1 BI212 Study Guide Animal Form and Function: Week 4 Vocabulary
advertisement

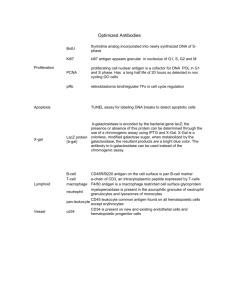
BI212 Study Guide Animal Form and Function: Week 4 Vocabulary words: Glomerulus Proximal tubule Loop of Henle Distal tubule Collecting duct Vasa recta Nerve nets Central nervous systems Peripheral nervous systems Ganglia Cephalization Sensory input Integration Motor output Receptor Sensory neuron Interneuron Motorneuron Effector cell Dendrite (review) Cell body (review) Axon (review) Synapse Myelin sheath Schwann cell Ungated ion channel Gated ion channel Resting potential Polarization Lymphocytes B cell T cell Antigen receptor antibody antigen Helper T cell MHC complex Antigen presentation Cell-mediated response Cytotoxic T cell Perforin Humoral response Clonal selection Memory Osmolarity Osmolyte Osmoconformer TMAO Isoosmotic Osmoregulator Hypoosmotic Hyperosmotic Excretion Ammonia Urea Uric acid Protonephridium Malphighian tubules Kidney Nephron Understand the antigen receptors occur on the outside ob B cells and T cells. Understand that they are unique and specific to that particular cell. Understand what antigen receptors are recognizing. What is antigen presentation in the helper T cell and in the cytotoxic T cell. What cell types and what molecules are involved? What is the end result in the case of helper T cells? What is the end result in cytotoxic T cells? 1 What is the role of the helper T cell in the acquired immune response? What is the cell-mediated response? How do cytotoxic T cells kill target cells? What is the humoral response? What is the involvement of B cells? What is memory? How does it occur at the cellular level? Understand how it is the basis for the development of vaccines. What is osmotic homeostatis? What is osmolarity? What are the units we used in our discussions? What is an osmolyte? What are some examples of different kinds of osmolytes? What is an osmoconformer? What environments to they occur in? How do osmoconformers keep the same osmolarity of seawater without destabilizing their macromolecules? Understand how marine invertebrates and sharks osmoconform to seawater. What is an osmoregulator? What kinds of environments do these animals occur in? How do bony fish osmoregulate in seawater and in freshwater? Are they hyper- or hypoosmotic to these environments? What strategies do vertebrates use to prevent dessication? What is excretion? Compare and contrast the 3 excretory products made by organisms. What are the benefits and drawbacks to the use of each of these compounds? What is the general construction of an excretory system? What 4 functions so all excretory systems perform? Describe and form and function of protonephridia and Malphighian tububles. Understand the structure of the vertebrate kidney and nephron. Understand the function of the vertebrate nephron. Understand the location where each of the 4 functions of an excretory system are performed. 2 Compare and contrast the kidneys of 1) desert kangaroo rats and beavers 2) bony fish in seawater and freshwater and understand how environment plays a role in their contrasting structures. Understand the phylogenetic diversity of nervous systems. Understand that complexity increases with increased cephalization. Do sensory cells occur only in the most cephalized animals? Compare and contrast the nervous systems of chitons and squids. How does lifestyle affect nervous system development? What are the general components of a neural circuit? What parts of the nervous system are involved? In the specific case of the knee-jerk reflex, what are the component of this circuit? What are the effector cells? What is the other major kind of effector cells in the body? What is a synapse? Where does it occur on the neuron? What is the myelin sheath? Compare and contrast gated and ungated ion channels. How are they different than pumps? What is resting potential? How is it maintained in a neuron? What is the actual value in mV of the resting potential of a neuron. Is it – in the inside or outside? 3