INF 2149 Administrative Decision Making in Information Organizations
advertisement

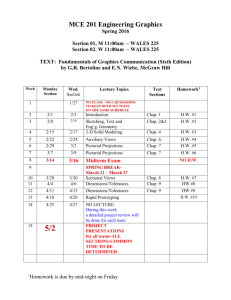
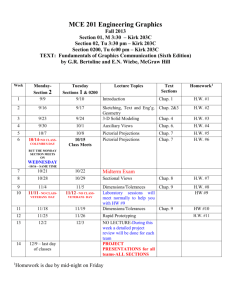
INF 2149 Administrative Decision Making in Information Organizations Course Description Instructor: Chun Wei Choo The study of decision making in organizations has a long, active tradition and many researchers contend that analyzing decision making processes is the key to understanding how organizations function. Yet the research on organizational decision making has yielded apparently contradictory analytical frameworks, from models that depict decision making as rational and sequential to models that describe decision making as random and anarchical. This course integrates these perspectives in a contingency view of organizational decision making as a social activity that varies its form and content depending on the nature of the problem, context of the organization, cognitive traits of individuals, the availability of information, and other factors. Course Objectives The purpose of this course is to introduce major models that have been developed to understand, analyze, and manage decision making processes in information organizations. These frameworks are based on research in organization theory, social psychology, and information needs and uses studies. Course Learning Outcomes At the end of this course, students should be able to: Understand and evaluate major modes of organizational decision making and the role of information seeking and use in each mode Identify and address information challenges and pitfalls that organizations face in decision making Apply their understanding of organizational decision making to improve information services, systems and practices Apply theoretical models of organizational decision making to analyze and assess the effectiveness of actual cases or episodes of decision making. Relationship to MI Program Learning Outcomes This course helps students to understand and be conversant with the concepts that explain decision making as an information-intensive activity of all organizations (Program Outcome 1). The knowledge and values imparted in the course enable students to exercise leadership and care in the design and provision of information services (Program Outcome 2). Through their case analysis projects, students learn to apply and critique theoretical models of decision making in relation to actual organizational experiences (Program Outcome 3). Finally, students gain a theoretical understanding of how information seeking and use affects decision making (Program Outcome 4). Prerequisite INF 1230 (Management of Information Organizations) is a requirement. Recommended Texts The treatment of organizational decision making in this course is summarized in: Choo, Chun Wei. 2006. The Knowing Organization: How Organizations Use Information to Construct Meaning, Create Knowledge, and Make Decisions. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press. Full text available from Oxford Scholarship Online. Much of the argument is laid out in Chapter 1 and 5. Other useful texts are: Harrison, E. Frank. 1999. The Managerial Decision-Making Process. 5th ed. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin. March, James G. 1994. A Primer on Decision Making: How Decisions Happen. New York, NY: Free Press. Heath, Chip and Dan Heath. 2013. Decisive: How to Make Better Choices in Life and Work. New York: Random House. Simon, Herbert A.. 1997. Administrative Behavior: A Study of Decision-Making Processes in Administrative Organizations. New York, NY: Free Press. Evaluation There are two assignments. The first asssignment requires the student to write an essay on a relevant topic in organizational decision making. For suggested topics please see the assignment page. Students may also choose their topic which must be approved by the instructor. [40%] The second assignment requires students to work in groups of three to prepare a presentation of an actual case of decision making in an organization. The instructor may recommend suitable cases for analysis, but students are encouraged to select their own cases, based on their own experience or reading. [40%] Students should prepare for each class by reviewing suggested cases and readings so that they come prepared to discuss them during class. [20%] Instructor Availability Students should feel free to discuss course-related matters with the instructor at any time. Chun Wei's office is Room 628; telephone 416.978.5266; e-mail cw.choo@utoronto.ca. Office hours TBA. Course Website and Wiki Course descriptions, schedules, reading list, slides, and the course wiki may be accessed from http://choo.ischool.utoronto.ca/. Academic Policies Academic integrity Please consult the University's site on Academic Integrity. The iSchool has a zerotolerance policy on plagiarism as defined in section B.I. 1. (d) of the University's Code of Behaviour on Academic Matters. You should acquaint yourself with the Code and