/.21 65 .21/.26 66 .16/.21 67 .42/.49 Mn Cr .95/1.25 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .70/.90 .70/.90 .85/1.25 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .90/1.20 .70/1.05 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 1.25 max 1.00/1.30 1.00/1.30 1.00/1.30 .75/1.10 1.00/1.30 1.00/1.30 .40/.70 .80/1.20 .25/.40 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .45/.65 .45/.65 .20 min .40/.60 .45/.65 .45/.65 .45/.65 .45/.65 .40/.70 .45/.65 .45/.65 17.00/19.00 .45/.65 .70/.90 .70/.90 .45/.65 .70/.90 .70/.90 .45/.75 .85/ 1.20 Ni Unless Specified: Si 5 .15/.35, P 5 .035 max, S 5 .040 max † P 5 .040 max, S 5 .15/.35, Si 5 1.00 max Note: PS Nos. 15, 24 and 30 are now standard grades. (See SAE Nos. 4120, 4121 and 4715) 8 Mo Other .20/.40 .05/.10 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 B .............. .08/.15 .0005-.003 .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .70/1.00 .45/.60 .............. .70/1.00 .45/.60 .............. .20 min .05 min .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .13/.20 .............. .............. .05 min .............. 1.65/2.00 .65/.80 .............. 1.65/2.00 .65/.80 .............. .............. 1.75/2.25 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. B .............. .............. .0005-.003 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. V 1.65/2.00 .08/.15 .10/.15 .............. .25/.35 .............. STANDARD H STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo Other 1330 H .27/.33 1.45/2.05 ............. .............. ............ ............. 1335 H .32/.38 1.45/2.05 ............. .............. ............ ............. 1340 H .37/.44 1.45/2.05 ............. .............. ............ ............. 1345 H .42/.49 1.45/2.05 ............. .............. ............ ............. 4027 H .24/.30 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............. .24/.30 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............. 4028 Ha 4032 H .29/.35 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............. 4037 H .34/.41 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............. 4042 H .39/.46 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............. 4047 H .44/.51 .60/1.00 ............. .............. .20/.30 ............ 4118 H 4130 H 4135 H 4137 H 4140 H 4142 H 4145 H 4147 H 4150 H 4161 H .17/.23 .27/.33 .32/.38 .34/.41 .37/.44 .39/.46 .42/.49 .44/.51 .47/.54 .55/.65 .60/1.00 .30/.70 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .30/.70 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .75/1.20 .65/.95 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .08/.15 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .25/.35 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 4320 H 4340 H E4340 H .17/.23 .37/.44 .37/.44 .40/.70 .55/.90 .60/.95 .35/.65 .65/.95 .65/.95 1.55/2.00 1.55/2.00 1.55/2.00 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 ............. ............. ............. 4620 H 4718 H .17/.23 .15/.21 .35/.75 .60/.95 ............. .30/.60 1.55/2.00 .85/1.25 .20/.30 .30/.40 ............. ............. 4720 H .17/.23 .45/.75 .30/.60 .85/1.25 .15/.25 ............. 4815 H 4817 H 4820 H .12/.18 .14/.20 .17/.23 .30/.70 .30/.70 .40/.80 ............. ............. ............. 3.20/3.80 3.20/3.80 3.20/3.80 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 ............. ............. ............. 50B40 Hb 50B44 Hb 5046 H 50B46 Hb 50B50 Hb 50B60 Hb .37/.44 .42/.49 .43/.50 .43/.50 .47/.54 .55/.65 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .65/1.10 .30/.70 .30/.70 .13/.43 .13/.43 .30/.70 .30/.70 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. S 5 .035/.050 b B 5 .0005/.003 a 9 STANDARD H STEELS – continued SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo 5120 H .17/.23 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 5130 H .27/.33 .60/1.00 .75/1.20 .............. .............. 5132 H .29/.35 .50/.90 .65/1.10 .............. .............. 5135 H .32/.38 .50/.90 .70/1.15 .............. .............. 5140 H .37/.44 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 5147 H .45/.52 .60/1.05 .80/1.25 .............. .............. 5150 H .47/.54 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 5155 H .50/.60 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .............. ............. 5160 H .55/.65 .65/1.10 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 51B60Hb .55/.65 .65/1.10 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 6118 H .15/.21 .40/.80 .40/.80 .............. .............. 6150 H .47/.54 .60/1.00 .75/1.20 .............. .............. Other .............. .............. .............. ............ .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. V .10/.15 .15 min. 81B45 Hb .42/.49 .70/1.05 .30/.60 .15/.45 .08/.15 .............. 8617 H 8620 H 8622 H 8625 H 8627 H 8630 H 86B30 Hb 8637 H 8640 H 8642 H 8645 H 86B45 Hb 8650 H 8655 H 8660 H 8720 H 8740 H .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .70/1.05 .60/.95 .70/1.05 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.65 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .35/.75 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .20/.30 .20/.30 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .14/.20 .17/.23 .19/.25 .22/.28 .24/.30 .27/.33 .27/.33 .34/.41 .37/.44 .39/.46 .42/.49 .42/.49 .47/.54 .50/.60 .55/.65 .17/.23 .37/.44 8822 H .19/.25 .70/1.05 .35/.65 .35/.75 .30/.40 .............. Si 9260 H .55/.65 .65/1.10 ............. .............. .............. 1.70/2.20 9310 H 94B15 Hb 94B17 Hb 94B30 Hb .07/.13 .12/.18 .14/.20 .27/.33 .40/.70 1.00/1.45 2.95/3.55 .70/1.05 .25/.55 .25/.65 .70/1.05 .25/.55 .25/.65 .70/1.05 .25/.55 .25/.65 .08/.15 .08/.15 .08/.15 .08/.15 .............. .............. .............. .............. Unless specified: Si 5 .15/.35, P 5 .030 max (SAE J1268), S 5 .040 max, Cu 5 .35 max, Ni 5 .25 max, Cr 5 .20 max, Mo 5 .06 max b B 5 .0005/.003 10 STANDARD CARBON and CARBON BORON H STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn 1038 H 1045 H 1522 H 1524 H 1526 H 1541 H 15B21* 15B28H 15B30H 15B35H* 15B37H* 15B41H* 15B48H* 15B62H* .34/.43 .42/.51 .17/.25 .18/.26 .21/.30 .35/.45 .17/.24 .25/.34 .27/.35 .31/.39 .30/.39 .35/.45 .43/.53 .54/.67 .50/1.00 .50/1.00 1.00/1.50 1.25/1.75 1.00/1.50 1.25/1.75 .70/1.20 1.00/1.50 .70/1.20 .70/1.20 1.00/1.50 1.25/1.75 1.00/1.50 1.00/1.50 P Max S Max Si .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .40/.60 For electric furnace steels P & S 5 .025 max and the prefix E is added. * B 5 .0005/.003 RESTRICTED HARDENABILITY STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges SAE No. C Mn Si 15B21RH* 15B35RH* 3310RH 4027RH 4118RH 4120RH 4130RH 4140RH 4145RH 4161RH 4320RH 4620RH 4820RH 50B40RH* 5130RH 5140RH 5160RH 8620RH 8622RH 8720RH 8822RH 9310RH .17/.22 .33/.38 .08/.13 .25/.30 .18/.23 .18/.23 .28/.33 .38/.43 .43/.48 .56/.64 .17/.22 .17/.22 .18/.23 .38/.43 .28/.33 .38/.43 .56/.64 .18/.23 .20/.25 .18/.23 .20/.25 .08/.13 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .40/.60 .70/.90 .70/.90 .90/1.20 .40/.60 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .45/.65 .45/.65 .50/.70 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .45/.65 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 Ni Cr Unless specified: Cu 5 .35 max, Ni 5 .25 max, Cr 5 .20 max, Mo 5 .06 max * B 5 .0005 /.003 11 Mo ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 3.25/3.75 1.40/1.75 ............. ............. ............. .20/.30 ............. .40/.60 .08/.15 ............. .40/.60 .13/.20 ............. .80/1.10 .15/.25 ............. .80/1.10 .15/.25 ............. .80/1.10 .15/.25 ............. .70/.90 .25/.35 1.65/2.00 .40/.60 .20/.30 1.65/2.00 ............. .20/.30 3.25/3.75 ............. .20/.30 ............. .40/.60 ............. ............. .80/1.10 ............. ............. .70/.90 ............. ............. .70/.90 ............. .40/.70 .40/.60 .15/.25 .40/.70 .40/.60 .15/.25 .40/.70 .40/.60 .20/.30 .40/.70 .40/.60 .30/.40 3.00/3.50 1.00/1.40 .08/.15 FORMERLY STANDARD STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn 1009 1033 1034 1037 1059 1062 1064 1069 1075 1084 1085 1086 1108 1109 1110 1111 1112 1113 1114 1115 1116 1119 1120 1123 1139 1145 1152 1211 1320 1345 1513 1518 1525 1533 1534 1536 1544 1545 1546 1551 1553 1561 1570 1572 1580 1590 .15 max .30/.36 .32/.38 .32/.38 .55/.65 .54/.65 .60/.70 .65/.75 .70/.80 .80/.93 .80/.93 .80/.94 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .13 max .13 max .13 max .10/.16 .13/.18 .14/.20 .14/.20 .18/.23 .20/.27 .35/.43 .42/.49 .48/.55 .13 max .18/.23 .43/.48 .10/.16 .15/.21 .23/.29 .30/.37 .30/.37 .30/.37 .40/.47 .43/.50 .44/.52 .45/.56 .48/.55 .55/.65 .65/.75 .65/.76 .75/.88 .85/.98 .60 max .70/1.00 .50/.80 .70/1.00 .50/.80 .85/1.15 .50/.80 .40/.70 .40/.70 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .30/.50 .50/.80 .60/.90 .30/.60 .60/.90 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 1.00/1.30 .60/.90 1.10/1.40 1.00/1.30 .70/1.00 1.20/1.50 1.35/1.65 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 .60/.90 1.60/1.90 1.60/1.90 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 .80/1.10 1.10/1.40 1.20/1.50 1.20/1.50 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 1.00/1.30 .85/1.15 .80/1.10 .75/1.05 .80/1.10 1.00/1.30 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 12 P Max S Max .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .07/0.12 .07/0.12 .07/0.12 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .07/.12 .040 .035 .030 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .08/.13 .08/.13 .08/.13 .10/.15 .16/.23 .24/.33 .08/.13 .08/.13 .16/.23 .24/.33 .08/.13 .06/.09 .13/.20 .04/.07 .06/.09 .10/.15 .040 .040 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 .050 FORMERLY STANDARD STEELS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo Other 2317 2330 2340 2345 2512 2515 2517 3115 3120 3130 3135 X3140 3140 3145 3150 3215 3220 3230 3240 3245 3250 3310 3311 3312 3316 3325 3335 3340 3415 3435 3450 4012 4024† 4028† 4032 4042 4053 4063 4068 4119 4121a 4125 4131 4135 4147 4161 4317 4337 4419 .15/.20 .28/.33 .38/.43 .43/.48 .09/.14 .12/.17 .15/.20 .13/.18 .17/.22 .28/.33 .33/.38 .38/.43 .38/.43 .43/.48 .48/.53 .10/.20 .15/.25 .25/.35 .35/.45 .40/.50 .45/.55 .08/.13 .10/.16 .08/.13 .14/.19 .20/.30 .30/.40 .35/.45 .10/.20 .30/.40 .45/.55 .09/.14 .20/.25 .25/.30 .30/.35 .40/.45 .50/.56 .60/.67 .63/.70 .17/.22 .18/.23 .23/.28 .28/.33 .33/.38 .45/.50 .56/.64 .15/.20 .35/.40 .18/.23 .40/.60 .60/.80 .70/.90 .70/.90 .45/.60 .40/.60 .45/.60 .40/.60 .60/.80 .60/.80 .60/.80 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .45/.60 .30/.50 .45/.60 .45/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .50/.70 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .45/.65 .60/.80 .45/.65 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .55/.75 .55/.75 .55/.75 .55/.75 .70/.90 .55/.75 .70/.90 .70/.90 .90/1.25 .90/1.25 .90/1.25 .90/1.25 .90/1.25 .90/1.25 1.40/1.75 1.30/1.60 1.40/1.75 1.40/1.75 1.25/1.75 1.25/1.75 1.25/1.75 .60/.95 .60/.95 .60/.95 ............. ............. .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .40/.60 .45/.65 .40/.60 .90/1.20 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .70/.90 .40/.60 .70/.90 .............. 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 4.75/5.25 4.75/5.25 4.75/5.25 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.10/1.40 1.50/2.00 1.50/2.00 1.50/2.00 1.50/2.00 1.50/2.00 1.50/2.00 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 3.25/3.75 2.75/3.25 2.75/3.25 2.75/3.25 ............. ............. .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .............. ............. .............. ............. .............. ............. 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 .............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .15 max ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .15/.25 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .25/.35 .20/.30 .20/.30 .45/.60 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. † S 5 .035/.050 a Formerly PS 24 13 FORMERLY STANDARD STEELS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo 4419H .17/.23 .35/.75 .............. .............. .45/.60 4422 .20/.25 .70/.90 .............. .............. .35/.45 4427 .24/.29 .70/.90 .............. .............. .35/.45 4608 .06/.11 .25/.45 .............. 1.40/1.75 .15/.25 46B12* .10/.15 .45/.65 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 4615 .13/.18 .45/.65 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 4617 .15/.20 .45/.65 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 .18/.23 .50/.70 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 X4620 4621 .18/.23 .70/.90 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 4621H .17/.23 .60/1.00 .............. 1.55/2.00 .20/.30 4626 .24/.29 .45/.65 .............. .70/1.00 .15/.25 4640 .38/.43 .60/.80 .............. 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 b 4715 .13/.18 .70/.90 .45/.65 .70/1.00 .45/.60 4718 .16/.21 .70/.90 .35/.55 .90/1.20 .30/.40 4720 .17/.22 .50/.70 .35/.55 .90/1.20 .15/.25 4812 .10/.15 .40/.60 .............. 3.25/3.75 .20/.30 4815 .13/.18 .40/.60 .............. 3.25/3.75 .20/.30 4817 .15/.20 .40/.60 .............. 3.25/3.75 .20/.30 5015 .12/.17 .30/.50 .30/.50 .............. .............. 50B40* .38/.43 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .............. .............. 50B44* .43/.48 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .............. .............. 5045 .43/.48 .70/.90 .55/.75 .............. .............. 5046 .43/.48 .75/1.00 .20/.35 .............. .............. 50B50* .48/.53 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .............. .............. 5060 .56/.64 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .............. .............. 50B60* .56/.64 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .............. .............. 5115 .13/.18 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. 5117 .15/.20 .70/.90 .............. .............. .70/.90 5135 .33/.38 .60/.80 .80/1.05 .............. .............. 5145 .43/.48 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. 5145H .42/.49 .60/1.00 .60/1.00 .............. .............. 5147 .46/.51 .70/.95 .85/1.15 .............. .............. 5152 .48/.55 .70/.90 .90/1.20 .............. .............. 5155 .51/.59 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. 50100 .98/1.10 .25/.45 .40/.60 .............. .............. 6115 .10/.20 .30/.60 .80/1.10 .............. .............. 6117 .15/.20 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. 6118 .16/.21 .50/.70 .50/.70 .............. .............. 6120 .17/.22 .70/.90 .70/.90 .............. .............. 6125 .20/.30 .60/.90 .80/1.10 .............. .............. 6130 .25/.35 .60/.90 .80/1.10 .............. .............. .............. .............. 6135 .30/.40 .60/.90 .80/1.10 6140 .35/.45 .60/.90 .80/1.10 .............. .............. 6145 .43/.48 .70/.90 .80/1.10 .............. .............. 6195 .90/1.05 .20/.45 .80/1.10 .............. .............. 71360 .50/.70 .30 max 3.00/4.00 .............. .............. 71660 .50/.70 .30 max 3.00/4.00 .............. .............. 7260 .50/.70 .30 max .50/1.00 .............. .............. * B 5 .0005/.003 b Formerly PS 30 14 Other .............. .............. .............. ............. ............. .............. ............. ............. ............. .............. .............. ............. ............. .............. ............. ............. ............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. V .15 min .10 min .10/.15 .10 min .15 min .15 min .15 min .15 min .15 min .15 min W 12.00/15.00 15.00/18.00 1.50/2.00 FORMERLY STANDARD STEELS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SAE No. C Mn Cr Ni Mo 8115 .13/.18 .70/.90 .30/.50 .20/.40 .08/.15 81B45* .43/.48 .75/1.00 .35/.55 .20/.40 .08/.15 8625 .23/.28 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8627 .25/.30 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8632 .30/.35 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8635 .33/.38 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8637 .38/.43 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8641† .38/.43 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8642 .40/.45 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 86B45* .43/.48 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8647 .45/.50 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8650 .48/.53 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8653 .50/.56 .75/1.00 .50/.80 .40/.70 .15/.25 8655 .51/.59 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8660 .56/.64 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .15/.25 8715 .13/.18 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8717 .15/.20 .70/.90 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8719 .18/.23 .60/.80 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8735 .33/.38 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8740 .38/.43 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8742 .40/.45 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8745 .43/.48 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 8750 .48/.53 .75/1.00 .40/.60 .40/.70 .20/.30 92501 .45/.55 .60/.90 ............. ............. ............. 92542 .51/.59 .60/.80 .60/.80 ............. ............. 92551 .51/.59 .70/.95 ............. ............. ............. 1 9261 .55/.65 .75/1.00 .10/.25 ............. ............. 92621 .55/.65 .75/1.00 .25/.40 ............. ............. 9310 .08/.13 .45/.65 1.00/1.40 3.00/3.50 .08/.15 9315 .13/.18 .45/.65 1.00/1.40 3.00/3.50 .08/.15 9317 .15/.20 .45/.65 1.00/1.40 3.00/3.50 .08/.15 94B15 .13/.18 .75/1.00 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 94B17 .15/.20 .75/1.00 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 94B30* .28/.33 .75/1.00 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 9437 .35/.40 .90/1.20 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 9440 .38/.43 .90/1.20 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 94B40* .38/.43 .75/1.00 .30/.60 .30/.60 .08/.15 9442 .40/.45 .90/1.20 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 9445 .43/.48 .90/1.20 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 9447 .45/.50 .90/1.20 .30/.50 .30/.60 .08/.15 9747 .45/.50 .50/.80 .10/.25 .40/.70 .15/.25 9763 .60/.67 .50/.80 .10/.25 .40/.70 .15/.25 9840 .38/.43 .70/.90 .70/.90 .85/1.15 .20/.30 9845 .43/.48 .70/.90 .70/.90 .85/1.15 .20/.30 9850 .48/.53 .70/.90 .70/.90 .85/1.15 .20/.30 438V12* .08/.13 .75/1.00 .40/.60 1.65/2.00 .20/.30 438V14* .10/.15 .45/.65 .40/.60 1.65/2.00 .08/.15 * B 5 .0005/.003 † S 5 .04/.60 1 2 Si 5 1.80/2.20 Si 5 1.20/1.60 15 Other ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. V .03 min .03 min 16 S S S S S S S S S S S S S .38/.43 .65/.85 1.00/1.15 1.60/1.90 .38/.43 .75/1.00 .38/.43 .75/1.00 .28/.33 .70/.90 .38/.43 .50/.70 .28/.33 .40/.60 .23/.28 1.20/1.50 .08/.13 .45/.60 .14/.19 .45/.60 .07/.13 .40/.70 .98/1.10 .25/.45 .48/.53 .70/.90 .025 .035 .025 .025 .025 .025 .025 .040 .025 .025 .025 .025 .025 3 2 1 Al 5 .020 max Al 5 .95/1.35 P & S 5 .025 max if Basic Electric Furnace Steel is specified 4 V 5 .15 min † Inactive/Cancelled Aircraft Quality Steels Except Where Indicated Cu 5 .35 max unless specified .025 .040 .025 .025 .025 .025 .025 .040 .025 .025 .025 .025 .025 .15/.35 .70/1.00 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.40 .15/.35 1.30/1.70 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .70/.90 .20 max .80/1.10 .40/.60 .40/.60 1.40/1.80 .80/1.10 .40 max. 1.25/1.75 1.25/1.75 1.00/1.40 1.30/1.60 .75/1.20 1.65/2.00 .25 max .25 max .40/.70 .40/.70 .............. .25 max 1.65/2.00 3.25/3.75 3.25/4.00 3.00/3.50 .............. .............. Solid or P S Tube C Mn Max Max Si Cr Ni * Some MIL numbers cancelled. Replaced by AMS numbers. ** Timken Company mill type. S-5000 S-507831 S-5626 S-6049 S-6050† S-67092 S-6758 S-71083 S-7393† S-7420 S-85034 MIL* Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits AMS SAE No. Nearest Equivalent .20/.30 6415 E4340 .06 max .15/.25 6382/6349 4140 .20/.30 6322/6325/6327 8740 .15/.25 6280 8630 .30/.40 6470/6472 .............. 