Pectoral Region and Axilla:
advertisement

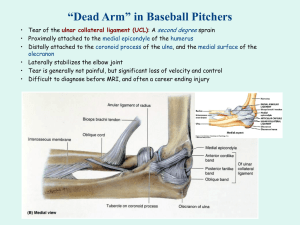
Guo-Fang Tseng, p.1 of 3 Joints of shoulder girdle and upper limb Shoulder girdle 1) Sternoclavicular joint: articular disc sternoclavicular lig costo-clavicular lig interclavicular lig 2) Coracoclavicular lig: no articular surface conoid lig trapezoid lig 3) Acromioclavicular joint: joint capsule Shoulder joint: Ball and socket: head of humerus + glenoid cavity of scapula Supraglenoid tubercle: biceps-long head Infraglenoid tubercle: triceps-long head Glenoid labrum: fibrocartilage Fibrous capsule and ligaments: loose capsule to allow great movement Coracohumeral ligament: top of capsule: prevents inf. dislocation of the adducted humerus and also limits lateral rotation. Posterior part blends with fibrous capsule. Synovial membrane: lines the fibrous capsule Interior of joint: thickening of fibrous capsule; visible when capsule is relaxed Glenohumeral lig: (posterior view) superior; middle: most prominent; inferior Long head of biceps: synovial bursa communicates with the joint space @ Transverse humeral ligament: across intertubercular sulcus @ Rotator cuff or guardian muscles, or Accessory dynamic ligaments: sup.: Supraspinatus (tendon fuses with joint capsule) post.: Infraspinatus, Teres Minor ant.: Subscapularis @ Bursae: Subscapularis bursa----subscapularis tendon (front) Biceps synovial sheath Subacromial (subdeltoid) bursa @ Coracoacromial arch: Coracoid process + Coracoacromial lig. + Acromion Secondary socket for head of humerus, prevent upward displacement. @ Summary of muscle innervation around the shoulder joint: C5, 6: flexion, abduction, and lateral rotation C5-T1: extension, adduction, and medial rotation damage of C5-6: "tip-taking" position of upper limb (upper trunk) Guo-Fang Tseng, p.2 of 3 Elbow Joint: Hinge joint (with collateral ligaments); continuous with proximal radioulnar joint Bones: 1) Humeroulnar part: A) Distal humerus: trochlea; coronoid fossa; olecranon fossa @ Medial epicondyle B) Proximal Ulna: coronoid process; olecranon; trochlear notch @ Olecranon bursa: underneath skin @ Radial notch of Ulna: facet on the lat. surface of coronoid process @ Brachialis inserts on the ant surface of coronoid process (ulnar tuberosity) 2) Humeroradial part: A) Distal humerus: capitulum @ Lateral epicondyle B) Proximal Radius: fovea: facet Ligaments and Capsule: Radial collateral ligament: lat. epicondyle side of annular ligament Ulnar collateral ligament: med. epicondyle medial margin of trochlear notch Fibrous capsule: Proximal radioulnar joint: Annular ligament: attaches to radial notch of the Ulna; cup-shaped Carrying angle: with the joint fully extended, humerus not in a straight line with ulna distal end of Ulna lies lateral to the axial line of humerus Radioulnar joint: Proximal: included in elbow joint Intermediate: interosseous membrane; note orientation of fibers Distal: Head of Ulna slides on the ulnar notch of Radius Articular disc at the end of the head of Ulna Articular disc: Pit (base, styloid process of Ulna) lower border of ulnar notch of Radius @ Test: fixing shoulder joint: pronation + supination = 180° free shoulder joint: pronation + supination = 270° Bones and Joints of Wrist and Hand 2 rows of carpal bones (from radial ulnar) Distal row: Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate Proximal row: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform Guo-Fang Tseng, p.3 of 3 Facts: Carpal bones: 1) Pisiform sits in front of Triquetrum and articulates with it only. 2) Scaphoid + Lunate + Triquetrum convex, ovoid articular surface Movement: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction 3) Capitate, the largest, with its head fits into the proximal row 4) Scaphoid elongated distally 6) Mid (transverse) carpal joint: sinuous, between prox. & distal rows of carpal bones Movement: most of the apparent flexion of the wrist (radiocarpal) joint, but not much abdution or adduction Carpo-metacarpals: 1) Saddle joint between Trapezium and 1st metacarpal great mobility 2) 2nd metacarpal fits tightly to Trapezium, Trapezoid & Capitate 3) 3rd metacarpal fits on Capitate 4) 4&5th metacarpals fit on Hamate: slight degree of flexion 5) Articulation between the lateral side of the bases of 2nd, 3rd, 4th & 5th metacarpals Wrist (Radiocarpal) Joint: Articular disc: attaches to fossa at the base of the styloid process of ulna, covers the surface of the head of ulna Socket: inferior articular surface of radius + articular disc Convex surface: proximal articular surface of Scaphoid, Lunate & Triquetrum + interosseous ligament binding these three bones. Ligaments: runs obliquely & inferomedially Palmar radiocarpal ligament Palmar ulnocarpal ligament Dorsal radiocarpal ligament: strong Dorsal ulnocarpal ligament: weak Radial (lateral) collateral ligament: radial styloid process scaphoid Ulnar (medial) collateral ligament: ulnar styloid process triquetrum Metacarpophalangeal joints: 2-5th digits, Condyloid joint (biaxial): flexion, extension, abduction, adduction. Collateral ligament Extensor expansion covers the posterior capsule Anteriorly, palmar ligament (plate) Deep transverse metacarpal ligament: connects the palmar ligaments of 4 digits. @ abd & add only when joints are extended. d. Phalanges and their joints: Extensor expansion on dorsal surface of proximal phalanx Osseofibrous tunnel: on palmar surface; flexor tendon slides in it Interphalangeal joint: hinge joint: flexion/extension