Appendix A Section 2. Please review the material you covered in Cite it Right and consult the site How Not to Plagiarize. Accommodation of students with disabilities Students with diverse learning styles and needs are welcome in this course. In particular, if you have a disability or health consideration that may require accommodations, please feel free to approach me and/or the Accessibility Services Office as soon as possible. The Accessibility Services staff are available by appointment to assess specific needs, provide referrals and arrange appropriate accommodations. The sooner you let them and me know your needs, the quicker we can assist you in achieving your learning goals in this course. Writing support The SGS Office of English Language and Writing Support provides writing support for graduate students. The services are designed to target the needs of both native and non-native speakers of English and include courses, workshops, individual writing consultations, and online resources. Please avail yourself of these services. Grading Please consult the iSchool's official interpretation of letter grades and the University's policy on Graduate Grading and Evaluation Practices. These will form the basis for grading in the course. INF 2149 Administrative Decision Making in Information Organizations 2015 Winter Term Course Schedule 1-2. Jan 7, 14. Individual Decision Making Introduction to decision making by individuals, groups, and organizations Cognitive biases and heuristics in human judgment and choice Read: Tversky and Kahneman (1974), also in Kahneman (2011), Appendix A Gilovich, Griffin, and Kahneman (2002): Introduction, pg. 1-18 Kahneman, D. (2004): Paper based on author's Nobel Prize lecture Choo (2006): Chap. 5 Gigerenzer and Gaissmaier (2011) Video: Judgment and Choice (1990/2001) PDF of lecture slides (Jan 7) PDF of lecture slides (Jan 14). 3. Jan 21. Group Decision Making Decision making in groups Groupthink Read before class: Case Discussion. NASA Space Shuttle Challenger Launch Decision, January, 1986. Come to class prepared to discuss the dynamics of group decision making in this case. Read: Janis (1982): Chap. 1, 10 Janis and Mann (1977) : Chap. 2 Choo (2006): Chap. 5 Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes Special Issue (Vol. 73, no. 2-3, Feb 1998) on the 25th Anniversary of Groupthink Video: Groupthink (1991) PDF of lecture slides 4-8. Organizational Decision Making Models Introduction to and comparison of major models of organizational decision making, including discussions of their implications for information seeking, information use, and information provision. 4. Jan 28. Rational Model Bounded rationality in organizations Decision premises, rules, and routines Read before class: Case discussion. Designing Decision Premises and Decision Routines - FI Admission Process Read: Simon (1997): Chap. 1, 3, 5 March and Simon (1993): Chap. 6 Choo (2006): Chap. 1 and 5 PDF of lecture slides 5. Feb 4. Strategic Decision Process Model Process model of organizational decision making Routines and dynamic factors in strategic decision making Read before class: Case discussion. AOL - Time Warner Merger. Read the following articles from the New York Times (Jan 16, 2000). Come prepared to discuss the events, phases, and cycles in the unfolding of the merger decision. Price of joining old and new was core issue in AOL deal [cache] How blind alleys led old media to new [cache] How the AOL-TW merger went so wrong - A retrospective [cache] Read: Mintzberg et al (1976) Lindblom (1959) Choo (2006): Chap. 5 PDF of lecture slides 6. Feb 11. Political Model Conflict, coalitions, and procedural rationality Information and power in decision making Read before class: Case discussion. Cuban Missile Crisis. Read the case, and come prepared to discuss the events, players and actions in the development of the US response to the crisis. For a fuller account read "Essence of Decision: Explaining the Cuban Missile Crisis" (Allison and Zelikow, 1999, Chapter 6, pg. 325-347). Read: Cyert and March (1992): Chap. 5, 7 Allison and Zelikow (1999): Essence of Decision - Explaining the Cuban Missile Crisis Forester (1984) Pfeffer (1992): Chap. 13 Choo (2006): Chap. 5 PDF of lecture slides Assignment 1 due Feb 17-20, Reading Week: no class. 7. Feb 25. Garbage Can Model Organizations as anarchies Technology of foolishness Read before class: Case discussion. Elimination of Speech Program in a University. Be prepared to discuss the flow of events, decisions, and decision makers in this case. For a fuller account read March and Olsen (1976) Ambiguity and Choice in Organizations: pg. 254258. Read: Cohen et al (1972) March (1979, 1991) Choo (2006): Chap. 5 PDF of lecture slides 8. Mar 4. Contingency Decision Making Framework Multiple modes of organizational decision making Task and organizational variables Read: Choo (2006): Chap. 5 March (1991) Hickson et al (1986) : Chap. 6 Perrow (1986): Chap. 4 Information Seeking and Use in Decision Making Information needs Information seeking Information use. Read: McCall and Kaplan (1990): Chap. 6 Choo (2005): Information Failures and Organizational Disasters PDF of lecture slides 9. Mar 11. Guest speakers To be announced. PDF of lecture slides 10-12. Mar 18, 25, Apr 1. Student Case Presentations Sign up for your presentation dates in the course wiki. Post your presentation materials in the course wiki at least one day before the presentation. