trier American Contract Law III.pptx

Contract Law
Lawrence Siry
This Class
• Remedies, aka Damages
– Expecta2on Damages
– Reliance Damages
– Res2tu2on Damages
Hawkins v. McGee (NH 1929)
• Hawkins,(P) had scarred hands from electrocuEon.
• McGee (D) was a doctor who promised a
100% good hand.
• D used skin graK from chest and D grew hair on his palms.
• P sued D.
Hawkins v. McGee (NH 1929)
• Writ of Assumupsit-‐ way of geOng into court-‐ this sounds more like a tort case then a contract case.
• Why is this not a tort case-‐ usually these cases are not contract cases-‐ why is this one different??
• Carbolic
Hawkins v. McGee (NH 1929)
• “….the difference between a the value to him of a perfect hand… and the value of his hand in its current condiEon.”
•
.
• Pain not included as that was expected under in any surgery.
EXPACTATION DAMAGES
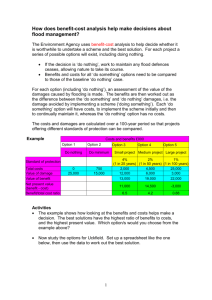
• Louise Caroline Nursing Home v. Dix ConstrucEon
(MA 1972)
-‐D contracted to build a nursing home for P.
-‐D breached.
-‐P sued, but it cost less to finish the construcEon than did the contract (P saved Money)
How should a court assess damages??
EXPACTATION DAMAGES
• CompensaEon is the value of the performance of the contract-‐ what the plainEff would have made had the contract been performed.
• Reasonable costs for compleEng the contract. In this case Nothing!
• Service contracts cannot put the plainEff in a be#er posi*on than if the K had not been entered into.
EXPACTATION DAMAGES
• Peevyhouse v Garland Coal (OK 1963) (not part of reading)
• Garland D contracted to do strip mining on
Peevyhouse’s property for five years. Under the
Contract, D was to return the property to its original condiEon aKer the mining.-‐ they did not.
• Lower court awarded damages equal to the amount that the value of the un-‐restored property had diminished.
• Peevyhouse wanted the cost of restoraEon.
EXPACTATION DAMAGES
• Peevyhouse v Garland Coal (OK 1963)
• The Court looked at the primary purpose of the
Contract and decided that it was for the mining-‐ the restoraEon was incidental.
• Therefore-‐ it would amount to economic waste to give damages for the restoraEon.
• Yet the court stated that if the contract provision was central, then the cost of performance would be the appropriate damages-‐
• Correct?
MiEgaEon of Damages
• PlainEff has a duty to miEgate-‐ or make less damages.
• §350. AVOIDABILITY AS A LIMITATION ON DAMAGES
• ( 1) Except as stated in Subsec2on (2), damages are not recoverable for loss that the injured party could have avoided without undue risk, burden, or humilia2on.
• (2) The injured party is not precluded from recovery by the rule stated in Subsec2on (1) to the extent that he has made reasonable but unsuccessful efforts to avoid loss.
MiEgaEon of Damages
• Rockingham County v. Luten Bridge (NC 1929)
• D had contracted with P to build a bridge.
• AKer P began D cancelled the contract.
• P conEnued work and sued for the damages.
• Court: P is enEtled to damages limited to the amount of damages that he would have been able to recover as of the Eme noEce of cancellaEon was given.
• What if the noEce was equivocal?
• Why is this good or bad? Clear or Unclear?
ConsequenEal Damages: Foreseeability
• ValenEne v. General American
– D fired sued for mental distress
– Loss of security
• Issue: Are mental distress damages awardable under contract law?
• All contract breaches are annoying-‐ get over it.
• What about discriminaEon claims?
ConsequenEal Damages: Foreseeability
• So….. What damages are recoverable….
Specific Performance
• Equity….
• What might be awarded and why?
Specific Performance
• London Bucket v Stewart (KY 1951)
• Contract to install heaEng
• D breached, P sued.
• Court ordered Specific Performance.
• Appeals Court-‐ where ordinary damages suffice-‐ use them.
• WHY?
Specific Performance
• Where is Specific performance preferable?
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
– Non-‐disclosure.
