Semester Test notes Chapter 1 1) Biology is the study of living things
advertisement

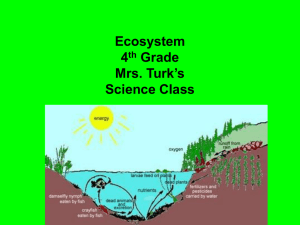
Semester Test notes Chapter 1 1) Biology is the study of living things 2) All experiments start with an observation. It can be qualitative or quantitative. Observations lead to questions. 3) The scientific method also starts with an observation. It consists of six steps a. Problem b. Research c. Hypothesis d. Experiment e. Analysis f. Conclusion 4) All experiments must have an independent variable, dependent variable, and a control. 5) The information gathered during an experiment is called data. 6) Technology is used to help society’s needs. 7) Scientist classify living things based on if they show the following characteristics a. They must have an orderly structure b. They must reproduce c. They must grow and develop d. They must adjust to change in the environment 8) Living things also react to a stimulus, undergo homeostasis, and adapt and evolve. Chapter 2 1) Ecology is the study of how living things interact with non-living things in the environment. Living things are biotic and non-living things are abiotic. 2) Living things are found in the biosphere. An organism (species) is the lowest level of organization. Next is population, followed by community, then ecosystem, then biosphere. 3) A habitat is where something lives and its niche is its role in the environment. 4) There are 3 types of symbiosis. a. Mutualism b. Commensalism c. Parasitism 5) Energy continuously flows through an ecosystem through a food web or a food chain. 6) The arrows show the direction that the energy flows. 7) A food chain or food web always starts with a producer/autotroph. It then flows to a primary consumer, then to a secondary consumer, then to a tertiary consumer and so on. Consumers are heterotrophs. The most amount of biomass is at the bottom of a trophic structure. 10% is passed on the next level. 8) Carbon, water, nitrogen, and phosphorous are cycled through the environment also. Chapter 3 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Succession is a natural change in a community over time. It can be either primary or secondary Primary starts on barren land Secondary starts on land that was destroyed They grow into a climax community Limiting factors will limit how much a community can grow. Chapter 4 1) A J curve represents exponential growth 2) Carrying capacity is how many of a population that the environment can support. Usually represented by an s graph. 3) Density dependent and density independent factors can also limit how big a population can get. 4) Demography is the study of populations Chapter 6 1) pH measures how acidic or how basic something is 2) Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration. Molecules move along the concentration gradient and stop moving when they have reached dynamic equilibrium. 3) water dissolves many things because of its polarity 4) A nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. 5) All organic molecules contain carbon. 6) Atoms are the building blocks of all matter.