SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
3.1 Movement Of Substances Across The Across The Plasma Membrane
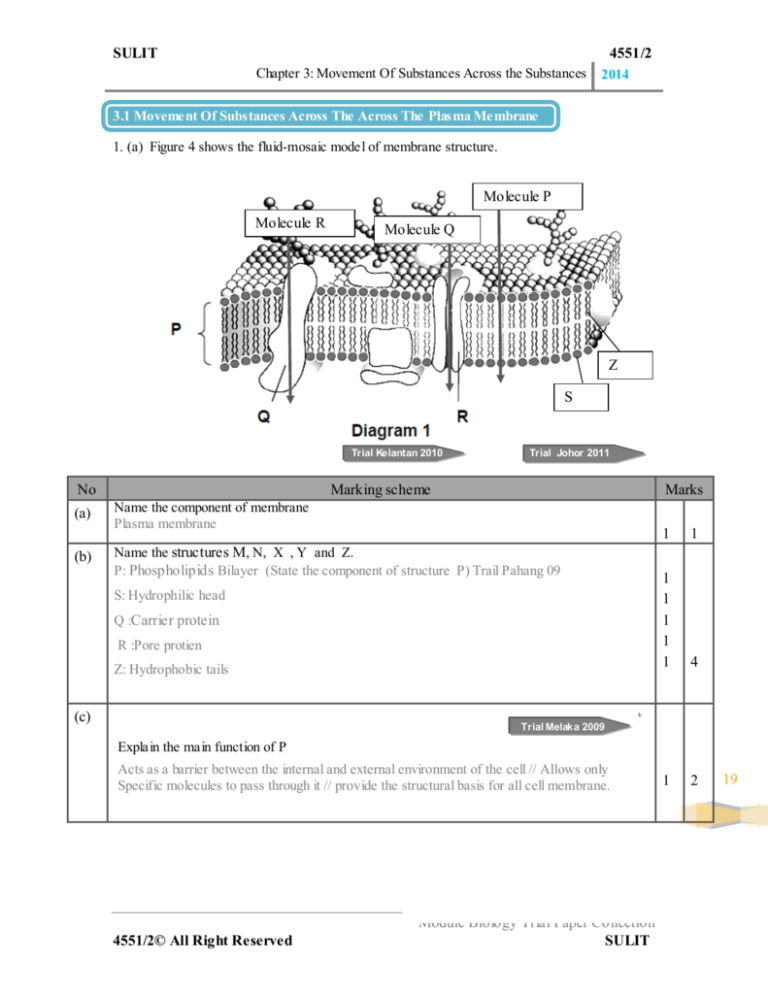
1. (a) Figure 4 shows the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure.
Molecule P
Molecule R
Molecule Q
Z
S
Trial Kelantan 2010
No
(a)
(b)
Trial Johor 2011
Marking scheme
Marks
Name the component of membrane
Plasma membrane
Name the structures M, N, X , Y and Z.
P: Phospholipids Bilayer (State the component of structure P) Trail Pahang 09
S: Hydrophilic head
Q :Carrier protein
R :Pore protien
Z: Hydrophobic tails
(c)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
1
2
Trial Melaka 2009
Explain the main function of P
Acts as a barrier between the internal and external environment of the cell // Allows only
Specific molecules to pass through it // provide the structural basis for all cell membrane.
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
19
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(d)
2014
Note: All the question refer to the Diagram 1
Marking scheme
Marks
The Plasma membrane is said to be semi premable membrane
What is the meaning of ‘semi-preamble’ membrane
Trial Kedah 2008
Negeri Sembilan 2011
A semi-permeable plasma membrane is a membrane that allows only certain substances to
Move freely across it.
(e)
State main component of layer P
(g)
1
1
1
Kedah Trial 2011
Lipid /Protein
(f)
1
(f) Explain the causes that make plasma membrane have fluidity structure [kedah2008]
P1-fluidity characteristics are caused by the protein molecules which are floating in the
phospholipids bilayer.
1
P2- the positions of the molecules also keep on changing / not fixed in the position.
Molecule P move across the plasma membrane follow the concentration gradient Whereas
1
2
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
3
1
1
2
Molecule Q
move across structure X against the concentration gradient
Name the process of movement substances across the plasma membrane as shown in
molecule P, Q molecule R
Molecule P: Facilitated diffusion
Molecule Q: Simple diffusion /osmosis
Molecule R: Active transport
(h)
Give one example of particle that move through P,Q and R
Trial Wilayah Persekutuan
R: Glucose /amino acid
P: Water /carbon dioxide/oxygen /small lipid soluble
Q: Natrium /Potassium
(i)
What type of passive transport occur at Q
Simple diffusion
(j)
State two feature of the particle that enables it to pass through the phospholipids bilayers of the
cell membrane
P1- Small
P2- Soluble to phospholipids bilayer/lipid soluble
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
20
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(k)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain how these molecules pass through the channel protein.
