7 - Cell Cycle.notebook
advertisement

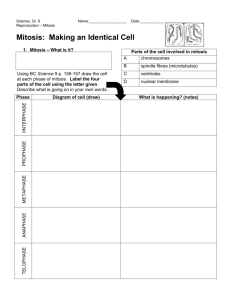
7 ­ Cell Cycle.notebook April 04, 2014 Notes March 2014 Why do cells need to divide? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O3_PNiLWBjY http://videolib.dvsdedu.org/library/359424 http://videolib.dvsdedu.org/library/86324 Cell Cycle - The life cycle of a cell; Broken up into three main parts beginning with 1. Interphase, followed by 2. Mitosis and ending with 3. Cytokinesis. % = ______ % = ______ % = ______ 1. Interphase - The first stage of the cell cycle where the following occurs: 1. The cell grows 2. The cell's DNA is replicated 3. The cell waits until Mitosis needs to start. 2. Mitosis - The second stage of the cell cycle where the nucleus splits, (Mitosis = nucleus division). Made up of 4 phases: a. Prophase b. Metaphase c. Anaphase d. Telophase Important Terms to Know for Mitosis Chromosome - Condensed (smushed), coiled-up DNA. Centrioles - Rod-shaped structures in the cell that produce spindle fibers. These spindle fibers are sticky and attach to the centromere of the chromosome to move them around the cell during Mitosis. 7 ­ Cell Cycle.notebook April 04, 2014 2a. Prophase - The first phase of Mitosis where the following occurs: - The nuclear membrane disintegrates - Chromosomes become visible - Centrioles produce spindle fibers 2b. Metaphase - The second phase of mitosis - The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell - The nuclear membrane is gone 7 ­ Cell Cycle.notebook April 04, 2014 2c. Anaphase -The third phase of mitosis -Spindle fibers pull the chromosomes apart into chromatids 2d. Telophase - The last stage of mitosis - Cell is stretched - Chromatids uncoil - The nuclear membrane reforms around the DNA 7 ­ Cell Cycle.notebook April 04, 2014 3. Cytokinesis - The last stage of the cell cycle - The cytoplasm splits to make two new daughter cells. Daughter Cell - Either of the two cells formed after cell division; each cell is genetically identical to the original parent cell.