Name
Date
Class
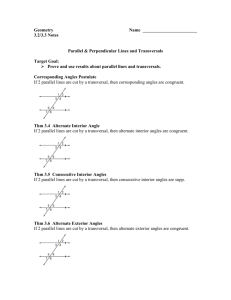
Reteach
LESSON
3-1
Lines and Angles
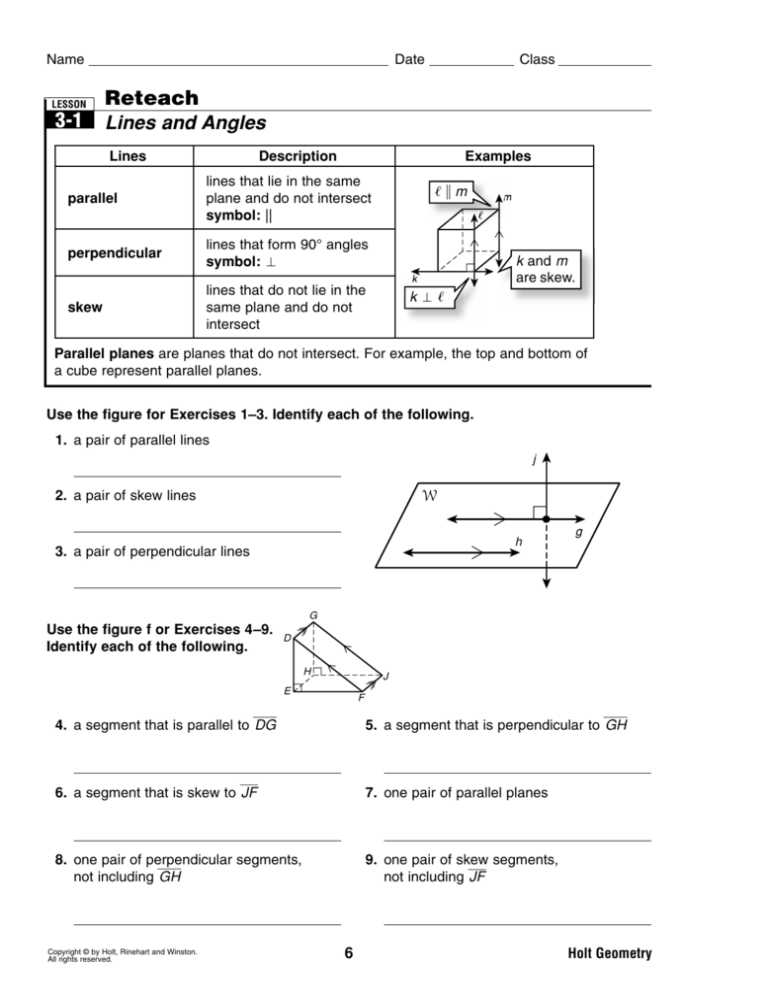
Lines
Description
Examples
parallel
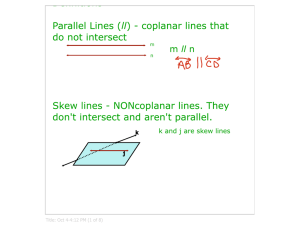
lines that lie in the same
plane and do not intersect
symbol: ||
perpendicular
lines that form 90° angles
symbol: ᐉm
k and m
are skew.
K
lines that do not lie in the
same plane and do not
intersect
skew
kᐉ
Parallel planes are planes that do not intersect. For example, the top and bottom of
a cube represent parallel planes.
Use the figure for Exercises 1–3. Identify each of the following.
1. a pair of parallel lines
g储h
J
2. a pair of skew lines
j and h
G
H
3. a pair of perpendicular lines
j⬜g
'
Use the figure f or Exercises 4 –9.
Identify each of the following.
$
(
*
%
&
_
_
4. a segment that is parallel to DG
5. a segment that is perpendicular to GH
_
_
_
Sample answer: HJ
Possible answers: EH or FJ
_
6. a segment that is skew to JF
7. one pair of parallel planes
_
plane DEF 储 plane GHJ
Sample answer: DE
8. one pair of perpendicular
segments,
_
not including GH
_
9. one pair of skew
_ segments,
not including JF
_
_
Sample answer: DE ⬜ EF
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
_
Sample answer: HE and DF
6
Holt Geometry
Name
LESSON
3-1
Date
Class
Reteach
Lines and Angles
continued
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
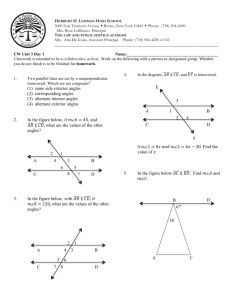
A transversal is a line that intersects two lines in a plane
at different points. Eight angles are formed. Line t is a
transversal of lines a and b.