637 .15/.25 4130 .35/.45 6425 4625M4** .............. 6250 3310 .............. .............. 3316 .08/.15 .............. 9310 .............. 6440/6444/6447 52100 .............. 6448 6150 Mo SELECTED MILITARY SPECIFICATIONS 17 .75/1.00 .70/1.00 .60/.90 .75/1.00 .040 .040 .040 .025 .040 .05/.09 .040 .020 7 6 5 P & S 5 .015 max if consumable vacuum melted steel is specified V 5 .05/.10 Al 5 .040 max 8 V 5 .20/.30 † Inactive/Cancelled Aircraft Quality Steels Except Where Indicated Cu 5 .35 max unless specified * Some MIL numbers cancelled. Replaced by AMS numbers. ** Timken Company mill type. .48/.55 .47/.55 .41/.49 .38/.45 .025 .040 .040 .040 .010 .010 .025 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .20/.35 .15/.35 1.45/1.80 .30 max .80/1.10 .80/1.15 .80/1.15 .95/1.25 .40/.60 ............. .75/.95 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.95 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .40/.70 ............. 1.65/2.00 .85/1.15 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 ............. S S S S .025 .040 .040 .040 .010 .010 .025 S-115957 S-115957 S-115957,8 S-460478 .70/1.00 .60/1.00 .80/1.00 .70/.90 .65/.90 .65/.90 .30/.60 S S S S S or T S or T T S-86905 S-86953 S-86993,6 S-8707† S-8844-1 S-8844-26 T-5066 18/.23 .34/.41 .28/.33 .38/.43 .38/.43 .40/.44 .22/.28 Solid or P S Tube C Mn Max Max Si Cr Ni MIL* Mo .15/.25 .15/.25 .30/.40 .55/.70 .15/.25 .20/.30 .35/.50 .20/.30 .20/.30 .35/.45 ............. SELECTED MILITARY SPECIFICATIONS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits ............. ............. ............. ............. 6274 6300 6411/6427 ............. 6414 6257 T5066 AMS 4150 41R50 4142M3V2* ............. 8620 4037 4330M4V1* 984 4340 300M 1025 SAE No. Nearest Equivalent 18 .07/.13 .07/.13 .11/.17 .14/.20 .07/.13 .08/.13 .13/.18 .15/.20 .17/.23 .15/.20 .28/.33 .28/.33 .33/.38 .11/.17 .15/.20 .17/.22 .17/.23 .35/.40 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .70/.90 .60/.95 .60/.95 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .45/.65 .45/.65 .45/.65 .40/.70 .70/.90 2 1 B 5 .001 max P & S 5 .015 max 4 3 B 5 .0005/.005 P & S 5 .040 max P & S 5 .025 max, Cu 5 .35 max unless specified 6250 62601 6263 6264 62652 62663 6270 6272 6274 62753 6280 6281 6282 6290 6292 6294 6299 63004 AMS Number C Mn .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .20/.40 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 1.25/1.75 1.00/1.40 1.00/1.40 1.00/1.40 1.00/1.40 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .35/.65 .30/.50 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .20 max .20 max .20 max .35/.65 .20 max 3.25/3.75 3.00/3.50 3.00/3.50 3.00/3.50 3.00/3.50 1.65/2.00 .40/.70 .40/.70 .35/.75 .30/.60 .40/.70 .40/.70 .40/.70 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.55/2.00 .25 max .06 max .08/.15 .08/.15 .08/.15 .08/.15 .20/.30 .15/.25 .15/.25 .15/.25 .08/.15 .15/.25 .15/.25 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .03/.08 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. Si Cr Ni Mo V Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits SELECTED AMS ALLOY STEEL SPECIFICATIONS 3310 9310 9315 9317 CV9310 43BV12 8615 8617 .............. 94B17 8630 8630 8735 4615 4617 4620 4320H 4037 SAE Designations 19 .28/.33 .25/.30 .40/.50 .38/.43 .33/.38 .38/.43 .38/.43 .38/.43 .38/.43 .48/.53 .38/.43 .28/.33 .33/.38 .38/.43 .38/.43 .27/.33 .38/.43 .45/.65 .60/.90 .40/.70 .60/.80 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .70/.90 .40/.60 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .75/1.00 .60/.80 .65/.85 .55/.75 .55/.75 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .40/.70 .15/.35 7 6 5 Cu 5 .50 max B 5 .0005/.005 P 5 .015 max, S 5 .008 max 1.00/1.50 1.00/1.50 .80/1.10 .20 max .40/.60 .30/.55 .40/.60 .40/.60 .55/.75 .40/.60 .70/.90 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 .80/1.10 1.00/1.35 .70/.90 .25 max. .50 max. .25 max. 1.65/2.00 .40/.70 .20/.40 .40/.70 .40/.70 .55/.85 .40/.70 .85/1.15 .25 max .25 max .25 max .25 max 1.85/2.25 1.65/2.00 SAE Designations .40/.60 .20/.30 17-22-AS® .40/.60 .75/.95 17-22-AV® .45/.65 .25/.35 .20/.30 .............. 4640 .20/.30 .............. 8735 .08/.15 .............. 81B40 .20/.30 .............. 8740 .20/.30 .............. 8740 .20/.30 .............. 8740 Mod .............. .20/.30 8750 .20/.30 .............. 9840 .15/.25 .............. 4130 .15/.25 .............. 4135 .15/.25 .............. 4140 .15/.25 .............. 4140 .35/.55 .............. HS220-07 .20/.30 4340* Si Cr Ni Mo V P & S 5 .025 max, Cu 5 .35 max unless specified * Special Aircraft Quality – Normalized and Tempered 6302 63035 6304 6312 6320 63216 6322 6323 6324 6328 6342 6371 6372 6381 6382 6407 64097 AMS Number C Mn SELECTED AMS ALLOY STEEL SPECIFICATIONS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits 20 .35/.40 .38/.43 .38/.43 .23/.28 .40/.45 .35/.40 .38/.43 .28/.33 .32/.38 .32/.38 .45/.50 .93/1.05 .98/1.10 .92/1.02 .48/.53 .65/.85 .65/.90 .65/.85 1.20/1.50 .60/.90 .65/.85 .65/.85 .75/1.00 .60/.80 .60/.90 .60/.90 .25/.45 .25/.45 .95/1.25 .70/.90 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 1.30/1.70 1.45/1.80 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .15/.35 .40/.60 .15/.30 .15/.35 .15/.35 .50/.70 .15/.35 9 8 10 P & S 5 .015 max P & S 5 .010 max B 5 .0005/.005 .70/.90 .70/.90 .70/.90 .20/.40 .70/.95 .70/.90 .70/.90 .75/1.00 .65/.90 .65/.90 .90/1.20 1.35/1.60 1.30/1.60 .90/1.15 .80/1.10 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 .70/1.00 .70/1.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 .40/.70 .25 max .25 max .25 max .25 max .20/.30 .20/.30 .20/.30 .35/.45 .30/.50 .15/.25 .15/.25 .35/.50 .30/.40 .30/.40 .90/1.10 .10 max .08 max .08 max .06 max .............. .............. .............. .............. .05/.10 .............. .01/.06 .05/.10 .17/.23 .17/.23 .08/.15 .............. .............. .............. .15/.30 Si Cr Ni Mo V P & S 5 .025 max, Cu 5 .35 max unless specified * Premium Aircraft Quality 6412 64148 6415 6418 64199 642110 642210 6427 6428 64308 64319 6440 64448 64458 6448 AMS Number C Mn SELECTED AMS ALLOY STEEL SPECIFICATIONS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits 4337 CV4340 4340 4625M4 CV300M 98B37 Mod 98BV40 Mod 4330M4V1 4335 Mod 4335M4V2 D6-AC 52100 CV52100* CV51100 Mod 6150 SAE Designations 21 .38/.43 .38/.43 .38/.43 .21/.26 * P 5 .035 max, S 5 .040 max 6470 6471 6472* 6475 .50/.80 .50/.80 .50/.80 .50/.70 AMS Number C Mn NITRIDING STEELS .20/.40 .20/.40 .20/.40 .20/.40 1.40/1.80 1.40/1.80 1.40/1.80 1.00/1.25 .25 max .25 max .25 max 3.25/3.75 .30/.40 .30/.40 .30/.40 .20/.30 .95/1.30 .95/1.30 .95/1.30 1.10/1.40 Si Cr Ni Mo Al Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits N 135M or #3 CV Nit #3 Other Designations 22 C Max Mn Max Si Max P Max S Max Cr Ni * At producers option, reported only when intentionally added. 201 .15 5.5/7.5 1.00 .060 .030 16.00/18.00 3.50/5.50 202 .15 7.5/10.0 1.00 .060 .030 17.00/19.00 4.00/6.00 301 .15 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 16.00/18.00 6.00/8.00 302 .15 2.00 .75 .045 .030 17.00/19.00 8.00/10.00 302B .15 2.00 2.00/3.00 .045 .030 17.00/19.00 8.00/10.00 303 .15 2.00 1.00 .200 .15 min 17.00/19.00 8.00/10.00 304 .08 2.00 .75 .045 .030 18.00/20.00 8.00/10.50 TP304 .08 2.00 .75 .040 .030 18.00/20.00 8.00/11.00 304L .03 2.00 .75 .045 .030 18.00/20.00 8.00/12.00 TP304L .035 2.00 .75 .040 .030 18.00/20.00 8.00/13.00 TP304H .04/.10 2.00 .75 .040 .030 18.00/20.00 8.00/11.00 305 .12 2.00 .75 .045 .030 17.00/19.00 10.50/13.00 308 .08 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 19.00/21.00 10.00/12.00 309 .20 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 22.00/24.00 12.00/15.00 310 .25 2.00 1.50 .045 .030 24.00/26.00 19.00/22.00 TP310 .15 2.00 .75 .040 .030 24.00/26.00 19.00/22.00 314 .25 2.00 1.50/3.00 .045 .030 23.00/26.00 19.00/22.00 316 .08 2.00 .75 .045 .030 16.00/18.00 10.00/14.00 TP316 .08 2.00 .75 .040 .030 16.00/18.00 11.00/14.00 316L .03 2.00 .75 .045 .030 16.00/18.00 10.00/14.00 Type Number Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits AUSTENITIC STAINLESS STEELS Others N 5 0.25 max N 5 0.25 max N 5 0.10 max N 5 0.10 max ............. Zr, Mo 5 .60 max* ............. .............. N 5 0.10 max .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. Mo 5 2.00/3.00 N 5 0.10 max Mo 5 2.00/3.00 Mo 5 2.00/3.00 N 5 0.10 max 23 .040 .040 .040 .045 .040 P Max .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 S Max Cr 16.00/18.00 .............. 18.00/20.00 17.00/19.00 17.00/20.00 Ni Others H 5 Grades for high temperature service. TP 5 Tubular Products Ti 5 4 3 C min, .60 max Cb 1Ta 5 10 3 C min Cb 1 Ta 5 10 3 C min 5 1.00 max Cb 1 Ta 5 8 3 C min 5 1.00 max Cb 1 Ta 5 10 3 C min Ta 5 .10 max Cb 1 Ta 5 10 3 C min Cb 1 Ta 5 1.00 max Cb 1 Ta 5 8 3 C min Ta 5 .10 max Cb 1 Ta 5 1.00 max .............. .............. .75 .75 .75 1.00 .75 Si Max TP321H .04/.10 2.00 .75 .040 .030 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 347 .08 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 17.00/19.00 9.00/13.00 TP347 .08 2.00 .75 .040 .030 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 TP347H .04/.10 2.00 .75 .040 .030 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 17.00/19.00 9.00/13.00 .08 348 TP348 .08 2.00 .75 .040 .030 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 TP348H .04/.10 2.00 .75 .040 .030 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 384 .08 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 15.00/17.00 17.00/19.00 385 .08 2.00 1.00 .045 .030 11.50/13.50 14.00/16.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 Mn Max Mo 5 2.00/3.00 Mo 5 2.00/3.00 Mo 5 3.00/4.00 Ti 5 5 3 C min, .60 max Ti 5 5 3 C min, .60 max .035 .04/.10 .08 .08 .08 C Max 10.00/15.00 11.00/14.00 11.00/14.00 9.00/12.00 9.00/13.00 TP316L TP316H TP317 321 TP321 Type Number AUSTENITIC STAINLESS STEELS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits 24 .15 .08 .08 .15 .15 .15 .15 Over .15 Over .15 .12 .12 .20 .60/.75 .75/.95 .95/1.20 .20 Over .10 .10 403 405 TP405 410 TP410 414 416 420 TP420 430 430F 431 440A 440B 440C TP443 501 502 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.25 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.25 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 Mn Max .50 1.00 .75 1.00 .75 1.00 1.00 1.00 .75 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 .75 1.00 1.00 Si Max .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .060 .040 .030 .040 .060 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 .040 P Max .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .150 min .030 .030 .030 .150 min .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 S Max Cr 11.50/13.00 11.50/14.50 11.50/13.50 11.50/13.50 11.50/13.50 11.50/13.50 12.00/14.00 12.00/14.00 12.00/14.00 16.00/18.00 16.00/18.00 15.00/17.00 16.00/18.00 16.00/18.00 16.00/18.00 18.00/23.00 4.00/6.00 4.00/6.00 Prefix TP denotes tubular products. Suffixes A, B and C denote differing carbon ranges for the same grade. F denotes a free machining grade. * At producer’s option, reported only when intentionally added. C Max Type Number Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits CHROMIUM STAINLESS STEELS Ni .............. .60 max .50 max .75 max .50 max 1.25/2.50 .............. .............. .50 max .............. .............. 1.25/2.50 .............. .............. .............. .50 max .............. ............. Others Turbine Quality AI 5 .10/.30 AI 5 .10/.30 .............. .............. .............. Zr, Mo 5 .60 max* .............. .............. .............. Mo 5 .60 max* .............. Mo 5 .75 max Mo 5 .75 max Mo 5 .75 max Cu 5 .90/1.25 Mo 5 .40/.65 Mo 5 .40/.65 25 A B C F11 F12 A T4 T5† T7† T9† T11† T21† T22† T91** T1 T1b Grade C .25 max .30 max .35 max .10/.20 .10/.20 .06/.18 .05/.15 .15 max .15 max .15 max .05/.15 .05/.15 .05/.15 .08/.12 .10/.20 .14 max Mn .27/.93 .29/1.06 .29/1.06 .30/.80 .30/.80 .27/.63 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.80 .30/.80 See current ASTM specifications for P & S limitations. † These grades also included in ASTM Specifications A213 and A335. * The combined elements of Cr, Ni, Mo, V and Cu must not exceed 1% ** Cb 5 .06/.10, N 5 .03/.07, Al 5 .04 max A106* A182 A192 A200 A209 ASTM Number .10 min .10 min .10 min .50/1.00 .10/.60 .25 max .50/1.00 .50 max .50/1.00 .25/1.00 .50/1.00 .50 max .50 max .20/.50 .10/.50 .10/.50 Si .40 max .40 max .40 max 1.00/1.50 .80/ 1.25 ............. 2.15/2.85 4.00/6.00 6.00/8.00 8.00/10.00 1.00/1.50 2.65/3.35 1.90/2.60 8.00/9.00 ............. ............. Cr Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits .40 max .40 max .40 max ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .40 max ............. ............. Ni SELECTED ASTM SPECIFICATIONS Mo .15 max .15 max .15 max .44/.65 .44/.65 ............. .44/.65 .45/.65 .45/.65 .90/1.10 .44/.65 .80/1.06 .87/1.13 .85/1.05 .44/.65 .44/.65 V .08 max .08 max .08 max ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .18/.25 ............. ............. 26 Grade C Mn Si Cr Ni Mo ‡ Mn .30/ .60 .45/ .65 .60/ .80 .80/1.20 .40/ .60 C .72/.85 .17/.22 .27/.33 .25/.31 .23/.28 Type TDS-10® TDS-30® TDS-50® TDS-70® TDS-90® Si .............. .15/.30 .40/.70 .50/.80 .15/.30 Cr .............. .40/ .60 1.00/1.35 1.90/2.40 3.00/3.50 Ni .............. 1.65/2.00 1.85/2.25 .25 max. .............. .............. .20/.30 .35/.55 .25/.35 .45/.60 Mo Ti 5 4 3 C min, .60 max Cb 1 Ta 5 8 3 C min,1.00 max Cb 1 Ta 5 10 3 C min, Ta 5 .10 max Cb 1 Ta 5 1.00 max These grades also included in ASTM Specifications A312 and A376. Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits Others Ti 5 4 3 C min, .70 max TIMKEN® TUBULAR HOLLOW DRILL STEELS See current ASTM specifications for P & S limitations A210 A1 .27 max .93 max .10 min ............. ............. ............. C .35 max .29/1.06 .10 min ............. ............. ............. A213 T5b .15 max .30/.60 1.00/2.00 4.00/6.00 ............. .45/.65 T5c .12 max .30/.60 .50 max 4.00/6.00 ............. .45/.65 T12 .05/.15 .30/.61 .50 max .80/1.25 ............. .44/.65 TP304H‡ .04/.10 2.00 max .75 max 18.00/20.00 8.00/11.00 ............. TP310H‡ .04/.10 2.00 max .75 max 24.00/26.00 19.00/22.00 ............. TP316H‡ .04/.10 2.00 max .75 max 16.00/18.00 11.00/14.00 2.00/3.00 ‡ TP321H .04/.10 2.00 max .75 max 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 ............. TP347H‡ .04/.10 2.00 max .75 max 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 ............. TP348 .08 max 2.00 max .75 max 17.00/20.00 9.00/13.00 ............. ASTM Number SELECTED ASTM SPECIFICATIONS – continued Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits 27 C Mn Si Cr Ni Mo Cb P 5 .015 max, S 5 .005 max Impact 7 .26/.32 .60/.90 .............. 1.20/1.50 .............. .65/.75 .02/.05 Impact 8 .26/.32 .90/1.10 .20/.40 1.00/1.50 .15 max .75/.85 .02/.05 Impact 10 .26/.32 .90/1.10 .15/.35 .70/.90 .50/.70 .65/.75 .02/.05 9Cr1Mo .15 max .30/.60 .25/1.00 8.00/10.00 .............. .90/1.10 .............. 410 .15 max 1.00 max 1.00 max 12.00/14.00 .............. .............. .............. 420 Mod .18/.22 1.00 max 1.00 max 12.50/14.00 .............. .............. .............. Type Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits TIMKEN® OIL COUNTRY STEELS P 5 .030 max S 5 .030 max P 5 .040 max P 5 .020 max Other 28 CORROSION RESISTANT ALLOYS .03 .03 .03 .03 .03 .04 .04 .03 44LN DP-3 3RE60 2205 2304 Uranus 50 Ferralium 255 7-Mo PLUS *Range indicates min to max mass functions. C max Designation 2.0 1.0 1.2-2.0* 2.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 2.0 Mn max 1.00 0.75 1.40-2.00* 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.60 Si max 24.0-26.0 24.0-26.0 18.0-19.0 21.0-23.0 21.5-24.5 20.5-22.5 24.0-27.0 26.0-29.0 Cr Duplex Stainless Steel Ranges and Limits (Not Manufactured by Timken) Ni 5.50-6.50 5.50-7.50 4.25-5.25 4.50-6.50 3.00-5.50 5.50-8.50 4.50-6.50 3.50-5.20 29 C .27/.33 .23/.28 .28/.33 .32/.38 .32/.38 Type HS-220-07 HS-220-18 HS-220-27 HS-220-28 HS-220-30 Mn Si .15/.30 .15/.30 Cr .65/.90 .70/.90 Ni .40/.70 1.55/2.00 Mo .15/.25 .20/.30 .60/.80 1.20/1.50 .75/1.00 .60/.80 .60/.90 Mn .40/.70 1.30/1.70 .15/.35 .15/.35 .40/.60 Si 1.00/1.35 .20/.40 .75/1.00 .65/.90 .65/.90 Cr 1.85/2.25 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 1.65/2.00 Ni TIMKEN® HIGH STRENGTH STEELS Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits 1.00/1.30 .60/ .80 TM - Trademark of The Timken Company C .13/.21 .20/.27 Type WHS 100TM WHS 130TM Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits .35/.55 .35/.45 .35/.50 .30/.40 .30/.40 Mo .03/.08 .............. V TIMKEN® WELDABLE HIGH STRENGTH STEELS B ............ ............ .05/.10 .17/.23 .17/.23 V .003 added .............. 30 0.28/0.33 0.28/0.33 0.32/0.36 0.32/0.36 0.31/0.35 0.36/0.40 0.36/0.41 0.36/0.41 0.36/0.40 0.38/0.43 0.53/0.57 0.52/0.57 0.52/0.57 0.52/0.57 MicroTec 3M80 MicroTec 3M80A MicroTec 3M80B MicroTec 3M80C MicroTec 3M85 MicroTec 4M85 MicroTec 4M90 MicroTec 4M90A MicroTec 4M95 MicroTec 4M95A MicroTec 5H85 MicroTec 5H90 MicroTec 5H95 MicroTec 5H95A C 0.10/0.18 0.16/0.20 0.16/0.20 0.16/0.22 0.28/0.33 0.26/0.30 0.28/0.32 MicroTec 2W60 MicroTec 2W65 MicroTec 2W70 MicroTec 2W75 MicroTec 3W70 MicroTec 3W75 MicroTec 3W75A Type 0.70/0.85 0.70/1.00 1.05/1.25 1.15/1.35 1.30/1.60 1.30/1.50 1.35/1.45 1.35/1.45 1.30/1.50 1.20/1.40 1.10/1.30 1.10/1.30 1.30/1.50 1.35/1.45 1.20/1.60 1.20/1.40 1.40/1.60 1.30/1.70 0.90/1.30 1.00/1.30 0.90/1.20 Mn 0.08/0.12 0.05/0.20 0.08/0.18 0.10/0.20 0.08/0.18 0.08/0.18 0.06/0.10 0.07/0.09 0.10/0.14 0.04/0.10 0.10/0.18 0.10/0.18 0.08/0.12 0.08/0.12 0.05/0.10 0.06/0.10 0.07/0.11 0.10/0.20 0.07/0.18 0.13/0.23 0.13/0.18 V 0.020/0.035 0.025/0.035 0.040/0.060 0.040/0.060 .............. 0.025/0.050 0.010 max. 0.005/0.020 0.030/0.050 0.030/0.050 .............. 0.030/0.050 0.045 max. 0.030/0.045 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. S Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits TIMKEN® MICROALLOY STEELS Si .............. 0.15/0.35 0.45/0.65 0.45/0.65 .............. .............. 0.40/0.50 0.20/0.30 .............. 0.30/0.50 .............. .............. 0.50/0.70 0.50/0.65 .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. Cr = .15/.45 N = .008/.015 N = .008/.015 Other 31 .10/.20 .15 max .15 max .15 max .15 max .12 max .15 max .15 max .15 max .15 max .08/.12 .10/.50 .50/1.00 .50 max .50 max .50 max .50 max 1.00/2.00 1.00/1.50 .50/1.00 .25/1.00 .20/.50 .............. 1.00/1.50 .80/1.25 1.90/2.60 4.00/6.00 4.00/6.00 4.00/6.00 4.00/6.00 6.00/8.00 8.00/10.00 8.00/9.50 .44/.65 .44/.65 .44/.65 .87/1.13 .45/.65 .45/.65 .45/.65 .09/1.10 .45/.65 .90/1.10 .85/1.05 1 11 .............. 22 5 5c 5b .............. 7 9 91 .040 .040 .040 .45/.65 .45/.65 .60/.90 17-22-A® 17-22-AS® 17-22-AV® .41/.48 .28/.33 .25/.30 P Max .55/.75 .55/.75 .55/.75 1.00/1.50 1.00/1.50 1.00/1.50 .40/.60 .40/.60 .40/.60 .20/.30 .20/.30 .75/.95 S Max Si Cr Mo V .040 .040 .040 ASTM No .............. 6302 6303 AMS No *** Ni 5 .40 max, V 5 .18/.25, Cb 5 .06/.10, N 5 .03/.07, Al 5 .04 max .045 .030 .............. .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .010 S Max Si Cr Mo Chemical Composition Ranges Type C Mn .045 .030 .............. .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .020 ** Ti 5 4 3 C min, .70 max .30/.80 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 .30/.60 P Max TIMKEN® HIGH TEMPERATURE ENGINEERING STEELS *.50 Mo steel also available with .08/.14 C. .50Mo* DM® DM-2 2 1/4 Cr 1 Mo 5 Cr 1/2 Mo 5 Cr 1/2 Mo+Ti** 5 Cr 1/2 Mo+Si 5 Cr 1 Mo+Si 7 Cr 1/2 Mo 9 Cr 1 Mo T9*** Type C Mn Chemical Composition Range and Limits TIMKEN® ALLOY STEELS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE SERVICE 32 Type C .98/1.10 .90/1.05 .85/1.00 .95/1.10 .95/1.10 .95/1.10 .16/.22 .10/.16 .11/.15 .70/.80 .77/.85 .95/1.20 .89/1.01 * 52100 shown for reference purposes only ** Max Cu .10, Co .25, W .25, P .015, S .010 a Deep hardening steels. 