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF INFORMATION INF 2149H Administrative Decision Making in Information Organizations Reading List Instructor: Chun Wei Choo 973.923 A438E2 (2 hour loan) Allison, Graham T. and Philip Zelikow. Essence of Decision: Explaining the Cuban Missile Crisis. 2nd edition. New York: Addison-Wesley, 1999. HM31 .B37 2003 Baron, Robert S., and Norbert L. Kerr. Group Process, Group Decision, Group Action. 2nd ed. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2003. (Chap. 1 - Introduction; Chap. 6 - Extremity in Groups). AZ999 .B89 2008X Burns, Christopher. Deadly decisions: How false knowledge sank the Titanic, blew up the shuttle and led America into war. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books, 2008. 658.45 C548K2 (2 hour loan) Choo, Chun Wei. Chapter 1 (The Knowing Organization), 5 (The Management of Uncertainty: Organizations as Decision Making Systems), IN The Knowing Organization: How organizations use information to construct meaning, create knowledge, and make decisions. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press, 2006. Full text available in Oxford Scholarship Online. 658.4038 I43K Choo, C.W. The Social Use of Information in Organizational Groups. In A. Huizing & E.J. de Vries (Eds.), Information Management: Setting the Scene (Vol. 1). Oxford, UK: Elsevier Science, 2007. (PDF) Choo, Chun Wei. Information Failures and Organizational Disasters. Sloan Management Review 46 no.3 (2005): 8-10. (cache) Choo, Chun Wei. Organizational Disasters: Why They Happen and How They May be Prevented. Management Decision, 46 no.1 (2008): 32-46. Cohen, Michael D., James G. March, and Johan P. Olsen. A Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice. Administrative Science Quarterly 17 no. 1 (1972): 1-25. 658.403 C995B2 Cyert, Richard Michael and James G. March. A Summary of Basic Concepts in the Behavioral Theory of the Firm. IN A Behavioral Theory of the Firm. 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1992. Chap. 5 (Organizational Choice), 7 (Summary). Douglas, K., & Jones, D. How To Make Better Choices. New Scientist 194 no. 2602 (2007): 35-43. (cache) Eden, Colin, & Ackermann, Fran. 2010. Decision Making in Groups: Theory and Practice. In P.C. Nutt & D.C. Wilson (Eds.), Handbook of Decision Making (pp. 231272). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Xerox File Estrin, Teviah L. The Roles of Information Providers in Decision-Making. Journal of General Management 15 no. 3 (1990): 80-95. Forester, John. Bounded Rationality and the Politics of Muddling Through. Public Administration Review 44 no. 1 (1984): 23-31. 363.34 G383F Gerstein, M.S., & Ellsberg, M. 2008. Flirting with Disaster: Why Accidents Are Rarely Accidental. New York: Union Square Press. (Chernobyl, Merck Vioxx, Hurricane Katrina) BF315.5 G54 2007X Gigerenzer, Gerd. Gut Feelings: The Intelligence of the Unconscious. New York: Penguin Press, 2007. Chap. 1, 6. Gigerenzer, G., & Gaissmaier, W. 2011. Heuristic Decision Making. Annual Review of Psychology, 62(1), 451-482. BF447 .H48 2002 Gilovich, Thomas, Dale Griffin, and Daniel Kahneman, eds. Heuristics and Biases: The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2002. (Introduction, p. 1-18) 658.403 H318M5 (2 hour loan) Harrison, E. Frank. The Managerial Decision-Making Process. 5th ed. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, c1999. (Chapter 2 - The DM Process; 3 - Rational DM; 9 - Political Aspects of DM; case studies.) BF448 .H42 2013 (Rotman) Heath, Chip and Dan Heath. Decisive: How to Make Better Choices in Life and Work. Toronto: Random House Canada, 2013. 025.1 H558E (2 day loan) Hernon, Peter and Charles R. McClure. Evaluation and Library Decision Making. Norwood NJ: Ablex Pub, 1990. Hickson, David J., C.R. Hinings, C.A. Lee, R.E. Schneck, and J.M. Pennings. A Strategic Contigencies' Theory of Intraorganizational Power. Administrative Science Quarterly 16 no. 2 (1971): 216-229. Hodgkinson, G.P., & Starbuck, W.H. (Eds.). 2008. Oxford Handbook of Organizational Decision Making. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. Xerox File; BF441 .J3 Roba / 153.83 J33D OISE Janis, Irving L., and L. Mann. Chapter 2 (Decision Making Strategies). IN Decision Making. New York, NY: Free Press, 1977. 327.73 J33G2 1982 (2 hour loan) Janis, Irving L. Groupthink: Psychological Studies of Policy Decision. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 1982. Introduction, Chap. 1 and 10. Kahneman, Daniel. 