Heizer/Render, Operations Management 7th Edition
advertisement

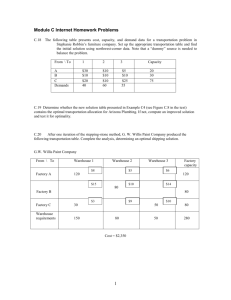
Additional Homework Problems to accompany MODULE C: Transportation Models C.14 The following table presents cost, capacity, and demand data for a transportation problem in Stephanie Robbin’s furniture company. Set up the appropriate transportation table and find the initial solution using northwest-corner data. Note that a “dummy” source is needed to balance the problem. From \ To 1 2 $30 $10 $5 $10 $10 $10 $20 $10 $25 A B C Demands 40 3 60 Capacity 20 30 75 55 C.15 Determine whether the new solution table presented in Example C4 (see Figure C.8 in the text) contains the optimal transportation allocation for Arizona Plumbing. If not, compute an improved solution and test it for optimality. C.16 After one iteration of the stepping-stone method, G. W. Willis Paint Company produced the following transportation table. Complete the analysis, determining an optimal shipping solution. G.W. Willis Paint Company From \ To Factory A Warehouse 1 $8 Warehouse 2 $5 $15 $10 $14 80 80 $3 Warehouse Requirements $9 30 150 Factory Capacity 120 120 Factory B Factory C Warehouse 3 $6 $10 50 80 Cost = $2,350 1 50 80 280 C.17 Sound Track Stereos assembles its high-fidelity stereophonic systems at three plants and distributes them from three regional warehouses. The production capacities at each plant, demand at each warehouse, and unit shipping costs are presented in the following table: Sound Track Stereos From \ To Plant W Warehouse A $6 Plant Y Plant Z Warehouse Demands Warehouse B $4 Warehouse C $9 $10 $5 $6 $12 $7 $8 250 100 150 Plant Capacity 200 175 75 500 \ 450 a) Set up this transportation problem by adding a dummy plant. Then use the northwest-corner rule to find an initial basic feasible solution. b) What is the optimal solution? C.18 Jim Lloyd, vice president for operations of HHN, Inc., a manufacturer of cabinets for telephone switches, is constrained from meeting his 5-year forecast by limited capacity at the company’s three existing plants. These plants are Waterloo, Pusan, and Bogota. As his able assistant, you have been told that because of existing capacity constraints and the expanding world market for HHN cabinets, a fourth plant is to be added. The real estate department has advised Lloyd that two sites seem particularly good because of stable political situations and tolerable exchange rates. These two locations are Dublin, Ireland, and Fontainebleau, France. Lloyd suggests that from the data in the following table, which provide production and transportation costs, you should be able to determine where the fourth plant should be located. (Note: This problem is degenerate with the data for both locations.) Market Area Canada: Demand 4,000 Production cost Transportation cost South America: Demand 5,000 Production cost Transportation cost Pacific Rim: Demand 10,000 Production cost Transportation cost Europe: Demand 5,000 Production cost Transportation cost Capacity Plant Location Bogota Fontainebleau Waterloo Pusan 50 10 30 25 40 20 50 25 45 25 50 20 30 25 40 10 50 30 45 30 50 25 30 10 40 25 50 40 45 40 50 25 8,000 30 40 2,000 40 30 5,000 50 10 9,000 45 20 9,000 2 Dublin