52100* ASTM-A485-1(#1 Mod.)a ASTM-A485-2(#2 Mod.) ASTM-A485-3(T-1)a ASTM-A485-4(T-2)a TBS-600TM b CBS-600TM c CBS1000MTM d CBS-50NiL** TBA-2e M-50 440C TBS-9® Mn .70/1.00 .70/1.00 Cr .70/.90 .80/1.20 Ni 1.65/2.00 2.00/2.50 d c b Si .15/.35 .45/.75 .50/.80 .15/.35 .15/.35 .85/1.20 .90/1.25 .40/.60 .10/.25 .15/.35 .25 max. 1.00 max. .15/.35 Cr 1.30/1.60 .90/1.20 1.40/1.80 1.10/1.50 1.10/1.50 1.25/1.65 1.25/1.65 .90/1.20 4.00/4.25 .90/1.20 3.75/4.25 16.00/18.00 .40/.60 Through hardening steel for service up to 600 F. Carburizing steel for service up to 600 F. Carburizing steel for service up to 1000 F. .25/.45 .95/1.25 1.40/1.70 .65/.90 1.05/1.35 .60/.80 .40/.70 .40/.60 .15/.35 1.05/1.35 .35 max. 1.00 max. .50/.80 Mn Ni e Mo .............. .............. .............. .20/.30 .45/.60 .25/.35 .90/1.10 4.00/5.00 4.00/4.50 1.20/1.40 4.00/4.50 .75 max. .08/.15 Mo .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .25/.50 1.13/1.33 .............. .90/1.10 .............. .............. V .35/.45 .50/.65 Through hardening steel can be air quenched. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. 2.75/3.25 3.20/3.60 1.30/1.65 .10 max. .............. .25 max. Chemical Composition Ranges and Limits TIMKEN® SPECIAL BEARING STEELS C .30/.38 .30/.38 Type 4333M4 4333M6 Chemical Composition Ranges TIMKEN® TUBING FOR POLYETHYLENE PRODUCTION 33 C 0.83 0.85 0.98 1.02 1.20 1.32 1.02 0.87 1.08 0.84 0.89 1.57 M1 M2 M2-HC M3-1 M3-2 M4 M7 M10 M42 M50 M52 T15 O6 A10 ASTM Type Graph-Mo® Graph-Air® ASTM C 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.45 0.50 0.45 0.50 Si 1.45 1.35 Mn 0.25 0.28 0.28 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.30 0.25 0.30 0.25 0.30 Mn 1.00 1.80 Si 0.90 1.20 Cr ............ ............ 1.75 6.15 6.15 6.00 6.00 5.35 1.75 0.75 1.50 ............ 1.10 12.25 W 3.75 4.15 4.15 4.10 4.10 4.50 3.75 4.00 3.85 4.10 4.00 4.00 Cr 1.15 1.85 1.85 2.40 3.00 3.85 1.90 1.90 1.20 1.00 1.85 5.00 V Nominal Chemical Composition HIGH-SPEED STEELS 0.015 0.015 S Nominal Chemical Composition 8.50 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 4.40 8.50 8.00 9.50 4.25 4.50 0.50 Mo ............ 1.85 Ni Mo 0.25 1.50 TIMKEN® GRAPHITIC TOOL STEELS Other Other ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ Alloy Sulfides ............ ............ ............ ............ Nitrogen ............ 8.00 ............ ............ 5.00 Co W ............ ............ 34 A2 A6 A7 A8 A10 D2 D3 D5 D7 L6 O1 O6 S1 S5 S7 ASTM C 1.00 0.70 2.60 0.55 1.35 1.50 2.15 1.50 2.30 0.70 0.94 1.45 0.53 0.61 0.50 Si 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.95 1.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.40 0.25 0.30 0.90 0.25 1.90 0.25 Mn 0.75 2.00 0.60 0.30 1.80 0.30 0.40 0.35 0.40 0.60 1.20 1.00 0.25 0.90 0.75 ............ ............ ............ 1.25 ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ 0.50 ............ 2.00 ............ ............ W 5.00 1.00 8.25 5.00 ............ 12.00 12.25 11.65 12.50 0.70 0.50 ............ 1.35 0.18 3.25 Cr 0.25 ............ 4.50 ............ ............ 0.90 0.25 ............ 4.00 ............ ............ ............ 0.25 0.28 ............ V Nominal Chemical Composition COLD WORK DIE STEELS Mo 1.00 1.25 1.20 1.25 1.50 0.75 ............ 0.80 1.10 ............ ............ 0.25 ............ 1.40 1.40 Ni ............ ............ ............ ............ 1.85 ............ ............ ............ ............ 1.40 ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ Co 5 2.80 Other 35 H10 H11 H12 H13 H14 H19 H21 P20 ASTM C 0.35 0.40 0.35 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.33 0.33 Si 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.30 0.45 0.65 Mn 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.40 0.25 0.30 0.25 0.80 ............ ............ 1.30 ............ 4.75 4.25 9.15 ............ W 3.30 5.00 5.00 5.25 5.25 4.25 3.30 1.75 Cr 0.65 0.50 0.30 1.00 ............ 2.00 0.45 ............ V Nominal Chemical Composition HOT WORK DIE STEELS Mo 2.45 1.30 1.40 1.35 ............ ............ ............ 0.40 Co 2.00 ............ ............ ............ ............ 4.25 ............ ............ Other 36 Wear Resistance Toughness Hot Hardness T15 M52 M50 M42 M35 M10 M7 M4 M3-2 M3-1 M2 M1 ASTM Grindability COMPARATIVE PROPERTIES FOR THE SELECTION AND USE OF HIGH SPEED STEELS 37 H21 H19 H14 H13 H12 H11 H10 Mod ASTM Wear Resistance Toughness Temper Resistance Machinability COMPARATIVE PROPERTIES FOR THE SELECTION AND USE OF HOT WORK DIE STEELS 38 S7 O6 O1 L6 D7 D3 D2 A10 A8 A6 A2 ASTM Wear Resistance Toughness Dimensional Stability Machinability COMPARATIVE PROPERTIES FOR THE SELECTION AND USE OF COLD WORK DIE STEELS 39 L6 H13 S7 S5 S1 A8 ASTM Wear Resistance Toughness Dimensional Stability Machinability COMPARATIVE PROPERTIES FOR THE SELECTION AND USE OF SHOCK STEELS 40 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 58 56 55 53 49 43 37 33 30 29 28 27 27 26 26 25 25 24 23 21 ... ... ... ... 51 42 34 29 26 24 23 22 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 62 61 59 56 52 46 38 34 33 32 32 31 31 30 30 29 29 28 27 26 25 23 22 21 55 52 42 34 31 29 28 27 26 26 25 25 25 24 24 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... 50 48 47 46 45 42 39 37 34 32 30 28 27 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41 41 32 27 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... “J” Distance 1038 H 1045 H 1522 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 51 49 48 47 45 43 39 38 35 34 32 30 29 28 27 26 25 23 22 20 ... ... ... ... Max. 42 42 38 34 29 25 22 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 1524 H GRADE 53 50 49 47 46 42 39 37 33 31 30 28 27 26 26 24 24 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... Max. 44 42 38 33 26 25 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 1526 H 60 59 59 58 57 56 55 53 52 50 48 46 44 41 39 35 33 32 31 30 30 29 28 26 Max. 53 52 50 47 44 41 38 35 32 29 27 26 25 24 23 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... Min. 1541 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 1038 H to 15B21 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 48 48 47 47 46 45 44 42 40 38 35 32 27 22 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41 41 40 39 38 36 30 23 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 15B21 H Max. 41 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 53 53 52 51 51 50 49 48 46 43 40 37 34 31 30 29 27 25 25 24 23 22 21 20 47 47 46 45 42 32 25 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 55 53 52 51 50 48 43 38 33 29 27 26 25 24 23 22 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 48 47 46 44 32 22 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 58 56 55 54 53 51 47 41 ... 30 ... 27 ... 26 ... 25 ... 24 ... 22 ... 20 ... ... 51 50 49 48 39 28 24 22 ... 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... “J” Distance 15B28 H 15B30 H 15B35 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 58 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 ... 45 ... 40 ... 33 ... 29 ... 27 ... 25 ... 23 ... 21 Max. 50 50 49 48 43 37 33 26 ... 22 ... 21 ... 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 15B37 H GRADE 60 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 46 42 39 36 34 33 31 31 Max. 53 52 52 51 51 50 49 48 44 37 32 28 26 25 25 24 23 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... Min. 15B41 H 63 62 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 53 51 48 45 41 38 34 32 31 30 29 29 28 28 Max. 56 56 55 54 53 52 42 34 31 30 29 28 27 27 26 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 ... ... Min. 15B48 H ... ... ... ... 65 65 64 64 64 63 63 63 62 62 61 60 58 54 48 43 40 37 35 34 Max. 60 60 60 60 59 58 57 52 43 39 37 35 35 34 33 33 32 31 30 30 29 28 27 26 Min. 15B62 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 15B28 H to 1330 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 56 56 55 53 52 50 48 45 43 42 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 31 31 30 30 49 47 44 40 35 31 28 26 25 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 1330 H Max. 42 60 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 52 51 50 48 46 44 42 41 39 38 37 36 35 35 34 34 * Formerly Standard Steels 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 53 52 51 49 46 40 35 33 31 29 28 27 26 25 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 20 63 63 62 61 61 60 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 49 48 47 46 45 45 45 45 56 56 55 54 51 44 38 35 33 32 31 30 29 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 43 43 42 42 42 42 41 41 41 40 40 40 39 39 38 38 37 37 37 36 36 36 35 35 36 36 35 35 34 33 32 31 30 30 29 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 25 25 25 25 “J” Distan 1340 H 1345 H 3310 H* Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 47 47 47 46 46 46 45 45 45 45 45 45 45 44 44 44 44 43 43 43 42 42 42 41 Max. 40 39 38 38 37 37 36 35 34 33 33 32 32 32 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 30 30 30 Min. 3316 H* GRADE 52 50 46 40 34 30 28 26 25 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... Max. 45 40 31 25 22 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4028 H 57 54 51 46 39 34 31 29 28 26 26 25 24 24 23 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 ... ... Max. 50 45 36 29 25 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4032 H 59 57 54 51 45 38 34 32 30 29 28 27 26 26 26 25 25 25 25 24 24 24 23 23 Max. 52 49 42 35 30 26 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4037 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 1335 H to 4037 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 62 60 58 55 50 45 39 36 34 33 32 31 30 30 29 29 28 28 28 27 27 27 26 26 55 52 48 40 33 29 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 23 22 22 22 21 20 20 ... ... ... ... Min. 4042 H Max. 43 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 64 62 60 58 55 52 47 43 40 38 37 35 34 33 33 32 31 30 30 30 30 29 29 29 57 55 50 42 35 32 30 28 28 27 26 26 25 25 25 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 48 46 41 35 31 28 27 25 24 23 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41 36 27 23 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 48 47 44 41 37 34 32 30 29 28 27 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 23 23 23 22 22 22 41 37 32 37 23 21 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... “J” Distance 4047 H 4118 H 4120 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 56 55 53 51 49 47 44 42 40 38 36 35 34 34 33 33 32 32 32 31 31 30 30 29 Max. 49 46 42 38 34 31 29 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4130 H GRADE 58 58 57 56 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 42 41 40 39 38 38 37 Max. 51 50 49 48 47 45 42 40 38 36 34 33 32 31 30 30 29 28 27 27 27 26 26 26 Min. 4135 H 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 46 45 44 43 42 42 41 41 Max. 52 51 50 49 49 48 45 43 40 39 37 36 35 34 33 33 32 31 30 30 30 29 29 29 Min. 4137 H 60 60 60 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 56 55 55 54 54 53 52 51 49 48 47 46 45 44 Max. 53 53 52 51 51 50 48 47 44 42 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 33 32 32 31 31 30 Min. 4140 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 4042 H to 4142 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 62 62 62 61 61 61 60 60 60 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 54 53 53 52 51 51 50 55 55 54 53 53 52 51 50 49 47 46 44 42 41 40 39 37 36 35 34 34 34 33 33 Min. 4142 H Max. 44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 63 63 62 62 62 61 61 61 60 60 60 59 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 55 55 55 54 56 55 55 54 53 53 52 52 51 50 49 48 46 45 43 42 40 38 37 36 35 35 34 34 64 64 64 64 63 63 63 63 63 62 62 62 61 61 60 60 59 59 58 57 57 57 56 56 57 57 56 56 55 55 55 54 54 53 52 51 49 48 46 45 42 40 39 38 37 37 37 36 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 64 64 64 64 63 63 62 62 62 61 60 59 59 58 58 58 58 59 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 56 55 54 53 51 50 48 47 45 43 41 40 39 38 38 38 “J” Distance 4145 H 4147 H 4150 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 64 64 64 64 64 64 63 63 63 63 63 63 63 Max. 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 59 59 59 59 58 58 57 56 55 63 50 48 45 43 42 41 Min. 4161 H GRADE 48 47 45 43 41 38 36 34 33 31 30 29 28 27 27 26 25 25 24 24 24 24 24 24 Max. 41 38 35 32 29 27 25 23 22 21 20 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4320 H 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 59 59 59 58 58 58 58 57 57 57 57 56 56 56 Max. 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 52 52 52 51 51 50 49 49 48 48 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 Min. 4340 H 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 59 59 59 58 58 58 57 57 57 57 57 Max. 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 53 52 52 52 52 51 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 Min. E 4340 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 4145 H to 4620 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 48 45 42 39 34 31 29 27 26 25 24 23 22 22 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... 41 35 27 24 21 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4620 H Max. 45 51 48 41 33 29 27 25 24 23 22 22 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... * Formerly Standard Steels 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 45 36 29 24 21 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 47 47 45 43 40 37 35 33 32 31 30 29 29 28 27 27 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 24 40 40 38 33 29 27 25 24 23 22 22 21 21 21 20 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 48 47 43 39 35 32 29 28 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 22 21 21 21 20 ... ... ... ... 41 39 31 27 23 21 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... “J” Distance 4626 H* 4718 H 4720 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 45 44 44 42 41 39 37 35 33 31 30 29 28 28 27 27 26 25 24 24 24 23 23 23 Max. 38 37 34 30 27 24 22 21 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4815 H GRADE 46 46 45 44 42 41 39 37 35 33 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 26 25 25 25 25 24 24 Max. 39 38 35 32 29 27 25 23 22 21 20 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4817 H 48 48 47 46 45 43 42 40 39 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 25 Max. 41 40 39 38 34 31 29 27 26 25 24 23 22 22 21 21 20 20 ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 4820 H 60 60 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 53 51 49 47 44 41 38 36 35 34 33 32 30 29 Max. 53 53 52 51 50 48 44 39 34 31 29 28 27 26 25 25 23 21 ... ... ... ... ... ... Min. 50B40 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 4626 H to 50B44 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 63 63 62 62 61 61 60 60 59 58 57 56 54 52 50 48 44 40 38 37 36 35 34 33 56 56 55 55 54 52 48 43 38 34 31 30 29 29 28 27 26 24 23 21 20 ... ... ... Min. 50B44 H Max. 46 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 63 62 60 56 52 46 39 35 34 33 33 32 32 31 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 23 56 55 45 32 28 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 54 51 47 43 40 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 56 54 52 50 41 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 26 25 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... 65 65 64 64 63 63 62 62 61 60 60 59 58 57 56 54 50 47 44 41 39 38 37 36 59 59 58 57 56 55 52 47 42 37 35 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 22 21 20 “J” Distance 5046 H 50B46 H 50B50 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 65 65 64 64 64 63 63 63 62 60 58 55 53 51 49 47 44 Max. 60 60 60 60 60 59 57 53 47 42 39 37 36 35 34 34 33 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 Min. 50B60 H GRADE 48 46 41 36 33 30 28 27 25 24 23 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Max. 40 34 28 23 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 5120 H 56 55 53 51 49 47 45 42 40 38 37 36 35 34 34 33 32 31 30 29 27 26 25 24 Max. 49 46 42 39 35 32 30 28 26 25 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 5130 H 57 56 54 52 50 48 45 42 40 38 37 36 35 34 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 Max. 50 47 43 40 35 32 29 27 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 5132 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 5046 H to 5135 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 58 57 56 55 54 52 50 47 45 43 41 40 39 38 37 37 36 35 34 33 32 32 31 30 51 49 47 43 38 35 32 30 28 27 25 24 23 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 5135 H Max. 47 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 60 59 58 57 56 54 52 50 48 46 45 43 42 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 34 33 33 32 53 52 50 48 43 38 35 33 31 30 29 28 27 27 26 25 24 23 21 20 .... .... .... .... 64 64 63 62 62 61 61 60 60 59 59 58 58 57 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 57 56 55 54 53 52 49 45 40 37 35 34 33 32 32 31 30 29 27 26 25 24 22 21 65 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 56 55 53 51 50 48 47 45 43 42 41 40 39 39 38 59 58 57 56 53 49 42 38 36 34 33 32 31 31 30 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 “J” Distance 5140 H 5147 H 5150 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. .... 65 64 64 63 63 62 62 61 60 59 57 55 52 51 49 47 45 44 43 42 41 41 40 Max. 60 59 58 57 55 52 47 41 37 36 35 34 34 33 33 32 31 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 Min. 5155 H GRADE .... .... .... 65 65 64 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 56 54 52 48 47 46 45 44 43 43 42 Max. 60 60 60 59 58 56 52 47 42 39 37 36 35 35 34 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 Min. 5160 H .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 65 65 64 64 63 61 59 57 55 53 51 49 47 Max. 60 60 60 60 60 59 58 57 54 50 44 41 40 39 38 37 36 34 33 31 30 28 27 25 Min. 51B60 H 46 44 38 33 30 28 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... Max. 39 36 28 24 22 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 6118 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 5140 H to 6150 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 65 65 64 64 63 63 62 61 61 60 59 58 57 55 54 52 50 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 59 58 57 56 55 53 50 47 43 41 39 38 37 36 35 35 34 32 31 30 29 27 26 25 Min. 6150 H Max. 48 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 63 63 63 63 63 63 62 62 61 60 60 59 58 57 57 56 55 53 52 50 49 47 45 43 56 56 56 56 55 54 53 51 48 44 41 39 38 37 36 35 34 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 46 44 41 38 34 31 28 27 26 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... 39 33 27 24 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 48 47 44 41 37 34 32 30 29 28 27 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 23 23 23 22 22 22 41 37 32 27 23 21 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... “J” Distance 81B45 H 8617 H 8620 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 50 49 47 44 40 37 34 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 24 24 24 24 24 Max. 43 39 34 30 26 24 22 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8622 H GRADE 52 51 48 46 43 40 37 35 33 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 25 25 25 Max. 45 41 36 32 29 27 25 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8625 H 54 52 50 48 45 43 40 38 36 34 33 32 31 30 30 29 28 28 28 27 27 27 27 27 Max. 47 43 38 35 32 29 27 26 24 24 23 22 21 21 20 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8627 H 56 55 54 52 50 47 44 41 39 37 35 34 33 33 32 31 30 30 29 29 29 29 29 29 Max. 49 46 43 39 35 32 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 22 21 21 20 20 .