T
A
B
Angle Pairs Formed by a Transversal
Angles
corresponding
alternate interior
Description
Examples
angles that lie on the same side of
the transversal and on the same
sides of the other two lines
T
4
A
8
angles that lie on opposite sides of
the transversal, between the other
two lines
B
T
4
A
5
B
alternate exterior
same-side interior
angles that lie on opposite sides of
the transversal, outside the other
two lines
T
2
A
7
angles that lie on the same side of
the transversal, between the other
two lines; also called consecutive
interior angles
Use the figure for Exercises 10–13.
Give an example of each type of
angle pair.
1 2
5 6
10. corresponding angles
T
4
A
6
B
3 4
7 8
11. alternate exterior angles
Sample answer: ⬔1 and ⬔3
Sample answer: ⬔1 and ⬔8
12. same-side interior angles
13. alternate interior angles
Sample answer: ⬔2 and ⬔3
Use the figure for Exercises 14 –16.
Identify the transversal and classify
each angle pair.
B
Sample answer: ⬔2 and ⬔7
M
2
N
1
3
14. 1 and 2
4
P
transv. n ; same-side int. ⭄
15. 2 and 4
16. 3 and 4
transv. m; alt. ext. ⭄
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
transv. p; corr. ⭄
7
Holt Geometry
Name
LESSON
3-1
Date
Class
Name
Practice A
LESSON
3-1
Lines and Angles
Complete the statements by matching the correct term.
Skew
1.
parallel
skew
and do not intersect.
intersect
90� or right
3. Perpendicular lines (�) intersect at
Parallel
4.
Class
Practice B
Lines and Angles
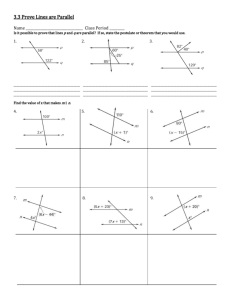
For Exercises 1–4, identify each of the following in the figure.
lines are not coplanar. They are not parallel
2. Parallel planes are planes that do not
Date
1. a pair of parallel segments
angles.
�
_
�
Sample
answers:
_
_
AC
� EG
_
AC and
DH are
_
_skew.
CG � EG
plane ABD � plane EFH
_
CF � EF
�
plane ABC � plane DEF
4. a pair of parallel planes
lines (�) are coplanar and do not intersect.
_
AB and CF are skew.
�
3. a pair of perpendicular segments
Sample_
answers:
_
BE � AD
_
�
2. a pair of skew segments
90� or right
intersect
.
�
For Exercises 5–8, identify each of the following in the figure.
5. a pair of parallel segments
�
�
�
�
6. a pair of skew segments
�
7. a pair of perpendicular segments
�
�
8. a pair of parallel planes
_
�
In Exercises 5–10, give one example of
each from the figure.
5. a transversal
line z
lines
9. A transversal is a line that intersects two coplanar
at two different points. The transversal j and the other two lines k and �
form eight angles.
�
Corresponding
�
outside
same
angles lie on the same side of the
transversal j, on the same sides of lines k and � .
corresponding
lines
alternate
11. Alternate exterior angles lie on opposite sides of the transversal j,
outside
lines k and � .
12.
Alternate
interior angles lie on opposite sides of
the transversal j, between lines k and � .
13. Same-side interior angles lie on the
side of the transversal j, between lines k and � .
������
�
3-1
Sample answer:
�2 and �3
3
Date
Class
Holt Geometry
tension wire
5
exterior angles
14. �5 and �3
transv.: utility pole; alternate
corresponding angles
interior angles
3-1
2. Line k is perpendicular to lines j and � .
Lines � and j are not coplanar.
�
�
�
Lines j and � are skew.
Lines j and � are parallel.
3. Line k is parallel to line j. Line � is
perpendicular to line k. Lines � and j are
coplanar.
4. Line j is parallel to line k and line � is
parallel to line k. Lines � , k, and j are
not coplanar.
�
Lines j and � are perpendicular.
Description
Examples
parallel
lines that lie in the same
plane and do not intersect
symbol: ||
perpendicular
lines that form 90° angles
symbol: �
skew
lines that do not lie in the
same plane and do not
intersect
��m
k and m
are skew.
