SOAR: The Science behind Solar Radiation, Greenhouse Gases
advertisement

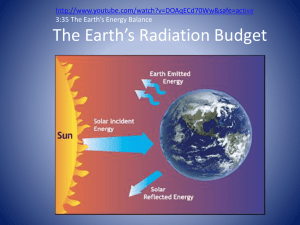
SOAR: The Science behind Solar Radiation, Greenhouse Gases, and Greenhouse Effect Suresh Dhaniyala, Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY 315 268 6574; sdhaniya@clarkson.edu Outline Agenda Introduction Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum Blackbody radiation Greenhouse gases (GHGs) EM emission spectrum of Sun, Earth lightbulb etc. Absorption of EM radiation GHG concentration and temperature All applets will be accessed from: Google “Clarkson K-12” (http://www.clarkson.edu/highschool/k12/) Click on Climate change education Project-based climate modules Greenhouse effect Current state of the climate Current state of the climate (NOAA) http://www.climate.gov/#climateWatch How globally-averaged temperatures have changed over the past decade Change in atmospheric CO2 concentrations over the past 50 years Climate change Documented increase in globally-averaged temperatures over the past 40 year or so Temperature increase has corresponded to increase in CO2 concentrations Questions: Why is the temperature rising? What is the connection with CO2 concentrations? Need to understand: Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases Solar radiation and Terrestrial radiation Electromagnetic radiation How do cell phones communicate with towers? Radiofrequency waves Radiofrequency waves In the spectrum of Electromagnetic waves Source: Planet Adirondack, The Wild Center; Electromagnetic (EM) radiation Examples of other kinds of EM radiation? Used for cooking in your kitchen Microwaves Night-time imaging Infrared Light, x-rays, gamma rays What’s common? They are all part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (SSC) Electromagnetic radiation EM radiation - background http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/k now_l1/emspectrum.html EM radiation – applets Under “Resources” - Click on “Electromagnetic Spectrum Applet” (http://lectureonline.cl.msu.edu/~mmp/a pplist/Spectrum/s.htm) Investigate: What wavelengths correspond to: Visible light Heat radiation Solar and Terrestrial radiation All bodies emit electromagnetic radiation Most of the energy is emitted in one form of Electromagnetic (EM) radiation The nature of emission depends on the body temperature. e.g., light, IR, etc Hotter bodies emit shorter wavelengths. Applet – Click on “Blackbody radiation applet” Investigate: What are the peak wavelengths of EM radiation corresponding to: Sun (~ 10,000 F) Earth (~ 70 F) Incandescent light bulb Applet Source: PhET, University of Colorado. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/blackbody-spectrum Note: Flash required to run this program (http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/ ) Emission profiles Sun (5777K) Earth (300K) Earth’s Energy Balance Solar radiation Terrestrial radiation Source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/EnergyBalance/ Greenhouse effect Energy radiated from Earth is trapped, but energy from Sun is allowed through Helps keep Earth’s temperature warm enough for humans to survive Applet Click on “Greenhouse effect simulation” In the applet, click on “Glass layers” tab Investigate: What is Earth’s temperature in the absence of any “glass layer” How does the temperature change as you add “glass layers” Applet Source: PhET, University of Colorado. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/greenhouse Note: Need Java to run this program Greenhouse gases Certain gases in the atmosphere can act as “glass layers” and absorb the out-going long-wave radiation Applet These gases are referred to as greenhouse gases (GHGs) Click on “Greenhouse effect simulation” In the applet, click on “Photon Absorption” tab Investigate: Which gases are greenhouse gases? Applet Source: PhET, University of Colorado. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/greenhouse Note: Need Java to run this program Greenhouse Gases and Earth’s Temperature The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere determines Earth’s temperature Applet Click on “Greenhouse effect simulation” In the applet, click on “Greenhouse effect” tab Investigate: What is Earth’s temperature with no greenhouse gases? What is Earth’s temperature considering the greenhouse gases during: Ice-age, pre-industrial era (1750) and today? Applet Source: PhET, University of Colorado. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/greenhouse Note: Need Java to run this program Radiation spectra Source: Wikipedia Future trends The future emissions of greenhouse gases depends on our lifestyle and societal developments We can imagine scenarios and model (i.e., calculate) what the future climate might look like IPCC models different “scenarios”. All models suggest much warmer climates Upcoming SOAR Classes: Susan Powers – “Sources of Greenhouse Gases and Your Own Carbon Footprint. (3/25; CAMP 163) Jon Rosales – “On the Front Lines.” (4/01; CAMP 175) Stephen Bird – “Integrating Science into the Policy Process.” (4/08; CAMP 175) Applets All Applets can be accessed from http://www.clarkson.edu/highschool/k12/ Other References: IPCC report, 2007 Hardy J.T., Climate change: Causes, Effects, and Solutions, Wiley Publications, 2006 www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov NOAA : www.climate.gov