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8630 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 81B45 H to 86B30 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 56 55 55 55 54 54 53 53 52 52 52 51 51 50 50 49 48 47 45 44 43 41 40 39 49 49 48 48 48 48 48 47 46 44 42 40 39 38 36 35 34 32 31 29 28 27 26 25 Min. 86B30 H Max. 49 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 59 58 58 57 56 55 54 53 51 49 47 46 44 43 41 40 39 37 36 36 35 35 35 35 52 51 50 48 45 42 39 36 34 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 25 24 24 24 24 23 23 60 60 60 59 59 58 57 55 54 52 50 49 47 45 44 42 41 39 38 38 37 37 37 37 53 53 52 51 49 46 42 39 36 34 32 31 30 29 28 28 26 26 25 25 24 24 24 24 62 62 62 61 61 60 59 58 57 55 54 52 50 49 48 46 44 42 41 40 40 39 39 39 55 54 53 52 50 48 45 42 39 37 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 “J” Distance 8637 H 8640 H 8642 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 63 63 63 63 62 61 61 60 59 58 56 55 54 52 51 49 47 45 43 42 42 41 41 41 Max. 56 56 55 54 52 50 48 45 41 39 37 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 28 27 27 27 27 Min. 8645 H GRADE 63 63 62 62 62 61 61 60 60 60 59 59 59 59 58 58 58 58 57 57 57 57 56 56 Max. 56 56 55 54 54 53 52 52 51 51 50 50 49 48 46 45 42 39 37 35 34 32 32 31 Min. 86B45 H 65 65 65 64 64 63 63 62 61 60 60 59 58 58 57 56 55 53 52 50 49 47 46 45 Max. 59 58 57 57 56 54 53 50 47 44 41 39 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 31 30 30 29 29 Min. 8650 H .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 65 65 64 64 63 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 53 Max. 60 59 59 58 57 56 55 54 52 49 46 43 41 40 39 38 37 35 34 34 33 33 32 32 Min. 8655 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 8637 H to 8660 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 65 64 64 63 62 62 61 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 59 58 57 55 53 50 47 45 44 43 42 40 39 38 37 36 36 35 35 Min. 8660 H Max. 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 48 47 45 42 38 35 33 31 30 29 28 27 26 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 23 23 22 22 41 38 35 30 26 24 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 60 60 60 60 59 58 57 56 55 53 52 50 49 48 46 45 43 42 41 40 39 39 38 38 53 53 52 51 49 46 43 40 37 35 34 32 31 31 30 29 28 28 27 27 27 27 26 26 50 49 48 46 43 40 37 35 34 33 32 31 31 30 30 29 29 28 27 27 27 27 27 27 43 42 39 33 29 27 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... “J” Distance 8720 H 8740 H 8822 H Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. .... .... 65 64 63 62 60 58 55 52 49 47 45 43 42 40 38 37 36 36 35 35 35 34 Max. 60 60 57 53 46 41 38 36 36 35 34 34 33 33 32 32 31 31 30 30 29 29 28 28 Min. 9260 H GRADE 43 43 43 42 42 42 42 41 40 40 39 38 37 36 36 35 35 35 34 34 34 34 33 33 Max. 36 35 35 34 32 31 30 29 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 26 26 25 25 25 25 25 24 24 Min. 9310 H 45 45 44 44 43 42 40 38 36 34 33 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 23 22 22 22 Max. 38 38 37 36 32 28 25 23 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 94B15 H 46 46 45 45 44 43 42 41 40 38 36 34 33 32 31 30 28 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 Max. 39 39 38 37 34 29 26 24 23 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 94B17 H These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 8720 H to 94B30 H END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 56 56 55 55 54 54 53 53 52 52 51 51 50 49 48 46 44 42 40 38 37 35 34 34 49 49 48 48 47 46 44 42 39 37 34 32 30 29 28 27 25 24 23 23 22 21 21 20 Min. 94B30 H Max. 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 47 46 44 42 37 30 24 22 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 42 41 39 33 24 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... ..... .... 57 55 54 53 50 46 42 36 32 28 .... 25 .... 24 .... 23 .... 22 .... 20 .... .... .... .... 52 51 50 49 41 33 28 24 23 21 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 42 42 42 41 41 41 40 40 39 39 39 39 38 38 37 37 36 36 35 35 35 34 34 34 37 37 37 36 36 35 33 33 32 32 31 31 30 30 29 29 28 28 27 27 27 26 26 26 “J” Distance 3310 RH 15B35 RH 15B21 RH Sixteenths Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. of an Inch Min. 50 48 44 40 36 34 32 30 28 27 26 26 26 25 25 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 21 20 55 54 52 49 46 44 41 39 37 35 33 32 32 31 31 31 30 30 30 29 29 28 28 27 42 39 35 30 26 24 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 47 45 41 38 34 31 29 28 26 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 42 38 30 25 22 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 47 44 38 33 29 27 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 46 42 34 28 24 22 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 51 48 43 37 32 28 26 24 23 22 22 21 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 4130 RH Max. Min. 4120 RH Max. Min. 4118 RH Max. Min. Max. 4027 RH GRADE These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 15B21 RH to 4130 RH RESTRICTED END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 52 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 59 59 59 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 52 51 50 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 54 54 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 46 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 37 36 35 35 34 33 62 62 61 61 60 60 59 59 58 58 58 57 57 56 56 55 54 53 52 51 51 50 50 49 57 57 56 56 55 55 54 53 52 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 44 43 42 40 40 39 38 37 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 64 64 64 63 63 62 62 61 60 59 58 57 57 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 59 59 59 58 57 56 54 53 51 49 47 46 45 “J” Distance 4161 RH 4145 RH 4140 RH Sixteenths Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. of an Inch Min. 54 54 53 53 52 50 47 43 38 35 33 32 31 30 29 28 26 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... 59 59 58 58 57 56 55 54 52 50 49 47 45 44 41 38 36 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 42 42 41 40 36 33 32 30 28 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 21 20 20 .... .... .... 47 47 46 45 43 41 40 38 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 25 25 24 23 42 37 30 27 24 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 47 44 40 37 32 29 27 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 42 40 37 34 31 29 27 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 47 46 44 41 39 36 34 32 31 29 28 26 25 24 24 23 22 22 21 21 21 21 21 21 50B40 RH Max. Min. 4820 RH Max. Min. 4620 RH Max. Min. Max. 4320 RH GRADE These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 4140 RH to 50B40 RH RESTRICTED END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 53 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 55 53 51 49 46 44 42 39 37 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 50 47 44 41 37 35 33 31 29 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 59 58 57 55 53 51 48 46 44 43 41 40 39 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 30 29 29 54 53 51 49 45 41 38 36 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 .... 65 65 65 65 64 63 62 60 58 56 55 53 51 50 48 47 44 43 42 41 40 39 39 38 60 60 60 59 58 57 54 50 45 42 40 39 38 37 36 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 29 “J” Distance 5130 RH 5140 RH 5160 RH Sixteenths of an Inch Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 47 45 41 38 34 31 29 28 26 25 24 23 23 22 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Max. 42 39 35 30 26 24 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8620 RH GRADE 49 47 45 41 38 35 32 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 Max. 44 41 37 32 29 27 24 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8622 RH 47 45 43 40 36 33 31 29 28 27 26 25 25 24 24 23 23 22 22 21 20 .... .... .... Max. 42 39 37 32 28 26 24 23 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8720 RH 49 48 47 43 40 37 35 33 32 31 30 30 29 28 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 25 25 25 Max. 44 43 40 35 31 29 27 26 25 25 24 23 23 23 22 22 21 20 .... .... .... .... .... .... Min. 8822 RH These values were adjusted to the nearest Rockwell “C” point, and are used when points are selected and specified Tabulations of Band Limits – 5130 RH to 9310 RH RESTRICTED END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY BANDS 42 42 42 41 41 40 40 39 38 37 37 36 35 34 34 33 33 32 32 32 32 32 31 31 37 36 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 29 28 28 28 28 27 27 26 26 26 26 26 25 25 Min. 9310 RH Max. INTRODUCTION TO JOMINY CORRELATION WITH ROUND BARS The following correlation of Jominy values with quenching severity and surface to center hardnesses obtainable in round bars is based on calculated and practical experience data. Since practical heat treatment results are subject to several variables that are always difficult to determine, i.e., surface condition of piece being quenched, furnace atmosphere, and quenching severity of the coolant, the metallurgist or heat treater may find some differences in applying this correlation to his particular heat treatment setup. However, as experience is gained by their use, it is believed that these charts will be found helpful as a guide to the selection of steel of proper hardenability based on Jominy end quench results. As a valueadded service, Timken Company hardenability data will be supplied upon request, with each heat of steel. 54 1" RD 3/4" RD 0 ∞ 5.0 1.5 2.0 1/2" RD 1.5 1.5 2.0 1.0 0.70 1.0 0.20 0.70 SURFACE 1/2 RADIUS 4 8 JOMINY DISTANCE 12 SURFACE 1/2 RADIUS CENTER SURFACE 16 1/2 RADIUS CENTER 20 ∞ 0.20 0.35 0.50 0.70 1.0 1.5 2.0 5.0 H VALUE 24 – Oil – Oil – Oil – Oil – Water – Water – Brine – Brine – Ideal Quench QUENCH 28 – – – – – – – – No Moderate Good Strong No Strong No Strong AGITATION 32 Select proper round bar size to be quenched. Select the curve most representative of quenching conditions (H value) to be used. Read the curve to the Jominy Distance. Insert Rockwell “C” hardness values corresponding to the Jominy Distance. These are obtained from The Timken Company CENTER 1. 2. 3. 4. 0.20 BAR SIZE 0.35 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF CHART Hardenability Data available with each shipment of steel. These hardness values represent the approximate surface-to-center hardness obtainable for the type of steel being heat treated. CHART FOR PREDICTING APPROXIMATE CROSS SECTION HARDNESS OF QUENCHED ROUND BARS USING JOMINY TEST RESULTS 0.20 0.50 0.35 0.50 1.0 0.70 0.35 0.50 55 4" RD 3" RD 0 0.35 12 5.0 2.0 1.0 0.50 2.0 0.35 0.70 5.0 0.50 1.0 ∞ 5.0 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.70 2.0 5.0 ∞ 4 8 JOMINY DISTANCE 1.5 2" RD 0.50 SURFACE 16 0.20 1.0 0.20 0.70 ∞ 1/2 RADIUS SURFACE ∞ 0.20 0.35 0.50 0.70 1.0 1.5 2.0 5.0 H VALUE 20 1/2 RADIUS CENTER 0.35 0.70 1-1/2" RD 0.50 CENTER QUENCH 24 – Oil – Oil – Oil – Oil – Water – Water – Brine – Brine – Ideal Quench 0.20 0.35 BAR SIZE 28 – – – – – – – – SURFACE 1/2 RADIUS CENTER No Moderate Good Strong No Strong No Strong AGITATION 32 0.20 56 1.5 1.5 ∞ SURFACE 1/2 RADIUS CENTER 57 8" RD 7" RD 6" RD 5" RD BAR SIZE 0 4 8 JOMINY DISTANCE 12 16 ∞ 5.0 20 1.5 24 1.0 ∞ 0.70 28 5.0 32 0.35 1.5 ∞ 0.35 1.5 ∞ 0.35 0.70 1.5 0.35 0.50 SURFACE 1/2 RADIUS SURFACE CENTER 1/2 RADIUS SURFACE CENTER 1/2 RADIUS SURFACE CENTER 1/2 RADIUS CENTER EXPLANATION OF COMBINED HARDENABILITY CHARTS The following charts present hardenability data for thirteen popular steels. They may be used to determine the approximate mid-radius hardness which is developed, in various sized rounds up to 9" in diameter using a good oil quench (.4-.5 Hv), or rounds up to 15" in diameter when air cooling. The effect of a subsequent 1000°F 2 hour temper is also illustrated. The relationship between hardness and section size was determined using data from the Jominy end quench test, and air hardenability test, and controlled cooling tests. It must be remembered that the results for a particular steel type are based on one chemical analysis and one austenitizing temperature. Variations of these will affect hardenability, as shown by the Jominy hardenability bands (shaded area). Therefore, the charts should be used to determine estimated, rather than exact, hardness values. 1. S elect steel type. USE OF CHARTS 2. F ind desired diameter for the quenching medium employed. 3. R ead the approximate as-quenched or tempered hardness using the appropriate curve; read hardness range using hardenability band. For example, a 2-inch round made of 1045 type steel will develop the following mid-radius hardnesses: As-Cooled Tempered 1000 °F-2 Hours Mild Water Oil .4-.5 Hv Air 28(25/32) Rc 25(22/29) Rc 91Rb 22.5 Rc 21 Rc 91Rb 58 1045 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 59 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" S .023 Si .22 Cr .11 Ni .18 Mo .04 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" ~9" 48 F 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" Al — B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Cu .04 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS P .019 NORMALIZED 1600° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. Mn .79 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .42 HEAT TREATMENT 1340 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 60 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .011 S .013 Si .24 Cr .08 Ni .09 Mo .02 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" F 48 ~9" 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al .019 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .11 NORMALIZED 1600° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn 1.87 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .40 HEAT TREATMENT 3310 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 61 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .012 S .012 Si .25 Cr 1.56 Ni 3.42 Mo .05 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" ~9" 48 F 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 6" 10" 15" B — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" W — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE (FROM ASM HANDBOOK) 19° /M F 4" V — LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al .032 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .10 NORMALIZED 1700° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .54 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .08 HEAT TREATMENT 4027 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 62 5 55°F/S 2" P .011 S .027 Si .29 Cr .05 Ni .09 Mo .22 10 15 12°F/S 4" 3" 5" 20 7°F/S 4" 7" 6" 27 48 ~9" 4" 80°F/M AIR QUENCH 1" 290°F/M 200°F/M 6" 5" 19°F/M 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13°F/M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1600˚ F. 27°F/M 3" Al .032 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32°F/M 2" Cu .07 NORMALIZED 1650° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1600° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS 25°F/S 3" 2" Mn .86 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .26 HEAT TREATMENT 4130 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 63 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .013 S .020 Si .30 Cr .96 Ni .20 Mo .21 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" ~9" 48 F 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1600˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al — AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .12 NORMALIZED 1650° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1600° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .51 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .31 HEAT TREATMENT 4140 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 64 5 55°F/S 2" P .031 S .021 Si .31 Cr .96 Ni .13 Mo .20 10 15 12°F/S 4" 3" 5" 20 7°F/S 4" 7" 6" 27 ~9" 48 4" 80°F/M AIR QUENCH 1" 290°F/M 200°F/M 6" 5" 19°F/M 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13°F/M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27°F/M 3" Al — AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32°F/M 2" Cu .08 NORMALIZED 1600° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS 25°F/S 3" 2" Mn .82 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .39 HEAT TREATMENT 4320 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 65 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .010 S .014 Si .29 Cr .50 Ni 1.79 Mo .23 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" F 48 ~9" 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1700˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al .021 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .09 NORMALIZED 1700° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1700° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .61 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .18 HEAT TREATMENT 4340 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 66 5 55°F/S 2" 10 P .014 S .015 Si .30 Cr .72 Ni 1.75 Mo .26 15 12°F/S 4" 3" 5" 20 7°F/S 4" 7" 6" 27 ~9" 48 4" 80°F/M AIR QUENCH 1" 290°F/M 200°F/M 6" 5" 19°F/M 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13°F/M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27°F/M 3" Al — AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32°F/M 2" Cu .13 NORMALIZED 1600° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS 25°F/S 3" 2" Mn .74 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .41 HEAT TREATMENT 4620 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 67 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .013 S .019 Si .32 Cr .20 Ni 1.75 Mo .22 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" ~9" 48 F 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1700˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al — AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .05 NORMALIZED 1700° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1700° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .60 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .19 HEAT TREATMENT 5130 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 68 5 55°F/S 2" P .022 S .026 Si .26 Cr .98 Ni .09 Mo .02 10 15 12°F/S 4" 3" 5" 20 7°F/S 4" 7" 6" 27 ~9" 48 4" 80°F/M AIR QUENCH 1" 290°F/M 200°F/M 6" 5" 19°F/M 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13°F/M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1600˚ F. 27°F/M 3" Al .019 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32°F/M 2" Cu .14 NORMALIZED 1650° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1600° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS 25°F/S 3" 2" Mn .79 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .30 HEAT TREATMENT 5160 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 69 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .014 S .016 Si .29 Cr .78 Ni .07 Mo .01 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" F 48 ~9" 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" 11/4" /4" 3 B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 400˚ F. TEMPER 1000˚ F. TEMPER SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al .023 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .05 NORMALIZED 1600° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .91 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .58 HEAT TREATMENT 8620 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 70 5 55°F/S 2" P .010 S .014 Si .30 Cr .50 Ni .51 Mo .19 10 15 12°F/S 4" 3" 5" 20 7°F/S 4" 7" 6" 27 ~9" 48 4" 80°F/M AIR QUENCH 1" 290°F/M 200°F/M 6" 5" 19°F/M 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13°F/M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1700˚ F. 27°F/M 3" Al .031 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32°F/M 2" Cu .09 NORMALIZED 1700° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1700° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS 25°F/S 3" 2" Mn .85 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .20 HEAT TREATMENT 9310 BRINELL HARDNESS – 3000 KG. 107 128 150 185 230 283 372 484 614 COOLING RATE OIL QUENCH .4-.5 Hv MILD WATER QUENCH 60 70 80 90 20 30 40 50 60 CHEMICAL ANALYSIS TYPE ROCKWELL “C” HARDNESS ROCKWELL “B” HARDNESS 71 5 55° /S 2" F F 10 25° /S 3" 2" P .012 S .015 Si .30 Cr 1.26 Ni 3.26 Mo .11 F 15 12° /S 4" 3" 5" 20 7° /S F 4" 7" 27 F 6" ~9" 48 F 4" 80° /M F AIR QUENCH 1" 290° /M 200° /M 6" 5" 19° /M F 4" B — 6" 10" 15" W — 13° /M 12°F/M 9°F/M 6°F/M F 5" V — 11/4" /4" 3 21/2" 6" INTERFACE LEGEND AS COOLED 1000˚ F. TEMPER-2 HOURS SAE HARDENABILITY BAND AUSTENITIZING TEMPERATURE 1550˚ F. 27° /M F 3" Al .044 AIR HARDENABILITY DISTANCE 11/2" 32° /M F 2" Cu .11 NORMALIZED 1700° F. — AUSTENITIZED 1550° F. ROUND SECTION WITH SAME HARDNESS AT MID-RADIUS Mn .58 SIXTEENTHS FROM QUENCHED END OF JOMINY BAR 1" 1" C .10 HEAT TREATMENT 72 ROCKWELL C HARDNESS 10 20 30 40 50 60 .10 .20 .30 .40 .50 PERCENT CARBON .60 .70 Note: Fine divisions added to simplify use of the graph. Hodge, J. M. and Orehoski, M. A. Relationship between hardenability and percentage of martensite in some low-alloy steels. Transactions. AIME, 1946, v. 167, pp. 627-642. 