�
k��
1. a pair of parallel lines
g�h
Lines j and � are parallel.
�
2. a pair of skew lines
�
j and h
Luke and JoAnne make up a game. For a game board, they draw two lines
crossed by a transversal and then they take turns placing Xs and Os in the
angles. Corresponding angles score 10, alternate interior angles score 20,
alternate exterior angles score 30, and same-side interior angles score 40.
Tally the score for X and O on each game board below.
o x
o o
x o
o x
j�g
Use the figure f or Exercises 4 –9.
Identify each of the following.
o x
o x
�
�
�
�
�
X � 10; O � 10
4. a segment that is parallel to DG
_
_
5. a segment that is perpendicular to GH
_
_
Sample answer: HJ
Possible answers: EH or FJ
Draw a filled-in game board that satisfies each condition.
_
6. a segment that is skew to JF
8. X scores the maximum possible amount.
oo
oo
�
_
X � 40; O � 70
7. Neither player scores any points.
ox
ox
7. one pair of parallel planes
_
plane DEF � plane GHJ
Sample answer: DE
xo
xo
8. one pair of perpendicular
segments,
_
not including GH
_
9. one pair of skew
_ segments,
not including JF
_
_
5
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
Holt Geometry
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
51
_
Sample answer: HE and DF
Sample answer: DE � EF
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
�
�
3. a pair of perpendicular lines
6.
5.
Holt Geometry
Use the figure for Exercises 1–3. Identify each of the following.
�
�
Class
Parallel planes are planes that do not intersect. For example, the top and bottom of
a cube represent parallel planes.
�
�
�
Date
Lines and Angles
Lines
������
�������
�
4
Reteach
LESSON
1. Line j is parallel to line k and line � is parallel
to line k. Lines � and j are coplanar.
xx
xx
telephone
line
utility pole
transv.: telephone line;
For Exercises 1–4, sketch an example and state the apparent relationship
between lines j and � .
x x
o x
electrical
line
6
transv.: tension wire; alternate
Name
Lines and Angles
�
3
2
12. �1 and �4
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
Practice C
�
4
1
�1 and �4
�2 and �3
LESSON
Sample answer:
�1 and �5
13. �1 and �2
�1 and �3 or �2 and �4
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
Sample answer:
�2 and �6
interior angles
�
d. alternate exterior angles
Name
10. same-side interior angles
transv.: utility pole; same-side
�
b. corresponding angles
c. alternate interior angles
Sample answer:
�1 and �3
lines x and y
9. alternate exterior angles
�
�
line r
7. corresponding angles
8. alternate interior angles
11. �5 and �6
�
�
a. a transversal
�
Use the figure for Exercises 11–14. The figure shows a
utility pole with an electrical line and a telephone line.
The angled wire is a tension wire. For each angle pair
given, identify the transversal and classify the angle
pair. (Hint: Think of the utility pole as a line for these
problems.)
same
14. Sudeep walks back and forth along parallel segments
in his yard. Then he walks back diagonally across the
yard. Identify each of the following in the figure.
�
6. parallel lines
�
Refer to the figure to match the correct terms for Exercises 9–13.
10.
18
27
36
45
�
6
Holt Geometry
Holt Geometry
Name
LESSON
3-1
Date
Class
Name
Reteach
Date
Challenge
LESSON
Lines and Angles
continued
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
A transversal is a line that intersects two lines in a plane
at different points. Eight angles are formed. Line t is a
transversal of lines a and b.
3-1
�
Spherical Geometry
In Euclidean geometry, a line is a straight path that extends forever in two directions
in a plane. In spherical geometry, a line is a great circle. This is a circle that divides
a sphere into equal halves.
�
�
Angle Pairs Formed by a Transversal
Angles
Description
corresponding
plane
Examples
angles that lie on the same side of
the transversal and on the same
sides of the other two lines
alternate interior
Class
line
�
4
8
angles that lie on opposite sides of
the transversal, between the other
two lines
Euclidean
�
�
4
5
great circle
angle
�
Spherical
Answer yes or no for Exercises 1 and 2.
�
1. Does a line have endpoints in Euclidean geometry? in spherical geometry?
�
alternate exterior
angles that lie on opposite sides of
the transversal, outside the other
two lines
same-side interior
2
7
angles that lie on the same side of
the transversal, between the other
two lines; also called consecutive
interior angles
Use the figure for Exercises 10–13.
