Tribology_lab01 (Static friction)
advertisement

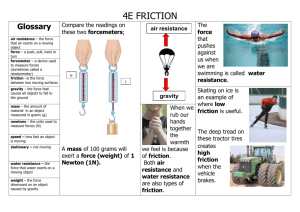
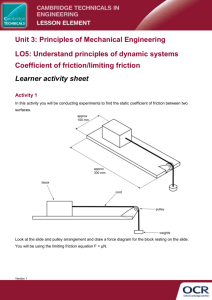
Tribology EXCERCISE No. 2 Author: Piotr Kowalewski Wroclaw University of Technology Department of Fundamentals of Machine Design and Tribology Subject: Static friction measurement 1. Static friction The subject of the exercise is measurement of friction coefficient of static friction. Static friction is very important, a specially at the beginning of machine movement. Static friction is friction between two solid objects that are not moving relative to each other. For example, static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface. The coefficient of static friction, typically denoted as µs or µ 0, is usually higher than the coefficient of kinetic friction µ, µ k. The static friction force must be overcome by an applied force before an object can move. The maximum possible friction force Ft between two surfaces before sliding begins is the product of the coefficient of static friction and the normal force Fn (1). Ft = µ s ⋅ Fn (1) Any force larger than Ft overcomes the force of static friction and causes sliding to occur. The instant sliding occurs, static friction is no longer applicable and kinetic friction becomes applicable. An example of static friction is the force that prevents a car wheel from slipping as it rolls on the ground. Even though the wheel is in motion, the patch of the tire in contact with the ground is stationary relative to the ground, so it is static rather than kinetic friction. The maximum value of static friction, when motion is impending, is sometimes referred to as limiting friction,[2] although this term is not used universally.[1] 2. Angle of friction For certain applications it is more useful to define static friction in terms of the maximum angle before which one of the items will begin sliding. This is called the angle of friction or friction angle. It is defined as (2): tan ρ = µ s (2) where ρ is the angle from horizontal [3]. This formula can also be used to calculate from empirical measurements of the static friction coefficient. 3. Measurement method Static fricton is measure on simple tribological device, which is base on inclined plane. The device measure a angle of repose (the angle when speciment start moving on the contrspeciment). The tester has a laser indicator which pointing on the scale (µ, ρ). Investigation could be done on different value of unite pressure p, and only in flat contact. Fig. 1. Main idea chart of static friction experimental device: 1 – Tilting bar, 2 – friction couple, 3 – electrical actuator, 4 – laser indicator, 5 – scale. Fig. 2. Static friction experimental device: 1 – Tilting bar, 2 – revolving grip, 3 – electrical actuator, 4 – laser indicator, 5 – weights, 6 – samples holder. REFERENCES: [1 ] - Beer, Ferdinand P.; E. Russel Johnston, Jr. (1996). "Vector Mechanics for Engineers" (Sixth ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 397. [2] - Bhavikatti, S. S.; K. G. Rajashekarappa. Engineering Mechanics. p. 112 Retrieved 2007-10-21. [3] - Nichols, Edward Leamington; Franklin, William Suddards (1898). The Elements of Physics. 1. Macmillan. p. 101. Addition from Competition Science Vision, Mar 2001, 136, Tom 4, Nr 37, Pratiyogita Darpan. (Attention different symbols !!!)