2003. A Perspective on Judgment and Choice: Mapping Bounded Rationality. American Psychologist, 58(9), 697-720. (cache) Kahneman, Daniel and Gary Klein. 2009. Conditions for Intuitive Expertise: A Failure to Disagree. American Psychologist, 64(6), 515-526. Kahneman, Daniel. 2011. Thinking, Fast and Slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. BF441 .J8 1982 Kahneman, Daniel, Paul Slovic, and Amos Tversky, eds. Judgement under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1982. R 020 A615A v.27 Katzer, Jeffrey and Patricia Fletcher. The Information Environment of Managers. IN Annual Review of Information Science and Technology , ed. Martha E. Williams, Medford, NJ: Learned Information, Inc, 1992. pp. 227-63. Kiesler, Sara and Lee Sproull. Group Decision making and Communication Technology. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 52 no. 1 (1992): 96-123. 658.403 K64S (Short term loan) Electronic copy Klein, Gary. Sources of Power: How People Make Decisions Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1998. Chap. 1, 16, 17. Also available online here. Lindblom, Charles E. The Science of Muddling Through. Public Administration Review 19 no. 2 (1959): 79-88. Xerox File; LB2806 .M353 1979 Roba / 658.403 M315A 1979 OIS March, James G. Chapter 5 (The Technology of Foolishness). IN Ambiguity and Choice in Organizations, ed. James G. March and Johan Olsen. 2nd ed. Bergen: Universitetsforlaget, 1979. HD 30.23 M3725 1989 ROBA March, James G. Decisions and Organizations. Cambridge, MA:Basil Blackwell, Inc, 1989. (Introduction, p. 1-21.) March, James G. How Decisions Happen in Organizations. Human-Computer Interaction 6 no. 2 (1991): 95-117. 658.403 M315P (2 hour loan) March, James G. A Primer on Decision Making: How Decisions Happen. New York, NY: Free Press, 1994. (Chap. 1 - Limited Rationality; Chap. 2 - Rule Following; Chap. 5 Ambiguity and Interpretation.) 658 M315P2 March, James G. and Herbert A. Simon. Chapter 6 (Cognitive Limits on Rationality). IN Organizations. 2nd ed. New York, NY: John Wiley, 1993. 026. 3321 M368I (2 day loan) & 026. 3321 M368IA (2 hour loan) Marshall, Joanne G. The Impact of the Special Library on Corporate Decision Making. Special Libraries Association, 1993. Xerox File McCall, Morgan W., Jr.; Robert E. Kaplan. Chapter 6 (Awash in Decision Streams: Implications for Staying Afloat). IN Whatever It Takes: The Realities of Managerial Decision Making. 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc, 1990. Mintzberg, Henry, Duru Raisinghani, and Andre Theoret. The Structure of "Unstructured" Decision Processes. Administrative Science Quarterly 21 no. 2 (1976): 246-275. Nutt, Paul C. and David Wilson. (Eds.) 2010. Handbook of Decision Making. Administrative Science Quarterly Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley. Xerox File; HM131 .P382 1986 Perrow, Charles. Chapter 4 (The Neo-Weberian Model: Decision Making, Conflict and Technology). IN Complex Organizations: A Critical Essay. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1986. Pettigrew, Andrew M. Information Control as a Power Resource. Sociology 6 no. 1 (1972): 187-204. 658.4 P524M (2 day loan) Pfeffer, Jeffrey. Chapter 13 (The Politics of Information and Analysis). IN Managing with Power: Politics and Influences in Organizations. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 1992. Pfeffer, Jeffrey and Gerald R. Salancik. Organizational Decision Making as a Political Process: The Case of a University Budget. Administrative Science Quarterly 19 no. 2 (1974): 135-151. Pinfield, Lawrence T. A Field Evaluation of Perspectives on Organizational Decision Making. Administrative Science Quarterly 31 no. 3 (1986) 365-388. Ross, Jerry and Barry Staw. 1986. Expo 86: An Escalation Prototype. Administrative Science Quarterly 31(2): 274-297. 658.403 R969W Russo, Jay E., and Schoemaker, Paul J. H. Winning Decisions: Getting It Right the First Time. New York: Doubleday, 2002. 350 S594A4 Simon, Herbert A. Chapter 1 (Decision Making), 3 (Fact and Value), 5 (Psychology of Administrative Decisions). IN Administrative Behavior: A Study of Decision-Making Processes in Administrative Organization. 4th ed. New York, NY: The Free Press. 1997. 303.484 S958W (2 day loan) Sunstein, Cass R. 2003. Why Societies Need Dissent. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Chap. 6-8. 658.45 N532N Sutcliffe, Kathleen M. 2000. Organizational Environments and Organizational Information Processing. IN The New Handbook of Organizational Communication, ed. Fredric M. Jablin, Linda L. Putnam. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications. 658.403 T931D6 (2 hour loan) Turban, Efraim, Ramesh Sharda, Dursun Delen. 2011. Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems. 9th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. BF441 .J8 1982 Tversky, Amos and Daniel Kahneman. Judgement under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. IN Judgement Under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1982. Chap. 1. reprint of original article from Science 185 (1974): 1124-1131.