Give an example of each type of
angle pair.
1 2
5 6
10. corresponding angles
no; no
�
2. Does a line have a measurable length in Euclidean geometry? in spherical geometry?
�
�
no; yes
�
4
6
Use the figures at right for Exercises 3 and 4.
�
Use the figure for Exercises 14 –16.
Identify the transversal and classify
each angle pair.
counterclockwise direction, is much longer than the length of the path
Sample answer: �2 and �7
traveling from P to Q in a clockwise direction. So, PR � RQ � PQ.
�
2
Each statement below is true in Euclidean geometry. Explain why it is false in
spherical geometry.
�
1
3
14. �1 and �2
4
5. If two lines intersect, then their intersection is exactly one point.
�
Any two lines will intersect at exactly two points.
transv. n ; same-side int. �
15. �2 and �4
7
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
3-1
If the two points are at opposite “poles,” then infinitely many lines will pass
through them.
transv. p ; corr. �
transv. m ; alt. ext. �
LESSON
6. One and only one line contains two given points.
16. �3 and �4
Name
Date
Class
Holt Geometry
Problem Solving
3-1
_
�
�
_
_
�
is skew to AD, but AP is not skew to AD.
symbol for parallel
Parallel lines (� ) are coplanar lines that do not intersect. In a figure, they are
marked with matching arrows to indicate they are parallel.
�
�
symbol for perpendicular
2. If a segment is skew to one of two parallel segments, must it be skew to the other?
_
_
_
Holt Geometry
Connect Words with Symbols
�
�
_
Class
�
_
Sample answer: No; AP is skew to RS and RS
_
Date
Reading Strategies
LESSON
Use the diagram of the rectangular box for Exercises
1 and 2. Refer to the diagram to help justify your answer.
8
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
Name
Lines and Angles
1. Is the relationship “is skew to” transitive?
�
Spherical
The distance PR � RQ, the length of the path from P to Q traveling in a
13. alternate interior angles
Sample answer: �2 and �3
�
4. Can you draw the same conclusion about the spherical figure? Explain.
Sample answer: �1 and �8
12. same-side interior angles
�
PR � RQ � PQ
11. alternate exterior angles
�
Euclidean
�
3. In the Euclidean figure, what conclusion is
drawn from the Segment Addition Postulate?
3 4
7 8
Sample answer: �1 and �3
�
In each figure, P, Q, and R are collinear points
and R is between points P and Q.
�
Sample answer: No; PQ is skew to AD but not to PS.
Perpendicular lines (� ) intersect at 90� angles. In a figure, they are marked
with a right angle box.
Use the flag of Puerto Rico for Exercises 3 and 4.
3. If �DFC and �ACF are same-side interior angles,
identify the transversal.
�
�
�
�
CF
�
�
�
_
�
_
_ _
_
�
�
OS � NR, ON � LM
4. Name a pair of_
alternate interior angles if the
transversal is BE.
_
_ _
_
MQ � QR, PS � SR
Sample answer: �DEB and �CBE
�
�
Choose the best answer.
5. Describe the type of lines suggested by the two skis of a person water skiing.
A intersecting lines
�
_
B parallel lines
C perpendicular lines
_
G parallel
J skew
�
_
�LSK and �PHQ are corresponding angles.
�JSQ and �JQH are corresponding angles.
�LSK and �QSJ are same-side interior angles.
�PHQ and �RLS are same-side interior angles.
_
2. Is NR � SR ? Explain.
Yes, there is a right angle box at their intersection.
�
_ _ _
_
3. In the diagram, LM, ON, PQ, and SR are all parallel. How do you know this?
7. In the quilt pattern, which is a true statement
about
angles formed
by the transversal
_ the_
_
HK and HM and JL?
A
B
C
D
_
_
LP and MQ
D skew lines
H perpendicular
_
1. In the figure, OS � NR . What other segments are parallel to OS and NR ?
6. Describe the type of lines suggested by the paths of two people at a fair when
one person is riding the aerial ride from one end of the fair to the other, and
the other person is walking in a different direction on the ground.
F intersecting
�
_
�
�
�
�
�
�
All four segments are marked with the same arrows.
�
4. Explain the difference between parallel and perpendicular lines.
Sample answer: Parallel lines are coplanar lines that never intersect,
�
and perpendicular lines intersect at 90� angles.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
9
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
Holt Geometry
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
All rights reserved.
52
10
Holt Geometry
Holt Geometry