50% MARTENSITE 80% MARTENSITE 90% MARTENSITE 99.9% MARTENSITE 95% MARTENSITE AVERAGE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CARBON CONTENT, HARDNESS AND PERCENTAGE OF MARTENSITE IN QUENCHING 414 552 690 828 TENSILE STRENGTH, MPa 966 1104 1241 1379 1517 1655 1793 1931 EFFECTS OF SURFACE CONDITIONS AND MECHANICAL NOTCHES ON ENDURANCE OR FATIGUE LIMITS 160 1140 ENDURANCE LIMIT, 1000 psi 828 120 POLISHED 690 100 GROUND 552 80 MACHINED 60 414 276 40 HOT ROLLED, SEVERLY NOTCHED, AS FORGED 20 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 TENSILE STRENGTH, 1000 psi 240 260 138 280 Note: Endurance limits for surfaces exposed to corrosive environment fall below the band for hot rolled, severly notched, and as forged surfaces. Conditions Which Affect Fatigue Strength The fatigue strength of a material depends on many factors of which the following are considered among the most important: (1) the strength of the material and the magnitude of the stress being applied to the material in its application, (2) the surface integrity of the material including its finish and method of manufacture, magnitude of residual stress present, and the presence of decarburization, (3) the environment in which the material is exposed in service. It must be noted that fatigue data such as that represented by the curves shown above are averages obtained from laboratory tests which approach ideal conditions and should not be considered more than a guide. F.B. Stulen and W.C. Schulte, Metals Engineering Quarterly (Am. Soc. Metals), Vol. 5, No. 3, Aug. 1965 SAE Fatigue Design Handbook (AE4) - 1968 Proceedings of the International Conference on Fatigue of Metals, (IME-ASME) - 1956 73 ENDURANCE LIMIT, MPa 966 140 CARBURIZING INFORMATION For .10% Carbon (Approx.) Higher Alloy Carburizing Steels, i.e., 3310, 9310, etc. “EFFECTIVE” CASE DEPTH for VARIOUS CARBURIZING TIMES AND TEMPERATURES (Calculated in Inches to .40% CARBON LEVEL) Carburizing Carburizing Temperature (°F) Time, Hours 1600° 1650° 1700° 1750° 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 .011" .015" .019" .021" .024" .026" .028" .030" .032" .034" .036" .013" .019" .023" .026" .030" .033" .035" .038" .040" .042" .044" .016" .023" .028" .033" .037" .040" .043" .046" .049" .052" .054" .019" .027" .034" .039" .044" .048" .052" .056" .059" .062" .065" 12 .037" .046" .057" .068" 16 .043" .053" .065" .078" 20 .048" .059" .073" .088" 24 .052" .065" .080" .096" 30 .059" .073" .089" .108" Note: Case depth tables are based on data published in Metals Progress Data Sheet in May 1974 by F. E. Harris. 74 CARBURIZING INFORMATION For .20% Carbon (Approx.) Lower Alloy Carburizing Steels, i.e., 4017, 4620, 8620, etc. “EFFECTIVE” CASE DEPTH for VARIOUS CARBURIZING TIMES AND TEMPERATURES (Calculated in Inches to .40% CARBON LEVEL) Carburizing Carburizing Temperature (°F) Time, Hours 1600° 1650° 1700° 1750° 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 .013" .018" .022" .025" .029" .031" .034" .036" .038" .040" .042" .015" .022" .027" .031" .034" .038" .041" .044" .046" .049" .051" .019" .026" .032" .037" .042" .045" .049" .053" .056" .059" .062" .022" .031" .039" .045" .050" .055" .059" .063" .067" .071" .073" 12 .044" .053" .065" .077" 16 .051" .061" .075" .088" 20 .057" .069" .084" .099" 24 .062" .075" .092" .109" 30 .070" .085" .103" .122" Note: Case depth tables are based on data published in Metals Progress Data Sheet in May 1974 by F. E. Harris 75 PROCESS AND QUALITY CONTROL CONSIDERATIONS DEW POINT, °F -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 2 SURFACE CARBON CONCENTRATION, % Austenite cementite Low-carbon steel 1 760° C 0.6 815° C Austenite + ferrite 870° C 0.4 925° C 980° C 0.2 1040° C Workpiece temperature 1150° C 1095° C 0.1 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 DEW POINT, °C Variation of carbon potential with dew point for an endothermic-based atmosphere containing 20% CO and 40% H2 in contact with plain carbon steel at various workpiece temperatures. 76 74 77 SURFACE CARBON CONCENTRATION, % 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.6 1 2 0.02 0.04 0.1 0.2 980° C 1040° C 925° C 0.4 CARBON DIOXIDE IN ATMOSPHERE, % 0.06 1095° C 0.6 870° C 815° C 1 760° C 2 Austenite + ferrite Low-carbon steel Variation of carbon potential with carbon dioxide concentration for an endothermic-based atmosphere containing 20% CO and 40% H2 in contact with plain carbon steel at various workpiece temperatures. 0.01 Workpiece temperature 1150° C Austenite cementite PROCESS AND QUALITY CONTROL CONSIDERATIONS 4 DETERMINING CARBURIZING TIMES AND TEMPERATURES 100 80 1, 50 0 F 60 1, 70 0 F 1, 60 0 F 40 1, 90 0 F 1, 80 0 F 20 10 6 4 400 2 200 1 100 CASE DEPTH, 0.001 in. TIME AT HEAT, Hr 8 80 60 40 20 11 12 13 14 15 10 PARAMETER, P TO USE THE CHART In the upper grid, select a point (time and temperature) for which the case depth results are known. Go vertically down from that point to the known case depth and plot the point. Pass a line through this point parallel to the dashed line shown. Projecting a line vertically upward from any point on this line into the grid will give the combinations of time and temperature that will result in the same depth of case. For instance, a vertical line drawn upward from the dashed line at 100 thousandths indicates that a 0.100 in. case will be produced by 6 hr. at 1900°F, 11 hr. at 1800°F, or 22 hr. at 1700°F. Shop experience of the Cook Heat Treat Co., Houston, is depicted by this line and its related points. Adapted from information provided by Charles F. Lewis, Cook Heat Treating Co., Div. Lindberg Corp. 78 79 1325 1315 1340 1325 1285 1280 1285 1265 1290 1260 1355 1350 1345 1355 1355 1355 2317 2330 2340 2345 2512 2515 3115 3120 3130 3140 3141 3150 1370 1350 1350 1350 1350 1350 1340 ............. ............. 1015 1020 1030 1035 1040 1045 1050 1065 1090 1330 1335 1340 1345 Ac1 SAE No. 1500 1480 1460 1410 1410 1380 1400 1400 1435 1360 1350 1335 1470 1460 1420 1420 1565 1555 1485 1475 1460 1440 1420 ............. ............. Ac3 Heating (°F) 1480 1445 1360 1275 1300 1275 1150 1160 1265 1205 1185 1125 1340 1340 1310 1300 1545 1515 1465 1440 1420 1405 1390 ............. ............. Ar3 1240 1230 1220 1225 1215 1215 1060 1090 1065 910/1050 1060 1040 1160 1165 1160 1160 1270 1270 1270 1270 1270 1270 1270 ............. ............. Ar1 Cooling (°F) ............. ............. ............. 1550 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 1450 ............. ............. 1550 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 1500 1625 ............. ............. ............. 630 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 580 ............. ............. 640 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 525 420 ............. ............. ............. 440 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 400 ............. ............. 450 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 300 175 Quench Temp °F Ms (°F) Mf (°F) 3115 3120 3130 3140 3141 3150 2512 2515 2317 2330 2340 2345 1330 1335 1340 1345 1015 1020 1030 1035 1040 1045 1050 1065 1090 SAE No. APPROXIMATE CRITICAL TEMPERATURES AND Ms/Mf POINTS OF CARBON AND ALLOY STEELS 80 1335 1335 1360 1340 1340 1310 1360 1365 1385 1380 1380 ............. 1390 ............. 1355 1350 ............. 1340 1300 1325 ............. 1285 1285 1290 1360 1370 1380 1360 3310 3316 4027 4032 4042 4053 4063 4068 4118 4130 4140 4147 4150 4160 4320 4340 4342 4615 4620 4640 4695* 4718 4815 4820 5045 5060 5120 5140 1430 1410 1525 1450 1500 1500 1460 1400 1390 1395 1500 1475 1460 ............. 1450 ............. 1485 1425 ............. 1485 1490 1400 ............. 1510 1450 1440 1440 1425 Ac3 Ar3 1305 1305 1460 1345 1400 1350 1340 1320 1220 1215 1410 1350 1370 ............. 1290 ............. 1330 1220 ............. 1400 1335 1220 ............. 1410 1310 1260 1235 1235 * Represents the case of 4600 grades of carburizing steels Ac1 SAE No. 1255 1285 1305 1230 1230 1250 1210 1200 1190 1195 1275 1250 1280 ............. 1245 ............. 840/1170 725/1210 ............. 1200 1220 875/1130 ............. 1200 860/1110 825/1110 1160 1160 Ar1 Cooling (°F) ............. ............. ............. 1550 ............. ............. 1500 ............. 1500 ............. ............. 1600 1500 1500 ............. 1575 ............. 1550 1500 ............. ............. 1550 1550 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 630 ............. ............. 610 ............. 445 ............. ............. 710 640 590 ............. 500 ............. 550 530 ............. ............. 640 255 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 460 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 550 425 ............. ............. ............. ............. 330 ............. ............. ............. 490 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. Quench Temp °F Ms (°F) Mf (°F) CRITICAL TEMPERATURES AND Ms/Mf POINTS – continued Heating (°F) 5045 5060 5120 5140 4027 4032 4042 4053 4063 4068 4118 4130 4140 4147 4150 4160 4320 4340 4342 4615 4620 4640 4695* 4718 4815 4820 3310 3316 SAE No. 81 1645 1480 1600 1700 1415 1415 1490 1455 ............. 1435 1520 1450 1410 1430 1350 1460 1525 1365 1260 1305 1290 ............. 1280 1400 1300 1265 1455 1400 1340 1275 1240 ............. 1350 1245 1280 1230 1275 1150 830/1080 800 ............. 1190 1200 1180 1190 1265 1200 1210 1170 1195 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 1450 1460 ............. ............. 1700 1575 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 410 325 ............. ............. 170 620 ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. 690 ............. ............. 275 305 260 620 ............. ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ ............ 410 ............ ............ ............ ............. ............. 540 ............ ............ ............ ............. ............. 460 ............. 9 Cr 1 Mo 17-22-A® 17-22-AS® 17-22-AV® Graph Mo® Graph Air® 9310 9317 9395* 9442 8720 8740 8750 8615 8620 8630 8640 8650 8695* 6117 6120 6140 6150 ............. 51100 ............. ............. 52100 ............. 52100 SAE No. Note: (1) All data in this table is empirically derived unless noted otherwise. (2) When two temperatures are given for Ar1, the higher represents the pearlitic reaction and the lower represents the bainitic reaction. (3) See USEFUL EQUATIONS FOR HARDENABLE ALLOY STEELS (see Table of Contents) for formulas to calculate approximate critical temperatures and Ms points. * Represents the case of 8600 and 9300 grades of carburizing steels, respectively. 1515 1370 1440 1435 1380 1275 1315 1300 ............. 1350 9310 9317 9395* 9442 9 Cr 1 Mo 17-22-A® 17-22-AS® 17-22-AV® Graph Mo® Graph Air® 1380 1350 1350 8720 8740 8750 1550 1525 1480 1435 1390 ............. ............. ............. 1600 ............. ............. 1500 1360 1350 1350 1350 1325 ............. 1270 1300 ............. 1275 8615 8620 8630 8640 8650 8695* 1430 1440 ............. 1375 1650 1740 1550 ............. 1560 1530 ............. 1450 ............. 345 305 260 Quench Temp °F Ms (°F) Mf (°F) 1400 1410 ............. 1380 Ar1 Cooling (°F) Ar3 6117 6120 6140 6150 Ac3 ............. 1560 1650 1740 Ac1 51100 1385 1415 1320 1300 52100 1340 1415 1320 1270 52100 52100 SAE No. CRITICAL TEMPERATURES AND Ms/Mf POINTS – continued Heating (°F) RECOMMENDED MAXIMUM HOT WORKING TEMPERATURES FOR STEELS Temperature (°F) SAE No. Temperature (°F) 1008 1010 1015 1040 1118 1141 2250 2250 2250 2200 4320 4337 4340 2200 2200 2200 4422 4427 2250 2250 1350 2200 4520 2250 2317 2340 2250 2200 4615 4620 4640 2300 2300 2200 2512 2250 4718 2250 3115 3135 3140 2250 2200 2200 4820 2250 5060 2150 3240 3310 3316 3335 4017 4032 4047 4063 2200 5120 5140 5160 2250 2200 2150 2300 2200 2200 2150 51100 52100 2050 2050 6120 6135 6150 2250 2250 2200 4130 4132 4135 4140 4142 2200 2200 2200 2200 2200 8617 8620 8630 8640 8650 2250 2250 2200 2200 2200 SAE No. 2250 2200 2250 2250 2250 82 RECOMMENDED MAXIMUM HOT WORKING TEMPERATURES FOR STEELS – continued SAE No. Timken Type Temperature (°F) 8720 8735 8740 9310 302 303 304 309 310 316 317 321 347 2200 2200 2200 2150 2050 2150 2150 2150 2150 410 416 420 430 440A 440C 443 446 2200 2200 2200 2100 2100 2050 2100 1900 Temperature (°F) 2250 2200 2200 2 1/4 Cr 1 Mo 5 Cr 1/2 Mo (.05C) 5 Cr 1/2 Mo (.15C) 2250 2250 2250 2250 5 Cr 1/2 Mo (.25C) 5 Cr 1/2 Mo + Ti 5 Cr 1/2 Mo + Si 7 Cr 1/2 Mo 9 Cr 1 Mo 2250 2100 2200 2250 2200 8 1/2 Ni 2200 Graph-Mo® Graph-Air® 1950 1925 5 Cr Mo (1.00C) 5Cr Mo W (1.00W) 2050 2300 10105 Nitriding #3 2050 2200 17-22A® 17-22AS® 17-22AV® 2200 2200 2250 A 485-1 A 485-2 A 485-3 A 485-4 2050 2050 2100 2100 TBS-600 2050 CBS-600 CBS-1000M 2250 2200 C-Mo 2300 DM 2300 DM-2 2300 NOTE: Information obtained from hot-twist test data publshed in “Evaluating The Forgeability of Steels” (3rd edition,The Timken Company) occasionally modified by actual Forge Shop experience. 83 MECHANICAL TUBING TOLERANCES Standard Timken Company Tolerances HOT ROLLED, ROUND1 OD Tolerances As rolled or single thermal treatment: • inches TOD 5 6 (.0045 OD 1 .005) or 6.015 min. • mm TOD 5 6 (.0045 OD 1 .13) or 6.38 min. • over 10.75 inches (273mm) to 12.0 inches (305mm) inches TOD 5 6.095 mm TOD 5 62.41 • greater than 12.00 inches (305mm) to 13 inches (330mm)—refer to mill Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered: • inches TOD 5 61.5 (.0045 OD 1 .005) or 6.023 min. • mm TOD 5 61.5 (.0045 OD 1 .13) or 6.58 min. • over 10.75 inches (273mm) to 12.00 inches (305 mm) inches TOD 5 6.113 mm TOD 5 62.87 Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) OD to wall ratio over 10:1 or over 10.75 inches (273 mm) to 13.00 inches (330 mm) OD (all OD to wall ratios) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610% OD to wall ratio of 10:1 or less . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67.5% Note: Minimum wall tolerance is 6.020 inch (.51mm). OD - Outside Diameter T - Tolerance ID - Inside Diameter W - Wall Thickness 1 Hot rolled and rough turned tubes can be purchased to outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness (W) only. Timken Company guaranteed tube sizes are calculated using Timken Company tolerances. 84 MECHANICAL TUBING TOLERANCE – continued Standard Timken Company Tolerances ROUGH TURNED, ROUND1 OD Tolerances As turned or single thermal treatment: • under 6.75 inches (171.5mm) inches TOD 5 6.005 mm TOD 5 6.13 • 6.75 inches (171.5mm) and over inches TOD 5 6.010 mm TOD 5 6.25 Straightened and/or tempered or stress relieved after rough turning: inches mm TOD 5 6.010 TOD 5 6.25 Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered: • Under 6.75 inches (171.5mm) Heat Treated Before Rough Turned TOD 5 6.010 inches (6.25mm) Heat Treated After Rough Turned TOD 5 6.015 inches (6.38mm) • 6.75 inches (171.5mm) and over Heat Treated Before Rough Turned TOD 5 6.020 inches (6.51mm) Heat Treated After Rough Turned TOD 5 6.030 inches (6.76mm) Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) OD to wall ratio over 10:1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 612.5% OD to wall ratio of 10:1 or less . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610.0% Note: Minimum wall tolerance is 6.020 inch (.51mm). OD - Outside Diameter T - Tolerance ID - Inside Diameter W - Wall Thickness 1 Hot rolled and rough turned tubes can be purchased to outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness (W) only. Timken Company guaranteed tube sizes are calculated using Timken Company tolerances. 85 MECHANICAL TUBING TOLERANCE – continued Standard Timken Company Tolerances COLD DRAWN, Round2 OD Tolerances As drawn: inches TOD/ID 5 6 (.0023 OD 2 .003) or 6.004 min. mm TOD/ID 5 6 (.0023 OD 2 .08) or 6.10 min. Drawn and annealed, normalized, tempered or stress relieved: inches TOD/ID 5 61.8 (.0023 OD 2 .003) or 6.007 min. mm TOD/ID 5 61.8 (.0023 OD 2 .08) or 6.18 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered (OD & wall or ID & wall dimensions only): inches TOD/ID 5 62.5 (.0023 OD 2 .003) or 6.010 min. mm TOD/ID 5 62.5 (.0023 OD 2 .08) or 6.25 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered (OD & ID dimensions only): inches TOD/ID 5 63.75 (.0023 OD 2 .003) or 6.015 min. mm TOD/ID 5 63.75 (.0023 OD 2 .08) or 6.38 min. Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) OD to wall ratio over 10:1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67.5% OD to wall ratio 10:1 to 4:1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66% OD to wall ratio under 4:1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67.5% Note: (1) Minimum wall tolerance is 6.012 inch (.30mm) (2) When ID is under 1.000 inch (25.4mm), inquiry basis (3) Walls 6% of OD and lighter, inquiry basis OD - Outside Diameter T - Tolerance ID - Inside Diameter W - Wall Thickness 2 Tubes with a final OD/W ratio less than 4:1 or a nominal finish wall size greater than 1.250 inches (31.75mm) will have a hot rolled ID and will be produced to cold drawn OD tolerances and hot rolled wall tolerances. ASTM A-519 tolerances are acceptable except for cold finished sizes smaller than 2.500 inches (63.50mm) diameter, where Timken Company tolerances apply. 86 MECHANICAL TUBING TOLERANCE – continued Standard Timken Company Tolerances (4) When OD & ID dimensions, use 67.5% wall ROTOROLLED®, ROUND OD Tolerances As Rotorolled®: inches TOD/ID 5 6 (.0024 OD 1 .0016) or 6.005 min. OD 6.010 min. ID mm TOD/ID 5 6 (.0024 OD 1 .041) or 6.13 min. Rotorolled® and annealed, normalized, tempered or stress relieved: inches TOD/ID 5 6 (.0024 OD 1 .007) or 6.010 min. mm TOD/ID 5 6 (.0024 OD 1 .18) or 6.25 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered (OD & wall or ID & wall dimensions only): inches TOD/ID 5 62 (.0024 OD 1 .0016) or 6.010 min. mm TOD/ID 5 62 (.0024 OD 1 .041) or 6.25 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered (OD & ID dimensions only): inches TOD/ID 5 63 (.0024 OD 1 .0016) or 6.015 min. mm TOD/ID 5 63 (.0024 OD 1 .041) or 6.38 min. Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) All wall thicknesses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65% Note: Minimum wall tolerance is 6.012 inches (.30mm) OD - Outside Diameter T - Tolerance ID - Inside Diameter 87 W - Wall Thickness MECHANICAL TUBING TOLERANCES Special Processed Tubing Tolerances COLD DRAWN, SHAPED (Square, Rectangular or Oval) OD Tolerances As drawn or tempered: inches TOD/ID 5 6.005 OD or 6.020 min. mm TOD 5 6.005 OD or 6.51 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered: inches TOD/ID 5 6.01 OD or 6.040 min. mm TOD/ID 5 6.01 OD or 61.02 min. Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) All wall thicknesses 610% at center of flats COLD DRAWN, SHAPED3 (Dissimilar OD and ID Configuration) OD Tolerances As drawn or tempered: inches TOD/ID 5 6.005 OD or 6.010 min. mm TOD/ID 5 6.005 OD or 6.25 min. Quenched and tempered, or normalized and tempered: inches TOD/ID 5 6.01 OD or 6.020 min. mm TOD/ID 5 6.01 OD or 6.51 min. Wall Tolerances (All Thermal Conditions) All wall thicknesses 610% at center of flats OD - Outside Diameter T - Tolerance ID - Inside Diameter W - Wall Thickness 3 When corner radii and twist are important, they must be reviewed by our mill before we accept the order. 