Chem 2 AP HW 10
advertisement

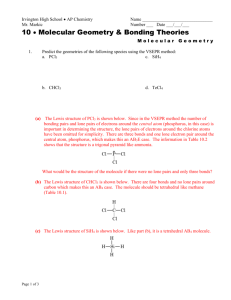
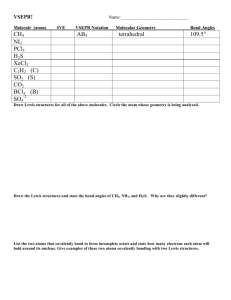
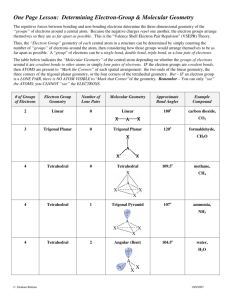
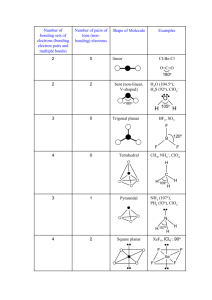
Chem 2 AP Homework #10-1: p. 428 # 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, 69 3 How many atoms are directly bonded to the central atom in a tetrahedral molecule, a trigonal bipyramidal molecule, and an octahedral molecule. 4 atoms are directly bonded to the central atom in a tetrahedral, 5 in a trigonal bipyramidal, and 6 in an octahedral molecule. 4 Discuss the basic features of the VSEPR model. Explain why the magnitude of the repulsion decreases in the following order: lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pairbonding pair. The electron pairs surrounding an atom repel each other, so arrange themselves in a geometry to minimize their interactions. Lone pairs sit closet to the atom than bonding pairs since there is no atom opposite them to pull them away from the central atom. Thus, two lone pairs will repel each other with a doubly-large effect, lone-pairs repel bonding pairs less because the bonding pairs take up less room and two bonding pairs repel each other the least because they take up less room. 5 In the trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, why does a lone pair occupy an equatorial position rather than an axial position? The lone pair of a trigonal bipyramidal occupies the equatorial position because there are approximately 120° to the next electron pairs in the equator and only 1 90° interaction, minimizing repulsion compared to 3 90° interactions it would experience in the axial position. 6 The geometry of CH4 could be square planar, with the four H atoms at the corners of a square and the C atom at the center of the square. Sketch this geometry and compare its stability with that of a tetrahedral CH4 molecule. In a square planar arrangement, each bonding region is 90° from two other regions, experiencing a large amount of repulsion compared to the three 109.5° interactions in the tetrahedral arrangement, so tetrahedral is more stable: H H 90° C H H C H H 7 109.5° H H Predict the geometries of the following species using the VSEPR method: (a) The Lewis structure of PCl3 is shown below. There are three bonds and one lone electron pair around the central atom, phosphorus, which makes this an AB3E case. Cl P P Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl (b) The Lewis structure of CHCl3 is shown below. There are four bonds and no lone pairs around carbon which makes this an AB4 case. H H Cl C Cl Cl C Cl Cl Cl 2 HOMEWORK #1-2 ANSWER KEY (c) The Lewis structure of SiH4 is shown below. Like part (b), it is a tetrahedral AB4 molecule. H H Si H H Si H H H H (d) The Lewis structure of TeCl4 is shown below. There are four bonds and one lone pair which make this an AB4E case. Cl Cl Te Cl Te Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Are TeCl4 and SF4 isoelectronic? Should isoelectronic molecules have similar VSEPR structures? 9 Predict the geometry of the following molecules using the VSEPR model: Lewis Structure 3-d Diagram e pair arrangement geometry − Br Br (a) Br C tetrahedral Br C Br Br (b) (c) (d) Cl B Cl Cl F N F Se trigonal planar Cl N tetrahedral F H B trigonal planar Cl F Se tetrahedral H O N O − bent trigonal planar H bent N O 11 trigonal pyramidal F F H (e) tetrahedral Br Br Cl O Predict the geometry of the following molecules using the VSEPR method. The lone pairs of electrons on the bromine atoms have been omitted for simplicity. Br Hg linear Br N N linear O S C linear N 3 HOMEWORK #10-1 ANSWER KEY 13 Describe the geometry around each of the three central atoms in the CH3COOH molecule. The Lewis structure is: O H H C C O H O H O H H C H AB3 trigonal planar C AB4 tetrahedral H O 14 H C C O H H H AB2E2 bent Which of the following species are tetrahedral? Only molecules with four bonds to the central atom and no lone pairs are tetrahedral (AB4). I Cl Cl Si I Cl C Cl I Cd Cl I Si C Cl Cl Cl Cd I I Cl Cl Cl I Cl 2− Cl Cl Cl Cl I What are the Lewis structures and shapes for XeF4 and SeF4? F F Xe F F F F F F Xe F F F S F F F F Square Planar 69 F Se See-Saw Which of the following species is not likely to have a tetrahedral shape? (a) SiBr4, (b) NF4+, (c) SF4, (d) BeCl42–, (f) AlCl4–. Only (c) will not be tetrahedral. All the others have central atoms with 8 electrons in AB4−type Lewis structures and will therefore be tetrahedral. For SF4 the Lewis structure is of the AB4E type (analogous and isoelectronic to SeF4 in problem 14) which gives rise to a see-saw geometry (Table 10.2 of the text). Br Si Br F F Br S N Br F F F F Cl F F Cl 2– Be Cl Cl Cl Al Cl Cl Cl