– Undue influence
– Duress
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Indefiniteness
– ParEes or Court do not understand the term
– Yet, Court may read in terms of reasonableness
– Eg: Land, Paint, Build
– Employment Contracts
– Policy determinaEons: Gap Fillers, Performance
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Indefiniteness
– DeterminaEon of Price
– Delivery
– Custom
– Agreements to Agree
– But, illusory or one sided agreements
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Indefiniteness
• Doctrine of Duty to NegoEate in Good Faith
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Mistake
– Mutual
• Basic assumpEon
• Materially effects the agreement
• Risk not assumed
– Unilateral
• Unconscionable
• No hardship for the non mistaken party
– MistranscripEon
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Mistake
– Mutual
• Basic assumpEon
• Materially effects the agreement
• Risk not assumed
• Sherwood v. Walker (Cow) (1887)
• Race Horse (voidable)
• Rock Band
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Mistake
– Mutual
• But one party can bear the risk
• Mistake in judgment
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Mistake
– Mutual
– Unilateral
• A mechanical mistake, computaEon, percepEon
– Awareness of palpable mistake
– Unconscionable
– No hardship for the non mistaken party
– Eg.: Contract bid
– Errors in Judgment?
Reasons not to enforce a contract
Mistake
– Mutual
– Unilateral
– MistranscripEon
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• MisrepresentaEon , (not in accord with the facts)
– Fraudulent
• IntenEon/knowledge
– Full knowledge
– Presents guess as truth
– Basis for asserEon
• would induce a reasonable person
• Eg shoes
– Material
• Non-‐disclosure
• Undue influence
• Duress
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• MisrepresentaEon ,
– Material MisrepresentaEon
• without fraud
• Would induce a reasonable person to agree OR THIS parEcular person agree
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• MisrepresentaEon
• Non-‐disclosure
– When does non disclosure = voidable
– Eg house contract
• Undue influence
• Duress
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• MisrepresentaEon
• Non-‐disclosure
• Undue influence
– Eg Uncle Bunky
• Duress
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• MisrepresentaEon
• Non-‐disclosure
• Undue influence
• Duress
– Threats
– Economic example
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Unconscionability
• So beyond the bounds (at the Eme made) that the court may void the contract or term
– Procedura l v. SubstanEve
– Bargaining power
– Adhesion terms (unfiar surprise)
– Life insureance, phones?
– Protect the weak
– SubstanEve
• Encyclopedias
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
– Non-‐disclosure.
– Undue influence
– Duress
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
Statute of Frauds
• Certain contracts MUST be reduced to wriEng.
• Marriage.
• Land.
• Contracts that take longer than a year.
• Executor
• Surety
• IT IS RAISED AS A DEFENSE
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
– Non-‐disclosure.
– Undue influence
– Duress
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Lack of Capacity
– Minority
– Mental impairment
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Lack of Capacity
– Minority
– minors can void or enforce contracts, and even past the age of majority.
– ResEtuEon
– Neccessaries
– Mental impairment
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Lack of Capacity
– Minority
– Mental impairment
• If mental defect is at the Eme of the making of the contract, then voidable if the impairment prevented him from
– Understanding the nature and consequences of the transacEon, or
– Unable to act in a reasonable manner and the other party knows this
– Yet, if fair terms or performed or equity requires the the court may enforce the contract
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Illegality
– At Eme of accord
– Subsequent illegality
– Aid to illegal act
– Contract is void-‐ no aid to either party
– Locus penitenEae
– Football announcer/ Usurious contract
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
– Non-‐disclosure.
– Undue influence
– Duress
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
Reasons not to enforce a contract
• Indefiniteness
• Mistake
• MisrepresentaEon
– Non-‐disclosure.
– Undue influence
– Duress
• Unconscionability
• Lack of wriEng (Statute of Fraud)
• Lack of Capacity
• Illegality
WHAT IS A CONTRACT
•
An Agreement between two or more parEes which creates rights and obligaEons between the parEes, with the intenEon of the parEes to create legally binding responsibiliEes.
43
Recipe for Contract
• Offer
• Acceptance
• ConsideraEon
• ParEes wish to be bound
Recipe for Contract
• Offer
– Offer v. InvitaEon To Treat
• Acceptance
– UncondiEonal v. Counter Offer
• ConsideraEon
– Real, detriment, future rather than Past
• ParEes wish to be bound
– MeeEng of the minds
Requirements of Contract
• When must the document be in wriEng?
• What precision is needed?
• Also…. InterpretaEon of the contract.
• Parole Evidence
• Historical development of Contract law.
Vielen Dank
lawrence.siry@uni.lu
47