88 LENGTH TOLERANCES All Conditions – Seamless Steel Tubing Random Lengths Tubing shipped on random-length orders has a length spread of 7 feet (2.1 meters) with a mean length 10 feet to 26 feet (3 to 8 meters) unless otherwise specified. Multiple Lengths For tubing ordered in multiple lengths, it is standard practice for the customer to make their own allowances for loss of steel due to cutting operations. These allowances will vary from one customer to another due to their cutting practices and the amount of facing required on the ends of the part. Therefore, tubing is furnished to the multiple length as specified by the individual customer. In Inches Specified Size Specified Length Outside Diameter 4 feet and under 4 feet and under 4 feet and under Over 4 feet to 10 feet, incl. Over 4 feet to 10 feet, incl. Over 10 feet to 24 feet, incl. Over 24 feet to 34 feet, incl. Over 34 feet to 44 feet, incl. Up to 2 inches incl. Over 2 inches to 4 inches incl. Over 4 inches Up to 2 inches incl. Over 2 inches All All All Permissible Variations Over Under 1/16 inch 0 3/32 inch 0 1/8 inch 3/32 inch 1/8 inch 3/16 inch 5/16 inch 7/16 inch 0 0 0 0 0 0 In Meters Specified Size Specified Length Outside Diameter Over Under 1 meter and under 1 meter and under 1mm 0 2mm 0 1 meter and under Over 1 meter to 3 meters Over 1 meter to 3 meters Over 3 meters to 7 meters Over 7 meters to 10 meters Over 10 meters to 13 meters Up to 50mm incl. Over 50mm to 100mm incl. Over 100mm Up to 50mm incl. Over 50mm All All All 89 Permissible Variations 3mm 2mm 3mm 5mm 8mm 11mm 0 0 0 0 0 0 STRAIGHTNESS TOLERANCES All Conditions – Seamless Steel Tubing Straightness tolerances (T) should not exceed those shown in the tables below. The tolerance (T) for any 3-foot (1 meter) length is measured as shown in Figure 1. The total tolerance, the maximum curvature in the total length, is measured as shown in Figure 2. The table applies to lengths not exceeding 22 feet (6.7 meters). The tolerances shown apply to conventional steel grades of as rolled, annealed, and heat treated tubing up to 302 Brinell maximum or micro alloy grades with a hardness of 229 Brinell or below. Heat treated tubes with a Brinell hardness of 302 maximum up to 401 maximum or micro alloy grades with a Brinell hardness exceeding 229 will have tolerance (T) twice the values shown in the table. Tubes with lighter walls, or with hardness exceeding 401 Brinell maximum, or weighing greater than 140 pounds per foot, require agreement on tolerances at time of order. FIGURE 1 Measuring technique for straightness in any three feet T max Three foot (one meter) straight-edge FIGURE 2 Measuring technique for overall straightness L Surface plate T max 90 91 Maximum Curvature in Total Lengths of 5 feet or more Ratio of 1.65mm per meter OD over 200mm to 280mm inclusive. 1.65mm Wall thickness, over 4% of OD 1.25 mm 3 length in meters Ratio of 1.25mm per meter Maximum Curvature for Lengths Under 1.5 meters OD over 125mm to 200mm inclusive. 1.25mm .85mm 3 length in meters Wall thickness, over 4% of OD Maximum Curvature in Total Lengths of 1.5 meters or more Ratio of 0.020 inch per foot Ratio of .85mm per meter Maximum Curvature in 1 meter .045 inch 3 length in feet 3 Ratio of 0.015 inch per foot Ratio of .010 inch per foot Maximum Curvature for Lengths Under 5 feet OD 125mm and smaller. Wall .85mm .55mm 3 length in meters thickness, over 3% of OD In Meters Specified Size OD over 8 inches to 11 inches .060 inch inclusive. Wall thickness, over 4% of OD .020 inch 3 length in feet 3 OD over 5 inches to 8 inches .045 inch .030 inch 3 length in feet inclusive. Wall thickness, over 3 4% of OD Maximum Curvature in any 3 feet OD 5 inches and smaller. Wall .030 inch thickness, over 3% of OD In Inches Specified Size STRAIGHTNESS TOLERANCES – continued All Conditions—Seamless Steel Tubing SEAMLESS STEEL TUBING SHAPES W � 10.68 (D � t) t M � .02466 (D � t) t A � � (D � t) t W � 10.68 (D � et) et M � .02466 (D � et) et et � D � 1.050 d 2 ed � 1.050 d W � 11.27 (D � t) t M � .02601 (D � t) t eD � 1.027 D ed � 1.027 d W � 10.68 (eD � et) et M � .02466 (eD � et) et et � 1.050 D � d 2 eD � 1.050 D W � 11.78 (D � t) t M � .02719 (D � t) t eD � 1.050 D ed � 1.050 d W � 10.68 (D � et) et M � .02466 (D � et) et et � D � 1.128 d 2 ed � 1.128 d W � 13.60 (D � t) t M � .03138 (D � t) t eD � 1.128 D ed � 1.128 d W � 10.68 (D � et) et M � .02466 (D � et) et et � D � 1.027 d 2 ed � 1.027 d 92 SEAMLESS STEEL TUBING SHAPES – continued W � 10.68 (eD � et) et M � .02466 (eD � et) et et � 1.027 D � d 2 eD � 1.027 D W � 13.60 (D � t) t M � .03138 (D � t) t eD � 1.128 D ed � 1.128 d W � 10.68 (D � et) et M � .02466 (D � et) et et � D � .7425 d 2 ed � .7425 d W � 5.34 (D1 � D2 � 2t) t M � .01233 (D1 � D2 � 2t) t eD � D1 � D2 2 ed � d1 � d2 2 Legend A 5 Tubing cross sectional area. Round OD and ID. ed 5 Equivalent round inside diameter in inches (or millimeters) W 5 Weight in pounds per foot et 5 Equivalent wall thickness in inches (or millimeters) M 5 Mass in kilograms per meter D1 5 Major outside diameter of oval tube in inches (or millimeters) D 5 Outside diameter or distance across flats in inches (or millimeters) d1 5 Major inside diameter of oval tube in inches (or millimeters) d 5 Inside diameter or distance across flats in inches (or millimeters) t5 D2 5 Minor outside diameter of oval tube in inches (or millimeters) d2 5 Minor inside diameter of oval tube in inches (or millimeters) Wall thickness in inches (or millimeters) eD 5 Equivalent round outside diameter in inches (or millimeters) 93 TUBE SIZE CALCULATIONS How Mechanical Tube Sizes Are Calculated The Timken Company has pioneered a method to determine the most economical tube size, which insures that all part dimensions will clean up during machining. This program has the capability to determine what we call a “guaranteed” tube size for either full or bright metal cleanup on the outer diameter and/or the inner diameter, based on the condition of the tube. The guaranteed tube size is based on the part’s critical finished dimensions and critical machining position. The required critical dimensions are: 1) maximum finished OD, 2) minimum finished ID, and 3) maximum finished part length. All applicable tolerances and surface finishes (“machined” or “ground”) should be included. The critical machining position is based on whether the tube is chucked on the tube OD or the tube ID during the initial machining operation. Critical finished part dimensions and machining position influence the amount of cleanup, the size tolerances and the tube eccentricity variables. These variables are then factored into the tube size calculation. Cleanup Allowance “Cleanup allowance” must be added to the finished OD dimension or subtracted from the finished ID dimension to provide for the elimination of surface imperfections, decarburization and camber (out-of-straightness). Other allowances specific to the application may be needed. (See table, page 98.) Examples of Tube Size Calculation Finished Part Dimensions 4.995 inches 6.005 inch OD 3 4.005 inches 6.005 inch ID 3 7 inches. Part is cut to length and held on one end. Allowance for camber is made for parts over 3 inches, measured from the end of the part to the face of the chuck. Examples on page 96 are for a hot rolled tube using Timken Company cleanup allowances. 94 7 inches TUBE SIZE CALCULATIONS – continued Figure 1 Cross section of finished part requiring full cleanup of OD and ID surfaces. Figure 2 Finished part with addition of cleanup stock to OD. (Refer to Example 1, Operation 1, page 96.) Figure 3 Finished part showing cleanup stock added to ID. (Refer to Example 1, Operaton 2.) Figure 4 Finished part with cleanup allowance added to OD and ID determines minimum wall required for part to clean up. (Refer to Example 1, Operation 3.) Were it not for eccentricity, this would be the recommended tube size. Figure 5 Same tube size machined true to OD showing effect of tube eccentricity. Tube ID is eccentric in relation to tube OD. Note that cleanup stock (dashed line) has been eliminated at A due to tube eccentricity. Part would not clean up at this point. Figure 6 Here enough stock has been added to ID to protect cleanup stock required at minimum wall point A. (Refer to Example 1, Operations 4 and 5.) When machining true to the ID, similar considerations apply except that stock to compensate for eccentricity is added to the tube OD. (See Example 2, page 97.) 95 96 Tube OD (Operation 1) Minus average wall doubled 2 Required tube ID 5. Determine nominal tube ID (see Figure 6) .589 in .925 4 .637 in 5.109 in 1.274 in 2 3.835 in Guaranteed Tube Size: 5.109 inches OD 6.028 inches 3 .637 inches 67.5% Theoretical Foot Weight: 30.42 lbs. Minimum tube wall Divide by the complement of minus tolerance 4 Average tube wall 5.109 in 3.931 in 2 1.178 in 2 4 .589 in 3. Determine minimum wall required Tube OD (Operation 1) (see Figure 4) Minus tube ID (Operation 2) 2 Divide by 2 4 Minimum tube wall 4. Determine average wall required (see Figure 6) 4.000 in .042 in 2 .027 in 2 3.931 in Minimum machined ID Minus cleanup stock 2 Minus camber allowance 2 Maximum tube ID Example 5.000 in .054 in 1 .027 in 1 .028 in 1 5.109 in 2. Determine maximum tube ID (see Figure 3) Formula Maximum machined OD Plus cleanup stock 1 Plus camber allowance 1 Plus OD negative tolerance 1 Nominal tube OD 1. Determine nominal tube OD (see Figure 2, page 95) Operation Example 1 – Machined True to OD TUBE SIZE CALCULATIONS – continued 129.77mm 32.34mm 97.43mm 14.95mm .925 16.17mm 129.77mm 99.84mm 29.93mm 2 14.96mm 101.60mm 1.07mm .69mm 99.84mm 127.00mm 1.37mm .69mm .71mm 129.77mm 97 Nominal tube ID (Operation 2) Plus average wall doubled 1 Nominal tube OD 5. Determine nominal tube OD .604 in .925 4 .653 in 3.861 in 1.306 in 1 5.167 in Guaranteed Tube Size: 5.167 inches OD 6.028 inches 3 .653 inches 67.5% Theoretical Foot Weight: 31.48 lbs. Minimum tube wall (Operation 3) Divide by the complement of minus tolerance 4 Average tube wall 5.069 in 3.861 in 2 1.208 in 2 4 .604 in 3. Determine minimum wall required Minimum tube OD (Operation 1) Minus nominal tube ID (Operation 2) 2 Divide by 2 4 Minimum tube wall 4. Determine average wall required 4.000 in .054 in 2 .027 in 2 .028 in 2 .030 in 2 3.861 in Minimum machined ID Minus minimum OD cleanup 2 Minus camber allowance 2 Minus OD tolerance 2 Minus (if hot rolled) 2 Nominal tube ID Example 5.000 in .042 in 1 .027 in 1 5.069 in 2. Determine nominal tube ID Formula Maximum machined OD Plus ID cleanup stock 1 Plus camber allowance 1 Minimum tube OD 1. Determine minimum tube OD Operation to the tube OD. This will result in a larger recommended tube size. 98.07mm 33.19mm 131.26mm 15.35mm .925 16.59mm 128.76mm 98.07mm 30.69mm 2 15.35mm 101.60mm 1.37mm .69mm .71mm .76mm 98.07mm 127.00mm 1.07mm .69mm 128.76mm When machining true to the ID, similar considerations apply, except that stock to compensate for tube eccentricity is added Example 2 – Machined True to ID TUBE SIZE CALCULATIONS – continued 98 Cleanup (inches) 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 12.0 0.762 0.508 0.254 0.03 0.02 0.01 Note: Total stock removal is calculated for the tube diameter Outside Diameter (inches) 1.016 0.04 11.0 1.270 0.05 10.0 1.524 0.06 9.0 1.778 0.07 2.032 2.286 0.08 2.540 0.09 3.048 3.302 3.556 3.810 2.794 2.0 304.80 0.10 1.0 279.40 HR-CD-ID Cleanup HR-OD Clean-up 254.00 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 CD-OD Cleanup 228.00 4.064 152.40 177.80 203.20 4.318 127.00 Outside Diameter (mm) 0.16 101.60 4.572 76.20 0.17 50.80 0.18 25.40 HOT ROLLED AND COLD DRAWN MECHANICAL TUBING CLEANUPS FOR FULL SURFACE INTEGRITY AND BASE METAL Cleanup (mm) Formulas for Calculating Surface Cleanup Hot Rolled OD Cleanup 5 [.022e.18 OD] Cold Drawn OD Cleanup 5 .86[.022e.18 OD] Hot Rolled and Cold Drawn ID Cleanup 5 .78[.022e.18 OD] Formulas for Calculating CAMBER (STRAIGHTNESS) CLEANUP Chucked on one end: • Part length 3 inches or less—no camber added • Part length over 3 inches—double the part length to calculate camber. Chucked on both ends: • Length 6 inches or less—no camber added • Length over 6 inches—use formulas below (do not double part length). Formulas (Calculate all length dimensions in inches): A) OD , 5.000 inches 5 (171 3 length) 2 444 2 (1.03 3 length squared) 100,000 B) OD $ 5.000 inches 5 (222 3 length) 2 222 2 (1.13 3 length squared) 100,000 C) OD , 5.000 inches and Part Length . 60 inches 5 450 1 (25 3 length) 30,000 D)OD 5.000 inches and Part Length . 60 inches: Use formula C 1 .030 inches 99 Bar Cross Sectional Tolerances For Hot Rolled steel Bars Specified Size of Rounds or Squares (inches) To 5/16 incl. Over 5/16 to 7/16 incl. Over 7/16 to 5/8 incl. Over 5/8 to 7/8 incl. Over 7/8 to 1 incl. Over 1 to 1-1/8 incl. Over 1-1/8 to 1-1/4 incl. Over 1-1/4 to 1-3/8 incl. Over 1-3/8 to 1-1/2 incl. Over 1-1/2 to 2 incl. Over 2 to 2-1/2 incl. Over 2-1/2 to 3-1/2 incl. Over 3-1/2 to 4-1/2 incl. Over 4-1/2 to 5-1/2 incl. Over 5-1/2 to 6-1/2 incl. Over 6-1/2 to 8-1/4 incl. Over 8-1/4 to 9-1/2 incl. Over 9-1/2 to 10 incl. Variation from Size Over (inches) Under (inches) Out-of-Round or Square (inches) .005 .006 .007 .008 .009 .010 .011 .012 .014 1/64 1/32 3/64 1/16 5/64 1/8 5/32 3/16 1/4 .005 .006 .007 .008 .009 .010 .011 .012 .014 1/64 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 .008 .009 .010 .012 .013 .015 .016 .018 .021 .023 .023 .035 .046 .058 .070 .085 .100 .120 BAR Length Tolerances FOR HOT ROLLED steel BARS Specified Sizes of Rounds, Squares, Hexagons, Octagons (inches) Up to 3-1/2, incl. Over 3-1/2 to 5, incl. Over 5 to 12 incl. 10' to 20' Excl. 20' to 30' Excl. 30' to 40' Excl. 40' to 60' Excl. 1-1/2 2 2-1/2 1-3/4 2-1/4 2-3/4 2-1/4 2-5/8 3 2-3/4 3 3-1/4 No Tolerance Under 100 STRAIGHTNESS TOLERANCE HOT ROLLED STEEL BARS Rounds, Squares, Hexagons, Octagons, Flats, and SpringFlats Measurement is taken on the concave side of the bar with a straight edge. Normal Straightness 1⁄4" Special Straightness 1⁄8" in any 5 ft. and in any 5 ft. and length in ft. length in ft. 1⁄8" 3 1⁄4" 3 5 5 Note: Because of warpage, straightness tolerances do not apply to bars if any subsequent heating operation or controlled cooling has been performed. Note: Tolerances shown are based upon ASTM A29 MACHINING ALLOWANCE FOR HOT ROLLED BARS Minimum Stock Removal (diameter) Standard Grades Resulfurized Grades 1.6% per side 2.4% per side Note: Based on bars within special straightness tolerance. Since straightness is a function of length, additional machining allowance may be required for turning on centers. 101 MASTER WEIGHT TABLES FOR ROUNDS AND SQUARES Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 1/8" 9/64" 5/32" 11/64" .0531 .0672 .0830 .1004 .0417 .0528 .0652 .0789 3/16" 13/64" 7/32" 15/64" .1195 .1403 .1627 .1868 1/4" 17/64" 9/32" 19/64" Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 3/4" 49/64" 25/32" 51/64" 1.9125 1.9930 2.0752 2.1590 1.5021 1.5653 1.6299 1.6957 .0939 .1102 .1278 .1467 13/16" 53/64" 27/32" 55/64" 2.2445 2.3317 2.4205 2.5110 1.7629 1.8313 1.9011 1.9721 .2125 .2399 .2689 .2997 .1669 .1884 .2112 .2354 7/8" 57/64" 29/32" 59/64" 2.6031 2.6969 2.7924 2.8895 2.0445 2.1182 2.1931 2.2694 5/16" 21/64" 11/32" 23/64" .3320 .3661 .4018 .4391 .2608 .2875 .3155 .3449 15/16" 61/64" 31/32" 63/64" 2.9883 3.0887 3.1908 3.2946 2.3470 2.4259 2.5061 2.5876 3/8" 25/64" 13/32" 27/64" .4781 .5188 .5611 .6051 .3755 .4075 .4407 .4753 1" 1-1/32" 1-1/16" 1-3/32" 3.400 3.616 3.838 4.067 2.6704 2.8399 3.0146 3.1945 7/16" 29/64" 15/32" 31/64" .6508 .6981 .7471 .7977 .5111 .5483 .5867 .6265 1-1/8" 1-5/32" 1-3/16" 1-7/32" 4.303 4.546 4.795 5.050 3.3797 3.5700 3.7656 3.9664 1/2" 33/64" 17/32" 35/64" .8500 .9040 .9596 1.0168 .6676 .7100 .7536 .7986 1-1/4" 1-9/32" 1-5/16" 1-11/32" 5.313 5.581 5.587 6.139 4.1724 4.3836 4.6001 4.8218 9/16" 37/64" 19/32" 39/64" 1.0758 1.1364 1.1986 1.2625 .8449 .8925 .9414 .9916 1-3/8" 1-13/32" 1-7/16" 1-15/32" 6.428 6.724 7.026 7.335 5.0486 5.2807 5.5180 5.7606 5/8" 41/64" 21/32" 43/64" 1.3281 1.3954 1.4643 1.5348 1.0431 1.0959 1.1500 1.2054 1-1/2" 1-17/32" 1-9/16" 1-19/32" 7.650 7.972 8.301 8.636 6.0083 6.2612 6.5194 6.7838 11/16" 45/64" 23/32" 47/64" 1.6070 1.6809 1.7564 1.8336 1.2622 1.3202 1.3795 1.4401 1-5/8" 1-21/32" 1-11/16" 1-23/32" 8.978 9.327 9.682 10.044 “Round Cornered” squares differ in weight from above schedule. 102 7.0514 7.3252 7.6043 7.8885 MASTER WEIGHT TABLES FOR ROUNDS AND SQUARES – continued Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 1-3/4" 1-25/32" 1-13/16" 1-27/32" 10.413 10.788 11.170 11.558 8.1780 8.4726 8.7725 9.0776 3" 3-1/32" 3-1/16" 3-3/32" 30.600 31.241 31.888 32.542 24.033 24.537 25.045 25.559 1-7/8" 1-29/32" 1-15/16" 1-31/32" 11.953 12.355 12.763 13.178 9.3880 9.7035 10.0243 10.3502 3-1/8" 3-5/32" 3-3/16" 3-7/32" 33.203 33.871 34.545 35.225 26.078 26.602 27.131 27.666 2" 2-1/32" 2-1/16" 2-3/32" 13.600 14.028 14.463 14.905 10.6814 11.0178 11.3595 11.7063 3-1/4" 3-9/32" 3-5/16" 3-11/32" 35.913 36.606 37.307 38.014 28.206 28.751 29.301 29.856 2-1/8" 2-5/32" 2-3/16" 2-7/32" 15.353 15.808 16.270 16.738 12.0583 12.4156 12.7781 13.1458 3-3/8" 3-13/32" 3-7/16" 3-15/32" 38.728 39.449 40.176 40.910 30.417 30.983 31.554 32.130 2-1/4" 2-9/32" 2-5/16" 2-11/32" 17.213 17.694 18.182 18.677 13.5187 13.8968 14.2802 14.6687 3-1/2" 3-9/16" 3-5/8" 3-11/16" 41.650 43.151 44.678 46.232 32.712 33.891 35.090 36.311 2-3/8" 2-13/32" 2-7/16" 2-15/32" 19.178 19.686 20.201 20.722 15.0625 15.4615 15.8657 16.2751 3-3/4" 3-13/16" 3-7/8" 3-15/16" 47.813 49.420 51.053 52.713 37.552 38.814 40.097 41.401 2-1/2" 2-17/32" 2-9/16" 2-19/32" 21.250 21.785 22.326 22.874 16.6898 17.1096 17.5346 17.9650 4" 4-1/16" 4-1/8" 4-3/16" 54.400 56.113 57.853 59.620 42.726 44.071 45.438 46.825 2-5/8" 2-21/32" 2-11/16" 2-23/32" 23.428 23.989 24.557 25.131 18.4004 18.8410 19.2870 19.7382 4-1/4" 4-5/16" 4-3/8" 4-7/16" 61.413 63.232 65.078 66.951 48.233 49.662 51.112 52.583 2-3/4" 2-25/32" 2-13/16" 2-27/32" 25.713 26.300 26.895 27.496 20.1946 20.656 21.123 21.595 4-1/2" 4-9/16" 4-5/8" 4-11/16" 68.850 70.776 72.728 74.707 54.075 55.587 57.121 58.675 2-7/8" 2-29/32" 2-15/16" 2-31/32" 28.103 28.717 29.338 29.996 22.072 22.555 23.042 23.535 4-3/4" 4-13/16" 4-7/8" 4-15/16" 76.713 78.745 80.803 82.888 60.250 61.846 63.463 65.100 “Round Cornered” squares differ in weight from above schedule. 103 MASTER WEIGHT TABLES FOR ROUNDS AND SQUARES – continued Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 5" 5-1/16" 5-1/8" 5-3/16" 85.000 87.138 89.303 91.495 66.759 68.438 70.139 71.860 7-1/2" 7-9/16" 7-5/8" 7-11/16" 191.25 194.45 197.68 200.93 150.21 152.72 155.26 157.81 5-1/4" 5-5/16" 5-3/8" 5-7/16" 93.713 95.957 98.228 100.526 73.602 75.364 77.148 78.953 7-3/4" 7-13/16" 7-7/8" 7-15/16" 204.21 207.52 210.85 214.21 160.39 162.99 165.60 168.24 5-1/2" 5-9/16" 5-5/8" 5-11/16" 102.850 105.20 107.58 109.98 80.778 82.62 84.49 86.38 8" 8-1/16" 8-1/8" 8-3/16" 217.60 221.01 224.45 227.92 170.90 173.58 176.29 179.01 5-3/4" 5-13/16" 5-7/8" 5-15/16" 112.41 114.87 117.35 119.86 88.29 90.22 92.17 94.14 8-1/4" 8-5/16" 8-3/8" 8-7/16" 231.41 234.93 238.48 242.05 181.75 184.52 187.30 190.11 6" 6-1/16" 6-1/8" 6-3/16" 122.40 124.96 127.55 130.17 96.13 98.15 100.18 102.24 8-1/2" 8-9/16" 8-5/8" 8-11/16" 245.65 249.28 252.93 256.61 192.93 195.78 198.65 201.54 6-1/4" 6-5/16" 6-3/8" 6-7/16" 132.81 135.48 138.18 140.90 104.31 106.41 108.53 110.66 8-3/4" 8-13/16" 8-7/8" 8-15/16" 260.31 264.04 267.80 271.59 204.45 207.38 210.33 213.31 6-1/2" 6-9/16" 6-5/8" 6-11/16" 143.65 146.43 149.23 152.06 112.82 115.00 117.20 119.43 9" 9-1/16" 9-1/8" 9-3/16" 275.40 279.2 283.1 287.0 216.30 219.3 222.4 225.4 6-3/4" 6-13/16" 6-7/8" 6-15/16" 154.91 157.79 160.70 163.64 121.67 123.93 126.22 128.52 9-1/4" 9-5/16" 9-3/8" 9-7/16" 290.9 294.9 298.8 302.8 228.5 231.6 234.7 237.8 7" 7-1/16" 7-1/8" 7-3/16" 166.60 169.59 172.60 175.64 130.85 133.19 135.56 137.95 9-1/2" 9-9/16" 9-5/8" 9-11/16" 306.8 310.9 315.0 319.1 241.0 244.2 247.4 250.6 7-1/4" 7-5/16" 7-3/8" 7-7/16" 178.71 181.81 184.93 188.08 140.36 142.79 145.24 147.71 9-3/4" 9-13/16" 9-7/8" 9-15/32" 323.2 327.4 331.6 335.8 253.9 257.1 260.4 263.7 “Round Cornered” squares differ in weight from above schedule. 104 MASTER WEIGHT TABLES FOR ROUNDS AND SQUARES – continued Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 10" 10-1/16" 10-1/8" 10-3/16" 340.0 344.3 348.5 352.9 267.0 270.4 273.8 277.1 10-1/4" 10-5/16" 10-3/8" 10-7/16" 357.2 361.6 366.0 370.4 10-1/2" 10-9/16" 10-5/8" 10-11/16" Weight Per Ft. - in Lbs. Size Sq. Cor. Squares Rounds 11-3/4" 11-13/16" 11-7/8" 11-15/16" 469.4 474.4 479.5 484.5 368.7 372.6 376.6 380.5 280.6 284.0 287.4 290.9 12" 12-1/16" 12-1/8" 12-3/16" 489.6 494.6 499.8 505.0 384.5 388.5 392.5 396.6 374.9 379.3 383.8 388.4 294.4 297.9 301.5 305.0 12-1/4" 12-5/16" 12-3/8" 12-7/16" 510.2 515.4 520.6 525.9 400.7 404.8 408.9 413.0 10-3/4" 10-13/16" 10-7/8" 10-15/16" 392.9 397.5 402.1 406.7 308.6 312.2 315.8 319.5 12-1/2" 13" 13-1/2" 14" 531.2 575 620 666 417.2 451 487 523 11" 11-1/16" 11-1/8" 11-3/16" 411.4 416.1 420.8 425.5 323.1 326.8 330.5 334.2 14-1/2" 15" 15-1/2" 16" 715 765 817 871 561 601 642 684 11-1/4" 11-5/16" 11-3/8" 11-7/16" 430.3 435.1 439.9 448.8 337.9 341.7 345.5 349.3 16-1/2" 17" 17-1/2" 18" 926 982 1040 1102 727 772 818 865 11-1/2" 11-9/16" 11-5/8" 11-11/16" 449.6 454.6 459.5 464.4 353.1 357.0 360.9 364.8 18-1/2" 19" 19-1/2" 20" 1164 1227 1293 1360 914 964 1015 1068 “Round Cornered” squares differ in weight from above schedule. 105 Reduction Ratios for Round Bars Product Diameter (inches) As Cast Size 28" Square Product Diameter (inches) 14" x 11.75" 15.000 4.4 14.500 4.7 14.000 5.1 13.500 5.5 13.000 5.9 — — — — — 12.500 6.4 12.000 6.9 11.500 7.5 — — 1.6 11.000 8.2 10.500 9.1 10.000 10.0 1.7 1.9 2.1 9.500 9.000 8.500 11.1 12.3 13.8 2.3 2.6 2.9 8.000 7.500 7.000 15.6 17.7 20.4 3.3 3.7 4.3 As Cast Size 28" Square 14" x 11.75" 6.500 23.6 5.0 6.000 27.7 5.8 5.500 33.0 6.9 5.000 39.9 8.4 4.500 49.3 10.3 4.000 62.4 13.1 3.500 81.5 17.1 3.000 110.9 23.3 2.500 159.7 33.5 2.000 1.500 1.000 249.6 52.4 443.7 93.1 998.2 209.4 Reduction Ratios for SQUARE Bars Product Diameter (inches) As Cast Size 28" Square 14" x 11.75" 15.000 3.5 14.500 3.7 14.000 4.0 13.500 4.3 13.000 4.6 — — — — — 12.500 5.0 12.000 5.4 11.500 5.9 — — 1.2 11.000 6.5 10.500 7.1 10.000 7.8 1.4 1.5 1.6 9.500 8.7 9.000 9.7 8.500 10.9 1.8 2.0 2.3 8.000 7.500 7.000 2.6 2.9 3.4 12.3 13.9 16.0 Product Diameter (inches) As Cast Size 28" Square 14" x 11.75" 6.500 18.6 3.9 6.000 21.8 4.6 5.500 25.9 5.4 5.000 31.4 6.6 4.500 38.7 8.1 4.000 49.0 10.3 3.500 64.0 13.4 3.000 87.1 18.3 2.500 125.4 26.3 2.000 1.500 1.000 106 196.0 41.1 348.4 73.1 784.0 164.5 IRON CARBON PHASE DIAGRAM Temperature °F CM 3000 2802 2800 2720 +L Temperature °C = Austenite = Ferrite = Delta iron = Cementite 2600 2552 1539 1492 L + +L 1400 2400 2200 L + Fe3C 2066° F 2066 2000 1130 Fe3C 1800 1670 1600 1400 1333 1200 1000 410 910 + Fe3C + 0.025 A1,2,3 1333° F Pearlite and Ferrite Austenite to Pearlite 760 723 Pearlite and Cementite + Fe3C Magnetic change of Fe3C 0.008% 0.50% 6.67 0.83% 1% Hypo-eutectoid 2% 3% 4% Hyper-eutectoid Steel Cast Iron 107 5% 210 6% 65% – CALCULATIONS FOR X AND R CHARTS AND CAPABILITY CONTROL CHARTS FOR VARIABLES PROCESS CAPABILITY – Calculate the Average (X) and Range (R) of each subgroup ˆ Estimated σ – (σ) σˆ 5 R/d2 X1 1 X2 1 . . . . . Xn – X5 n Estimated Process Capability (Cp) R 5 Xmax 2 Xmin Cp 5 – Calculate the Average Range (R) – and the process Average (X) = X5 Estimated Capability Ratio (Cr) X1 1 X2 1 . . . . . Xk k Cr 5 1/Cp 3 100 (%) R1 1 R2 1 . . . . . Rk – R5 k Estimated Process Capability (Cpk) CPU 5 Calculate the Control Limits = _ – UCL X 5 X 1 A2R = _ – LCL X 5 X 2 A2R USL 2 LSL 6σˆ – UCLR 5 D4R – LCLR 5 D3R = USL 2 X 3σˆ = X 2 LSL CPL 5 3σˆ CPK 5 Minimum of CPU or CPL Note:A2, D3, D4, d2 factors are dependent on subgroup size (n). See factor values table. Note:Calculations of Process capability (Cp, Cpk, Cr) are only valid for stable processes. FACTOR VALUES N D4 = 2 3 4 3.27 2.57 2.28 5 6 NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 12 2.11 2.00 1.72 D3 * * * A2 1.86 1.02 0.73 0.58 0.48 0.27 * * 0.26 d2 1.13 1.69 2.06 2.33 2.53 3.26 -3s * No constant for subgroup sizes below 7. 108 -2s -1s X +1s 68.3% 95.4% 99.7% +2s +3s CONTROL CHARTS FOR ATTRIBUTES The p p Chart Chart The The u Chart The u Chart – number of rejects in subgroup – total total nonconformities _p nonconformities 5 number of rejects in subgroup _ u __________________ 5 p = _________________________ number inspected in subgroups u = total units inspected total units inspected number inspected _ _in subgroups _ 3√u – 3√p ( 12 p ) – UCLP 5 P 1 UCL u5 u 1 ______ _ _ _ _ _ √n3√ u 3√ √np ( 1- p ) UCLu = u + _____ UCLP = P + _________ _ √_n _ – 3√ p ( 12 p ) _ _ LCLP 5 P 2_ 3√ √np ( 1- p ) LCLP = P - _________ √n √n The np Chart The np Chart np 5 Number of non-conforming units within a sample np = Number of non-conforming units within a sample – np _ 5 Average number of nonconforming np = Average numberunits of per sample nonconforming units per sample – 1 3 √ np –(12p –) UCL 5 np np _ _ √n 3√u _ – LCLu 5 u 2_ 3√ u LCLu = u -√n_____ _ UCLnp =–np + 3 √ –np (1 - p– ) np 2 3 √ np ( 1 2 p ) LCL np 5 _ _ _ LCL np = np - 3 √ np (1 - p ) The c Chart The u Chart c 5 The count (number) of nonconformities within c = The count (number) of a sample nonconformities within a – sample _ c 5 Average number of nonconfomities per sample c = Average number of nonconfomities per sample UCLc 5 c 1 3 √ c UCL = c + 3 √ c LCL cc 5 c 2 3 √ c LCL c = c - 3 √ c Identification of Control Conditions Identification ofOut-of Out-of Control Conditions (Each point point is is aa subgroup) subgroup) (Each One or More Points Outside Control Limits. A Run Of 7 Or More Points Increasing. A Run Of 7 Or More Points Decreasing. A Run Of 7 Or More Points On Either Side Of Aim Size. 109 HANDY PHYSICAL CONSTANTS Acceleration of gravity, g Density of water 32.17 ft/s2 5 9.807 m/s2 62.4 lbm/ft3 5 1 g/cm3 1 gal H2O 5 8.345 lbm Gas Constant, R Gas volume (STP: 68°F, 1 atm) Joule’s Constant, J Poisson’s ratio, µ 1545 ft-lbf/pmole-R 5 8.314 J/gmole-K 359 ft3/pmole 5 .02241 m3/gmole 778 ft-lbf/BTU .3 (for steel) Fe-Fe3C eutectoid composition Fe-Fe3C eutectoid temperature 0.77 w/o carbon 1340°F (727°C) Modulus of Elasticity (steel) 30 3 106 psi Densities: Carbon & Low-Alloy Steels 304 SS Tool Steels Moly High Speed Multiphase Alloys 0.283 lbm/in3 5 7.84 g/cm3 0.29 lbm/in3 5 7.88 g/cm3 Carbon Steels 3 1.000 Carbon Steels 3 1.035 Carbon Steels 3 1.074 Steel Tensile Strength (psi) ~ 500 3 Brinell Number STEEL CONSTANTS COMPARISON MATERIALS Material Density (g/cm3) Modulus of Elasticity (psi) Poisson’s Ratio Aluminum Alloys Nickel-base Superalloys Titanium Alloys 2.6-2.9 8.0-8.9 4.4-5.0 10.0 3 106 28.5 2 31.0 3 106 15.0 3 16.8 3 106 0.33 0.31 0.34 SI PREFIXES giga mega kilo hecto deka deci centi milli micro nano G M k h da d c m µ n 110 109 106 103 102 101 1021 1022 1023 1026 1029 ENGINEERING CONVERSION FACTORS Explanation of Dimensional Units All table entries are categorized according to their specific combination of basic dimensions of Length [L], Mass [M] and Time [t]. For example, all units of force have the dimensions [M][L][t]22. The following better illustrates this convention: Force 5 [M][L][t]22 5 (Mass) 3 (Acceleration) 1 kgf 5 (1 kg) 3 (9.80665 m/s2) Example Conversion Meters to Yards (50 m) 3 (3.28084 ft/m) 3 (1/3 yd/ft) 5 54.68066 yd Significant Digits The convention is to retain the number of digits which correctly infers the known accuracy of the numbers involved. Normally, this means using the same number of significant digits as occur in the original number. For the above example, the answer would therefore be rounded to 55 yards. When the accuracy of the measurement is known, additional digits may become significant. For example, if the measurement of 50 meters is known to be accurate to .01 meters (.0109 yards), then the conversion result may be rounded to 54.68 yards. 111 CONVERSION FACTORS EQUATION: A 3 B 5 C A Area [L]2 ft2 in2 in2 B 0.092903 645.16 6.45160 C m2 mm2 cm2 Energy, Work or Heat [M] [L]2 [t]22 Btu 1.05435 Btu 0.251996 Calories (cal) 4.184* ft-lbf 1.355818 ft-lbf 0.138255 hp-hr 2.6845 KWH 3.600 m-kgf 9.80665* N-m 1. kJ kcal Joules (J) J kgf-m MJ MJ J J Flow Rate [L]3 [t]21 ft3/min ft3/min gal/min gal/min l/s l/s 7.4805 0.471934 0.063090 Force or Weight [M] [L] [t]22 kgf 9.80665* lbf 4.44822 lbf 0.453592 Newton (N) N Kgf Fracture Toughness ksi√in 1.098800 MPa√m Heat Content Btu/lbm Btu/lbm Btu/ft3 0.555556 2.324444 0.037234 cal/g J/g MJ/m3 Heat Flux Btu/hr-ft2 Btu/hr-ft2 cal/s-cm2 7.5346 E-5 3.1525 4.184* cal/s-cm2 W/m2 W/cm2 Length [L] Foot (ft) Inch (in) Mile (mi) 0.304800 25.4000 1.609344 Meter (m) Millimeter (mm) Kilometer (km) * Indicates exact conversion(s) 112 CONVERSION FACTORS – continued EQUATION: A 3 B 5 C A B C Mass Density [M] [L]23 lbm/in3 lbm/ft3 27.68 16.0184 g/cm3 kg/m3 Power [M] [L]2 [t]23 Btu/hr ft-lbf/s Horsepower (hp) Horsepower 0.292875 1.355818 745.6999 550.* Watt (W) W W ft-lbf/s Pressure (fluid) [M] [L]21 [t]22 Atmosphere (atm) 14.696 atm 1.01325 E5* lbf/ft2 47.88026 lbf/in2 27.6807 lbf/in2 Pascal (Pa) Pa in. H2O at 39.2°F Stress [M] [L]21 [t]22 kgf/cm2 ksi N/mm2 kgf/mm2 9.80665 E-2* 6.89476 1. 1.42231 MPa MPa MPa ksi Volume [L]3 & Capacity in3 ft3 ft3 ft3 Gallon 16.3871 0.028317 7.4805 28.3168 3.785412 cm3 m3 Gallon Liter (l) Liter Specific Heat Btu/lbm-°F 1. cal/g-°C Temperature* Fahrenheit Fahrenheit Celsius Rankine (°F232)/1.8 °F1459.67 °C1273.16 R/1.8 Celsius Rankine Kelvin Kelvin Thermal Conductivity Btu-ft/hr-ft2-°F 14.8816 cal-cm/hr-cm2-°C * Indicates exact conversion(s) 113 METRIC-ENGLISH STRESS CONVERSION TABLE Kg Per Sq Mm to Psi to M Pa Kg per Psi sq mm M Pa Kg per Psi sq mm 10 14,223 98.1 11 15,646 107.9 12 17,068 117.7 13 18,490 127.5 14 19,913 137.3 50 51 52 53 54 71,117 72,539 73,962 75,384 76,806 490.3 500.1 510.0 519.8 529.6 90 91 92 93 94 128,011 129,433 130,855 132,278 133,700 15 21,335 16 22,757 17 24,180 18 25,602 19 27,024 147.1 156.9 166.7 176.5 186.3 55 56 57 58 59 78,229 79,651 81,073 82,496 83,918 539.4 549.2 559.0 568.8 578.6 95 96 97 98 99 135,122 136,545 137,967 139,389 140,812 20 28,447 21 29,869 22 31,291 23 32,714 24 34,136 196.1 205.9 215.7 225.6 235.4 60 61 62 63 64 85,340 86,763 88,185 89,607 91,030 588.4 598.2 608.0 617.8 622.6 25 35,558 26 36,981 27 38,403 28 39,826 29 41,248 245.2 255.0 264.8 274.6 284.4 65 66 67 68 69 92,452 93,874 95,297 96,719 98,141 30 42,670 31 44,093 32 45,515 33 46,937 34 48,360 294.2 304.0 313.8 323.6 333.4 70 71 72 73 74 35 49,782 36 51,204 37 52,627 38 54,049 39 55,471 343.2 353.0 362.8 372.7 382.5 40 56,894 41 58,316 42 59,738 43 61,161 44 62,583 45 64,005 46 65,428 47 66,850 48 68,272 49 69,695 Kg per Psi sq mm Kg per Psi sq mm M Pa 882.6 892.4 902.2 912.0 921.8 130 131 132 133 134 184,904 186,327 187,749 189,171 190,594 1274.9 1284.7 1294.5 1304.3 1314.1 931.6 941.4 951.2 961.0 970.9 135 136 137 138 139 192,016 193,438 194,861 196,283 197,705 1323.9 1333.7 1343.5 1353.3 1363.1 100 101 102 103 104 142,234 980.7 140 199,128 143,656 990.5 141 200,550 145,079 1000.3 142 201,972 146,501 1010.1 143 203,395 147,923 1020.0 144 204,817 1372.9 1382.7 1392.5 1402.4 1412.2 637.4 647.2 657.0 666.9 676.7 105 106 107 108 109 149,346 150,768 152,190 153,613 155,035 1029.7 1039.5 1049.3 1059.1 1068.9 145 146 147 148 149 206,239 207,662 209,084 210,506 211,929 1422.0 1431.8 1441.6 1451.4 1461.2 99,564 100,986 102,408 103,831 105,253 686.5 696.3 706.1 715.9 725.7 110 111 112 113 114 156,457 157,880 159,302 160,724 162,147 1078.7 1088.5 1098.3 1108.2 1118.0 150 151 152 153 154 213,351 214,773 216,196 217,618 219,040 1471.0 1480.8 1490.6 1500.4 1510.2 75 76 77 78 79 106,675 108,098 109,520 110,943 112,365 735.5 745.3 755.1 764.9 774.7 115 116 117 118 119 163,569 164,991 166,414 167,836 169,258 1127.8 1137.6 1147.4 1157.2 1167.0 155 156 157 158 159 220,463 221,885 223,307 224,730 226,152 1520.0 1529.8 1539.6 1549.5 1559.3 393.3 402.1 411.9 421.7 431.5 80 81 82 83 84 113,787 115,210 116,632 118,054 119,477 784.5 794.3 804.1 814.0 823.8 120 121 122 123 124 170,681 172,103 173,525 174,948 176,370 1176.8 1186.6 1196.4 1206.2 1216.0 441.3 451.1 460.9 470.7 480.5 85 86 87 88 89 120,899 122,321 123,744 125,166 126,588 833.6 843.4 853.2 863.0 872.8 125 126 127 128 129 177,792 179,215 180,637 182,059 183,482 1225.8 1235.6 1245.4 1255.3 1265.1 M Pa 114 M Pa WORK-ENERGY CONVERSION TABLE ft.-lbf 0.7376 1.4751 2.2127 2.9502 3.6878 4.4254 5.1629 5.9005 6.6381 7.3756 8.1132 8.8507 9.5883 10.3259 11.0634 11.8010 12.5386 13.2761 14.0137 14.7512 15.4888 16.2264 16.9639 17.7015 18.4391 19.1766 19.9142 20.6517 21.3893 22.1269 22.8644 23.6020 24.3396 25.0771 25.8147 26.5522 27.2898 28.0274 28.7649 29.5025 30.2400 30.9776 31.7152 32.4527 33.1903 33.9279 34.6654 35.4030 36.1405 36.8781 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 joules ft.-lbf 1.356 2.712 4.067 5.423 6.779 8.135 9.491 10.847 12.202 13.558 14.914 16.270 17.626 18.981 20.337 21.693 23.049 24.405 25.761 27.116 28.472 29.828 31.184 32.540 33.895 35.251 36.607 37.963 39.319 40.675 42.030 43.386 44.742 46.098 47.454 48.809 50.165 51.521 52.877 54.233 55.589 56.944 58.300 59.656 61.012 62.368 63.723 65.079 66.435 67.791 37.6157 38.3532 39.0908 39.8284 40.5659 41.3035 42.0410 42.7786 43.5162 44.2537 44.9913 45.7289 46.4664 47.2040 47.9415 48.6791 49.4167 50.1542 50.8918 51.6294 52.3669 53.1045 53.8420 54.5796 55.3172 56.0547 56.7923 57.5298 58.2674 59.0050 59.7425 60.4801 61.2177 61.9552 62.6928 63.4303 64.1679 64.9055 65.6430 66.3806 67.1182 67.8557 68.5933 69.3308 70.0684 70.8060 71.5435 72.2811 73.0186 73.7562 Examples: 1 ft-lbf 5 1.356 joules 1 joule 5 0.7376 ft-lbf 115 joules 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 69.147 70.503 71.858 73.214 74.570 75.926 77.282 78.637 79.993 81.349 82.705 84.061 85.417 86.772 88.128 89.484 90.840 92.196 93.551 94.907 96.263 97.619 98.975 100.331 101.686 103.042 104.398 105.754 107.110 108.465 109.821 111.177 112.533 113.889 115.245 116.600 117.956 119.312 120.668 122.024 123.379 124.735 126.091 127.447 128.803 130.159 131.514 132.870 134.226 135.582 TABLES FOR CONVERSION FROM INCHES INTO MILLIMETERS Inches Millimeters 1 ⁄64 1 ⁄32 3 ⁄64 1 ⁄16 5 ⁄64 3 ⁄32 7 ⁄64 1 ⁄8 9 ⁄64 5 ⁄32 11 ⁄64 3 ⁄16 13 ⁄64 7 ⁄32 15 ⁄64 1⁄ 4 17 ⁄64 9 ⁄32 19 ⁄64 5 ⁄16 21 ⁄64 11 ⁄32 23 ⁄64 3 ⁄8 25 ⁄64 13 ⁄32 27 ⁄64 7⁄ 16 29⁄ 64 15 ⁄32 31⁄ 64 1⁄ 2 .015625 .031250 .046875 .062500 .078125 .093750 .109375 .125000 .140625 .156250 .171875 .187500 .203125 .218750 .234375 .250000 .265625 .281250 .296875 .312500 .328125 .343750 .359375 .375000 .390625 .406250 .421875 .437500 .453125 .468750 .484375 .500000 * On the basis of the conversion factor 1 in. 5 25.4 mm. 116 .396875 .793750 1.190625 1.587500 1.984375 2.381250 2.778125 3.175000 3.571875 3.968750 4.365625 4.762500 5.159375 5.556250 5.953125 6.350000 6.746875 7.143750 7.540625 7.937500 8.334375 8.731250 9.128125 9.525000 9.921875 10.318750 10.715625 11.112500 11.509375 11.906250 12.303125 12.700000 TABLES FOR CONVERSION – continued Inches Millimeters 33⁄ 64 17 ⁄32 35⁄ 64 9⁄ 16 37⁄ 64 19 ⁄32 39⁄ 64 5⁄ 8 41⁄ 64 21 ⁄32 43⁄ 64 11⁄ 16 45⁄ 64 23 ⁄32 47⁄ 64 3⁄ 4 49⁄ 64 25 ⁄32 51⁄ 64 13⁄ 16 53⁄ 64 27 ⁄32 55⁄ 64 7⁄ 8 57⁄ 64 29 ⁄32 59⁄ 64 15⁄ 16 61⁄ 64 31 ⁄32 63⁄ 64 1 (All the values in these tables are exact). 117 .515625 .531250 .546875 .562500 .578125 .593750 .609375 .625000 .640625 .656250 .671875 .687500 .703125 .718750 .734375 .750000 .765625 .781250 .796875 .812500 .828125 .843750 .859375 .875000 .890625 .906250 .921875 .937500 .953125 .968750 .984375 1.000000 13.096875 13.493750 13.890625 14.287500 14.684375 15.081250 15.478125 15.875000 16.271875 16.668750 17.065625 17.462500 17.859375 18.256250 18.653125 19.050000 19.446875 19.843750 20.240625 20.637500 21.034375 21.431250 21.828125 22.225000 22.621875 23.018750 23.415625 23.812500 24.209375 24.606250 25.003125 25.400000 TEMPERATURE CONVERSION TABLES Albert Sauveur type of table. Values revised. —459.4 to 0 C F/C F 0 to 100 C -273 -268 -262 -257 -251 -459.4 -450 -440 -430 -420 -17.8 -17.2 -16.7 -16.1 -15.6 -246 -240 -234 -229 -223 -410 -400 -390 -380 -370 -218 -212 -207 -201 -196 F/C F 100 to 1000 C F/C 50 51 52 53 54 F 122.0 123.8 125.6 127.4 129.2 C F/C 100 110 120 130 140 212 230 248 266 284 260 266 271 277 282 C F/C F 32 33.8 35.6 37.4 39.2 10.0 10.6 11.1 11.7 12.2 -15.0 -14.4 -13.9 -13.3 -12.8 5 6 7 8 9 41.0 42.8 44.6 46.4 48.2 12.8 13.3 13.9 14.4 15.0 55 56 57 58 59 131.0 132.8 134.6 136.4 138.2 66 71 77 82 88 150 160 170 180 190 302 320 338 356 374 288 293 299 304 310 550 560 570 580 590 1022 1040 1058 1076 1094 -360 -350 -340 -330 -320 -12.2 -11.7 -11.1 -10.6 -10.0 10 11 12 13 14 50.0 51.8 53.6 55.4 57.2 15.6 16.1 16.7 17.2 17.8 60 61 62 63 64 140.0 141.8 143.6 145.4 147.2 93 99 100 104 110 200 210 212 220 230 392 410 413.6 428 446 316 321 327 332 338 600 610 620 630 640 1112 1130 1148 1166 1184 -190 -184 -179 -173 -169 -310 -300 -290 -280 -273 -459.4 -9.4 -8.9 -8.3 -7.8 -7.2 15 16 17 18 19 59.0 60.8 62.6 64.4 66.2 18.3 18.9 19.4 20.0 20.6 65 66 67 68 69 149.0 150.8 152.6 154.4 156.2 116 121 127 132 138 240 250 260 270 280 464 482 500 518 536 343 349 354 360 366 650 660 670 680 690 1202 1220 1238 1256 1274 -168 -162 -157 -151 -146 -270 -260 -250 -240 -230 -454 -436 -418 -400 -382 -6.7 -6.1 -5.6 -5.0 -4.4 20 21 22 23 24 68.0 69.8 71.6 73.4 75.2 21.1 21.7 22.2 22.8 23.3 70 71 72 73 74 158.0 159.8 161.6 163.4 165.2 143 149 154 160 166 290 300 310 320 330 554 572 590 608 626 371 377 382 388 393 700 710 720 730 740 1292 1310 1328 1346 1364 -140 -134 -129 -123 -118 -220 -210 -200 -190 -180 -364 -346 -328 -310 -292 -3.9 -3.3 -2.8 -2.2 -1.7 25 26 27 28 29 77.0 78.8 80.6 82.4 84.2 23.9 24.4 25.0 25.6 26.1 75 76 77 78 79 167.0 168.8 170.6 172.4 174.2 171 177 182 188 193 340 350 360 370 380 644 662 680 698 716 399 404 410 416 421 750 760 770 780 790 1382 1400 1418 1436 1454 -112 -107 -101 -96 -90 -170 -160 -150 -140 -130 -274 -256 -238 -220 -202 -1.1 - .6 0 .6 1.1 30 31 32 33 34 86.0 87.8 89.6 91.4 93.2 26.7 27.2 27.8 28.3 28.9 80 81 82 83 84 176.0 177.8 179.6 181.4 183.2 199 204 210 216 221 390 400 410 420 430 734 752 770 788 806 427 432 438 443 449 800 810 820 830 840 1472 1490 1508 1526 1544 -84 -79 -73 -68 -62 -120 -110 -100 -90 -80 -184 -166 -148 -130 -112 1.7 2.2 2.8 3.3 3.9 35 95.0 36 96.8 37 98.6 38 100.4 39 102.2 29.4 30.0 30.6 31.1 31.7 85 86 87 88 89 185.0 186.8 188.6 190.4 192.2 227 232 238 243 249 440 450 460 470 480 824 842 860 878 896 454 460 466 471 477 850 860 870 880 890 1562 1580 1598 1616 1634 -57 -51 -46 -40 -34 -70 -60 -50 -40 -30 -94 -76 -58 -40 -22 4.4 5.0 5.6 6.1 6.7 40 41 42 43 44 32.2 32.8 33.3 33.9 34.4 90 91 92 93 94 194.0 254 490 914 195.8 197.6 199.4 201.2 482 488 493 499 504 900 910 920 930 940 1652 1670 1688 1706 1724 203.0 204.8 206.6 208.4 210.2 212.0 510 516 521 527 532 538 950 960 970 980 990 1000 1742 1760 1778 1796 1814 1832 104.0 105.8 107.6 109.4 111.2 -29 -20 -4 7.2 45 113.0 -23 -10 14 7.8 46 114.8 -17.8 0 32 8.3 47 116.6 8.9 48 118.4 9.4 49 120.2 35.0 95 35.6 96 36.1 97 36.7 98 37.2 99 37.8 100 38 43 49 54 60 F 0 1 2 3 4 500 932 510 950 520 968 530 986 540 1004 Look up reading in middle column. If in degress Celsius, read Fahrenheit equivalent in right hand column; if in Fahrenheit degrees, read Celsius equivalent in left hand column. 118 TEMPERATURE CONVERSION TABLES – continued Albert Sauveur type of table. Values revised. 1000 to 2000 2000 to 3000 C F/C F C F/C F C F/C 538 543 549 554 560 1000 1010 1020 1030 1040 1832 1850 1868 1886 1904 816 821 827 832 838 1500 1510 1520 1530 1540 2732 2750 2768 2786 2804 F C F/C F 1093 1099 1104 1110 1116 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040 3632 3650 3668 3686 3704 1371 1377 1382 1388 1393 2500 2510 2520 2530 2540 4532 4650 4568 4586 4604 566 571 577 582 588 1050 1060 1070 1080 1090 1922 1940 1958 1976 1994 843 849 854 860 866 1550 1560 1570 1580 1590 2822 2840 2858 2876 2894 1121 1127 1132 1138 1143 2050 2060 2070 2080 2090 3722 3740 3758 3776 3794 1399 1404 1410 1416 1421 2550 2560 2570 2580 2590 4622 4640 4658 4676 4694 593 599 604 610 616 1100 1110 1120 1130 1140 2012 2030 2048 2066 2084 871 877 882 888 893 1600 1610 1620 1630 1640 2912 2930 2948 2966 2984 1149 1154 1160 1166 1171 2100 2110 2120 2130 2140 3812 3830 3848 3866 3884 1427 1432 1438 1443 1449 2600 2610 2620 2630 2640 4712 4730 4748 4766 4784 621 627 632 638 643 1150 1160 1170 1180 1190 2102 2120 2138 2156 2174 899 904 910 916 921 1650 1660 1670 1680 1690 3002 3020 3038 3056 3074 1177 1182 1188 1193 1199 2150 2160 2170 2180 2190 3902 3920 3938 3956 3974 1454 1460 1466 1471 1477 2650 2660 2670 2680 2690 4802 4820 4838 4856 4874 649 654 660 666 671 1200 1210 1220 1230 1240 2192 2210 2228 2246 2264 927 932 938 943 949 1700 1710 1720 1730 1740 3092 3110 3128 3146 3164 1204 1210 1216 1221 1227 2200 2210 2220 2230 2240 3992 4010 4028 4046 4064 1482 1488 1493 1499 1504 2700 2710 2720 2730 2740 4892 4910 4928 4946 4964 677 682 688 693 699 1250 1260 1270 1280 1290 2282 2300 2318 2336 2354 954 960 966 971 977 1750 1760 1770 1780 1790 3182 3200 3218 3236 3254 1232 1238 1243 1249 1254 2250 2260 2270 2280 2290 4082 4100 4118 4136 4154 1510 1516 1521 1527 1532 2750 2760 2770 2780 2790 4982 5000 5018 5036 5054 704 710 716 721 727 1300 1310 1320 1330 1340 2372 2390 2408 2426 2444 982 988 993 999 1004 1800 1810 1820 1830 1840 3272 3290 3308 3326 3344 1260 1266 1271 1277 1282 2300 2310 2320 2330 2340 4172 4190 4208 4226 4244 1538 1543 1549 1554 1560 2800 2810 2820 2830 2840 5072 5090 5108 5126 5144 732 738 743 749 754 1350 1360 1370 1380 1390 2462 2480 2498 2516 2534 1010 1016 1021 1027 1032 1850 1860 1870 1880 1890 3362 3380 3398 3416 3434 1288 1293 1299 1304 1310 2350 2360 2370 2380 2390 4262 4280 4298 4316 4334 1566 1571 1577 1582 1588 2850 2860 2870 2880 2890 5162 5180 5198 5216 5234 760 766 771 777 782 1400 1410 1420 1430 1440 2552 2570 2588 2606 2624 1038 1043 1049 1054 1060 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 3452 3470 3488 3506 3524 1316 1321 1327 1332 1338 2400 2410 2420 2430 2440 4352 4370 4388 4406 4424 1593 1599 1604 1610 1616 2900 2910 2920 2930 2940 5252 5270 5288 5306 5324 788 1450 2642 793 1460 2660 799 1470 2678 804 1480 2696 810 1490 2714 1066 1071 1077 1082 1088 1093 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 3542 1343 2450 4442 3560 1349 2460 4460 3578 1354 2470 4478 3596 1360 2480 4496 3614 1366 2490 4514 3632 1621 1627 1632 1638 1643 1649 2950 2960 2970 2980 2990 3000 5342 5360 5378 5396 5414 5432 Look up reading in middle column. If in degress Celsius, read Fahrenheit equivalent in right hand column; if in Fahrenheit degrees, read Celsius equivalent in left hand column. 119 HARDNESS CONVERSION TABLES BASED ON BRINELL (APPROXIMATE) BRINELL HARDNESS ROCKWELL HARDNESS Diameter Tungsten A-Scale B-Scale C-Scale mm Carbide 60 Kg 100 Kg 150 Kg Superficial 3000 Kg 10 mm Ball Brale 1/16" Ball Brale 30 N Diamond Pyramid Approx. Hardness Tensile Number Stength (Vickers) 1000 psi .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 757 86.5 86.0 85.6 85.0 84.4 .... .... .... .... .... 70.0 69.0 68.0 67.0 65.9 86.0 85.0 84.4 83.6 82.7 1076 1004 940 900 860 .... .... .... .... .... 2.25 .... .... 2.35 2.40 745 722 710 682 653 84.1 83.4 83.0 82.2 81.2 .... .... .... .... .... 65.3 64.0 63.3 61.7 60.0 82.2 81.1 80.4 79.0 77.5 840 800 780 737 697 .... .... .... .... .... 2.45 2.50 2.55 2.60 2.65 627 601 578 555 534 80.5 79.8 79.1 78.4 77.8 .... .... .... .... .... 58.7 57.3 56.0 54.7 53.5 76.3 75.1 73.9 72.7 71.6 667 640 615 591 569 323 309 297 285 274 2.70 2.75 2.80 2.85 2.90 514 495 477 461 444 76.9 76.3 75.6 74.9 74.2 .... .... .... .... .... 52.1 51.0 49.6 48.5 47.1 70.3 69.4 68.2 67.2 65.8 547 528 508 491 472 263 253 243 235 225 2.95 3.00 3.05 3.10 3.15 429 415 401 388 375 73.4 72.8 72.0 71.4 70.6 .... .... .... .... .... 45.7 44.5 43.1 41.8 40.4 64.6 63.5 62.3 61.1 59.9 455 440 425 410 396 217 210 202 195 188 3.20 3.25 3.30 3.35 3.40 363 352 341 331 321 70.0 69.3 68.7 68.1 67.5 .... (110.0) (109.0) (108.5) (108.0) 39.1 37.9 36.6 35.5 34.3 58.7 57.6 56.4 55.4 54.3 383 372 360 350 339 182 176 170 166 160 3.45 3.50 3.55 3.60 3.65 311 302 293 285 277 66.9 66.3 65.7 65.3 64.6 (107.5) (107.0) (106.0) (105.5) (104.5) 33.1 32.1 30.9 29.9 28.8 53.3 52.2 51.2 50.3 49.3 328 319 309 301 292 155 150 145 141 137 120 HARDNESS CONVERSION TABLES – continued BRINELL HARDNESS Diameter Tungsten mm Carbide 3000 Kg 10 mm Ball ROCKWELL HARDNESS A-Scale 60 Kg Brale B-Scale 100 Kg 1/16" Ball Diamond Pyramid Approx. C-Scale Hardness Tensile 150 Kg Superficial Number Stength Brale 30 N (Vickers) 1000 psi 3.70 3.75 3.80 3.85 3.90 269 262 255 248 241 64.1 63.6 63.0 62.5 61.8 (104.0) (103.0) (102.0) (101.0) 100.0 27.6 26.6 25.4 24.2 22.8 48.3 47.3 46.2 45.1 43.9 284 276 269 261 253 133 129 126 122 118 3.95 4.00 4.05 4.10 4.15 235 229 223 217 212 61.4 60.8 59.7 59.2 58.5 99.0 98.2 97.3 96.4 95.5 21.7 20.5 (18.8) (17.5) (16.0) 42.9 41.9 .... .... .... 247 241 234 228 222 115 111 .... 105 102 4.20 4.25 4.30 4.35 4.40 207 201 197 192 187 57.8 57.4 56.9 56.5 55.9 94.6 93.8 92.8 91.9 90.7 (15.2) (13.8) (12.7) (11.5) (10.0) .... .... .... .... .... 218 212 207 202 196 100 98 95 93 90 4.45 4.50 4.55 4.60 4.65 183 179 174 170 167 55.5 55.0 53.9 53.4 53.0 90.0 89.0 87.8 86.8 86.0 (9.0) (8.0) (6.4) (5.4) (4.4) .... .... .... .... .... 192 188 182 178 175 89 87 85 83 81 4.70 4.80 4.90 5.00 5.10 163 156 149 143 137 52.5 51.0 49.9 48.9 47.4 85.0 82.9 80.8 78.7 76.4 (3.3) (.9) .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 171 163 156 150 143 79 76 73 71 67 5.20 5.30 5.40 5.50 5.60 131 126 121 116 111 46.0 45.0 43.9 42.8 41.9 74.0 72.0 69.8 67.6 65.7 .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... 137 132 127 122 117 65 63 60 58 56 Values in ( ) are beyond normal range and are given for information only. The Brinell values in this table are based on the use of a 10mm tungsten carbide ball; at hardness levels of 429 Brinell and below, the values obtained with the tungsten carbide ball, the Hultgren ball, and the standard ball are the same. The Hardness Conversion Tables are based on SAE J417 and ASTM E140. 121 USEFUL EQUATIONS FOR HARDENABLE ALLOY STEELS Ae1 (°F) ~ 1333 2 25 3 Mn 1 40 3 Si 1 42 3 Cr 2 26 3 Ni ............... (1) Ae3 (°F) ~ 1570 2 323 3 C 2 25 3 Mn 1 80 3 Si 2 3 3 Cr 2 32 3 Ni.. (2) Ac1 (°C) ~ 723 2 10.7 3 Mn 1 29.1 3 Si 1 16.9 3 Cr 2 16.9 3 Ni 1 290 3 As 1 6.38 3 W ........................................................... (3) Ac3 (°C) ~ 910 2 203 3 √C 1 44.7 3 Si 15.2 3 Ni 1 31.5 3 Mo 1 104 3 V 1 13.1 3 W ...................................................................... (4) Ms (°F) ~ 930 2 600 3 C 2 60 3 Mn 2 20 3 Si 2 50 3 Cr 2 30 3 Ni 2 20 3 Mo 2 20 3 W........................................................ (5) M10 (°F) ~ Ms 2 18 ................................................................................. (6) M50 (°F) ~ Ms 2 85 ................................................................................. (7) M90 (°F) ~ Ms 2 185 ............................................................................... (8) Mf (°F) ~ Ms 2 387................................................................................ (9) Bs (°F) ~ 1526 2 486 3 C 2 162 3 Mn 2 126 3 Cr 2 67 3 Ni 2 149 3 Mo ............................................................................ (10) B50 (°F) ~ Bs 2 108 ............................................................................. (11) Bf (°F) ~ Bs 2 216 ............................................................................. (12) Carburized Case Depth (in.) ~ .025√t, for 1700°F ............................... (13) Carburized Case Depth (in.) ~ .021√t, for 1650°F ............................... (14) Carburized Case Depth (in.) ~ .018√t, for 1600°F ............................... (15) (t 5 time in hours) ___________________________________________________________________________ Note: 1 & 2: 3 & 4: 5: 6-12: 13-15: Each equation above is subject to the chemistry limitations under which it was developed. R. A. Grange, Metal Progress, 79, April 1961, p 73. K. W. Andrews, JISI, 203, 1965, p 721. E. S. Rowland and S. R. Lyle, Trans. ASM, 37, 1946, p 27. W. Steven and A. G. Haynes, JISI, 183, 1956, p 349. F. E. Harris, Metal Progress, 44, August 1943, p 265. 122 105 GLOSSARY OF METALLURGICAL TERMS Alloying Elements ALUMINUM - Al is used to deoxidize steel and control grain size. Grain size control is effected by forming a fine dispersion with nitrogen and oxygen which restricts austenite grain growth. Aluminum is also an extremely effective nitride former in nitriding steels. BORON - B is usually added between .0005-.003% to significantly increase the hardenability, especially for low carbon alloys. It does not affect the strength of ferrite, therefore not sacrificing ductility, formability or machinability in the annealed state. CALCIUM - Ca is used in certain steels to control the shape, size and distribution of oxide and/or sulfide inclusions. Benefits may include improved ductility, impact strength and machinability. CARBON - C is the most important alloying element which is essential for the formation of cementite, pearlite, spheriodite, bainite, and iron-carbon martensite. Compared to steels with similar microstructures, strength, hardness, hardenability, and ductile-to-brittle transition temperature are increased with increasing carbon content up to approximately .60%. Toughness and ductility of pearlitic steels are decreased with increasing carbon content. CHROMIUM - Cr is used in low alloy steels to increase 1) resistance to corrosion and oxidation, 2) high temperature strength, 3) hardenability, and 4) abrasion resistance in high carbon alloys. Straight chromium steels are susceptible to temper embrittlement and can be brittle. COPPER - Cu is detrimental to hot workability and subsequent surface quality. It is used in certain steels to improve resistance to atmospheric corrosion. LEAD - Pb improves machinability. It does not dissolve in steel but stays as globules. Environmental concerns are resulting in a decreased usage of lead in the steel industry. MANGANESE - Mn is important because it deoxidizes the melt and facilitates hot working of the steel by reducing the susceptibility to hot shortness. It combines with sulfur to form MnS stringers which increases machinability. Manganese contributes to the effectiveness of normalizing for strengthening, to the formation of fine pearlite, and lowers the Ms temperature, therefore increasing the probability of retained austenite. 123 GLOSSARY – continued MOLYBDENUM - Mo increases hardenability of steels and helps maintain a specified hardenability. It increases high temperature tensile and creep strengths. Molybdenum hardened steels require higher tempering temperatures for softening purposes. NICKEL - Ni is used in low alloy steels to reduce the sensitivity of the steel to variations in heat treatment and distortion and cracking on quenching. It also improves low temperature toughness and hardenability. NIOBIUM - Nb (Columbium - Cb) lowers transition temperature and raises the strength of low carbon steel. Niobium increases strength at elevated temperatures, results in finer grain size and forms stable carbides, lowering the hardenability of the steel. NITROGEN - N increases the strength, hardness and machinability of steel, but it decreases the ductility and toughness. In aluminum killed steels, nitrogen combines with the aluminum to provide grain size control, thereby improving both toughness and strength. Nitrogen can reduce the effect of boron on the hardenability of steels. PHOSPHORUS - P is generally restricted to below 0.04 weight percent to minimize its detrimental effect on ductility and toughness. Certain steels may contain higher levels to enhance machinability, strength and/or atmospheric corrosion resistance. SILICON - Si is one of the principal deoxidizers with the amount used dependent on the deoxidization practice. It slightly increases the strength of ferrite without a serious loss of ductility. In larger quantities, it aids the resistance to scaling up to 500°F in air and decreases magnetic hysteresis loss. SULFUR - S is detrimental to transverse strength and impact resistance. It affects longitudinal properties to a lesser degree. Existing primarily in the form of manganese sulfide stringers, sulfur is typically added to improve machinability. TITANIUM - Ti is added to boron steels because it combines with oxygen and nitrogen, thus increasing the effectiveness of boron. Titanium, as titanium nitride, also provides grain size control at elevated temperatures in microalloy steels. In excess, titanium is detrimental to machinability and internal cleanness. 124 GLOSSARY – continued TELLURIUM - Te is added to steel to modify sulfide type inclusion size, morphology and distribution. The resulting sulfide type inclusions are finer and remain ellipsoidal in shape following hot working, thereby improving transverse properties. VANADIUM - V inhibits grain growth during heat treating while improving strength and toughness of hardened and tempered steels. Additions up to .05% increase hardenability whereas larger amounts tend to reduce hardenability because of carbide formation. Vanadium is also utilized in ferrite/ pearlite microalloy steels to increase hardness through carbonitride precipitation strengthening of the matrix. Standard Mill Terminology ANNEALING A treatment consisting of heating uniformly to a temperature, within or above the critical range, and cooling at a controlled rate to a temperature under the critical range. This treatment is used to produce a definite microstructure, usually one designed for best machinability, and/or to remove stresses, induce softness, and alter ductility, toughness or other mechanical properties. BILLET A solid semifinished round or square that has been hot worked usually smaller than a bloom. Also a general term for wrought starting stock for forgings or extrusions. BLOOM A semifinished hot rolled rectangular product. The width of the bloom is no more than twice the thickness and the cross-sectional area is usually not less that 36 square inches. CAPPED STEEL A type of steel similar to rimmed steel, usually cast in a bottle top ingot, in which the application of a mechanical or chemical cap renders the rimming action incomplete by causing the top metal to solidify. DI (Ideal Diameter) The diameter of a round steel bar that will harden at the center to a given percent of martensite when subjected to an ideal quench (i.e., Grossman quench severity H=infinity) ELONGATION In tensile testing, the increase in gage length, measured after the fracture of a specimen within the gage length, usually expressed as a percentage of the original gage length. 125 GLOSSARY – continued END-QUENCH HARDENABILITY TEST (Jominy Test) A laboratory procedure for determining the hardenability of a steel or other ferrous alloy. Hardenability is determined by heating a standard specimen above the upper critical temperature, placing the hot specimen in a fixture so that a stream of cold water impinges on one end, and, after cooling to room temperature is completed, measuring the hardness near the surface of the specimen at regularly spaced intervals along its length. The data are normally plotted as hardness versus distance from the quenched end. HARDNESS Resistance of a metal to plastic deformation, usually by indentation. However, this may also refer to stiffness or temper, or to resistance to scratching, abrasion, or cutting. IMPACT TEST A test to determine the behavior of materials when subjected to high rates of loading, usually in bending, tension or torsion. The quantity measured is the energy absorbed in breaking the specimen by a single blow, as in the Charpy or Izod tests. INGOT A casting of a simple shape which can be used for hot working or remelting. KILLED STEEL Steel treated with a strong deoxidizer to reduce oxygen to a level where no reaction occurs between carbon and oxygen during solidification. LAP A surface imperfection which appears as a seam. It is caused by the folding over of hot metal, fins, or sharp corners and then rolling or forging them into the surface but not welding them. Laps on tubes can form from seams on piercing mill billets. MACHINABILITY This is a generic term for describing the ability of a material to be machined. To be meaningful, machinability must be qualified in terms of tool wear, tool life, chip control, and/or surface finish and integrity. Overall machining performance is affected by a myriad of variables relating to the machining operation and the workpiece. An overall review is provided in the ASM Metals Handbook: Machinability, Ninth Edition, Volume 16, 1989. NORMALIZING A treatment consisting of heating uniformly to temperature at least 100°F above the critical range and cooling in still air at room temperature. The treatment produces a recrystallization and refinement of the grain structure and gives uniformity in hardness and structure to the product. 126 GLOSSARY – continued PICKLING An operation by which surface oxide (scale) is removed by chemical action. Sulfuric acid is typically used for carbon and low-alloy steels. After the acid bath, the steel is rinsed in water. QUENCHING A treatment consisting of heating uniformly to a predetermined temperature and cooling rapidly in air or liquid medium to produce a desired crystalline structure. REDUCTION OF AREA The difference, expressed as a percentage of original area, between the original cross-sectional area of a tensile test specimen and the minimum cross-sectional area measured after complete separation. RIMMED STEEL A low carbon steel having enough iron oxide to give a continuous evolution of carbon monoxide during solidification giving a rim of material virtually free of voids. SCAB An imperfection which is a flat piece of metal rolled into the steel surface. SEAM A defect on the surface of a metal which appears as a crack. Experience indicates that most seams are created during the cooling or reheating of cast structures. SEMI-KILLED STEEL Incompletely deoxidized steel which contains enough dissolved oxygen to react with the carbon to form carbon monoxide to offset solidification shrinkage. SPHEROIDIZE ANNEAL A special type of annealing that requires an extremely long cycle. This treatment is used to produce globular carbides and maximum softness for best machinability in some analyses, or to improve cold formability. STRAND CASTING (Continuous Casting) Operation in which a cast shape is continuously drawn through the bottom of the mold as it solidifies. The length is not determined by mold dimensions. STRESS RELIEVE TEMPER A thermal treatment to restore elastic properties and to minimize distortion on subsequent machining or hardening operations. This treatment is usually applied to material that has been heat treated (quenched and tempered). Normal practice would be to heat to a temperature 100°F lower than the tempering temperatures used to establish mechanical properties and hardness. Ordinarily, no straightening is performed after the stress relieve temper. 127 GLOSSARY – continued TEMPERING A treatment consisting of heating uniformly to some predetermined temperature under the critical range, holding at that temperature a designated period of time and cooling in air or liquid. This treatment is used to produce one or more of the following end results: A) to soften material for subsequent machining or cold working, B) to improve ductility and relieve stresses resulting from prior treatment or cold working, and C) to produce the desired mechanical properties or structure in the second step of a double treatment. TENSILE STRENGTH In tensile testing, the ratio of maximum load to original crosssectional area. YIELD POINT The first stress in a material, usually less than the maximum attainable stress, at which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress. If there is a decrease in stress after yielding, a distinction may be made between upper and lower yield points. YIELD STRENGTH The stress at which a material exhibits a specified deviation from proportionality of stress and strain. An offset of .2% is commonly used. Information adapted from ASM and/or SAE publications. 128