P1- Small molecule /ion move through the pore protein in the channel protein by simple
1
diffusion
P2-The molecule are higher concentration (outside) diffuses the s\cell cause the molecule to
1
2
1
1
diffuse to a lower concentration into the cell through the pore /down the concentration gradient
(l)
On d iagram 2 ,draw arrow (
) to show the movement of oxygen across the cellular
component during the day time
Arrow from inside the cell to outside the cell, pass through phospholipids bilayer
(m)
Explain the answer in (b)(i)
E1-(during day time), photosynthesis occurs in cell to produce O 2
E2- O2 diffuses from a higher concentration region to lower concentration region// O 2
1
1
diffuses by following the concentration gradient
1
E3- O2 is non –polar molecule /small molecule Any 3
(n)
3
Explain the arrangement of molecule P (Lipid) in Plasma membrane
P1-Phospholipid molecule consists of two parts
P2-Hydrophilic head contact with the extracellular environment and hydrophobic tail point
1
1
toward each other
P3-Phospholipid are arrange in double layer called, phospholipids bilayer
(o)
1
3
State the characteristic of phospholipid bilayer
P1-it consist of hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
P2- Hydrophilic head contact with the extracellular environment and hydrophobic tail point
1
1
toward each other
1
P3-not rigid or static
3
21
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(a)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Essay Enhancement Coner
All movements of substances have to pass through a plasma membrane. Explain why the
plasma membrane is known as a semi permeable membrane
P1- it only allows the passage of certain molecules and limits the passage of other molecules.
P2-It consists of two layers of phospholipids with protein molecules scattered in them
P3-Molecules that can pass through the plasma membrane easily are those that can dissolve
1
1
1
in lipid and small uncharged molecules.
P4- Molecules which cannot move through the plasma membrane but require proteins include
1
large molecules that do not dissolve in lipid and small charged molecules.
P5 Channel protein does not require the binding of a molecule and conformational change to
1
open.
P6Channel protein allows molecules to steadily diffuse across the membrane through
1
diffusion.
P7However a carrier protein allows specific molecules to cross the cell membrane by
1
undergoing a conformational change upon the binding of the molecule.
P8 The conformational change opens a hole through which the molecule can enter or leave a
1
8
cell.
(b)
The figure below shows a fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane
Explain the functions of the structures X, Y and Z in the movement of substances across the
plasma membrane
P1- Structure X allows hydrophobic molecules which can dissolve in lipids such as fatty
acids, glycerol, steroid hormones, and vitamins A, D, E and K to move in and out of the cell.
1
P2-Structure Y allows bigger molecules which do not dissolve in lipids like glucose and
1
22
amino acids to move in and out of the cell.
P3-Structure Z allows small charged molecules to move in and out of the cell.
4551/2© All Right Reserved
1
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Simple Diffusion
No
(a)
2014
Trial Perak2009
Marking scheme
P1-The net movement of molecule /ions
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
P3-the potassium manganate (VII) ions move from an area of higher concentration to an area of
1
lower concentration
1
P4-Until dynamic equilibrium is achieved
1
P5-The ions are equally distributed throughout the whole system and turn the solution purple
1
5
P2-from a high concentration to a region of lower concentration
P3-down / follow the concentration gradient
P4-Untill the dynamic equilibrium is achieved
(b)
Marks
Define Simple diffusion? [ESSAY]
Based on the diagram, state one example of a substance that moves across the plasma
membrane. Describe the characteristic of that substances transport
P1-Fatty acid/glycerol/vitamin A/D/E/K, Steroid
S1-Small, non polar
E1-They are lipid soluble /van move through the phospholipids bilayer OR
P2-Carbon dioxide, water and oxygen
S2-Small uncharged molecules
E2-they are lipid soluble /can move through the phospholipids bilayer
(c)
SPM Clone 2003[Essay]
Explain briefly the process illustrated in the diagram
P1-The process is known as simple diffusion
P2-the concentration of potassium manganate (VII) is higher at the bottom of the beaker
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
23
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
Osmosis
A
No
(a)
B
Marking scheme
Osmosis
(b)
Marks
Based on the figure, name the process
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
Define Osmosis
(The net movement) of water molecules from a lower solute concentration region to a high
solute concentration region through a semi permeable membrane
(c)
Describe what happen to the volume of the solution on both side A and side B after five
Minutes
P1-Definition
P2-causing the level of solution rise on side A
(d)
State the molecule involved in this process
Water molecule
(e)
Describe what happen to solute concentration on side B . Explain your answer
P1-The solute concentration will increase on side B
P2-Salt diffuses from side A to side B, increasing the solute concentration
1
1
P3-Water diffuses from side B to side A, reducing the amount of water and increasing the
1
solute concentration
(f)
3
State the differences of the process simple diffusion and osmosis
D1-Simple diffusion involves the movement of any molecule, Osmosis involved only the
1
24
movement of water molecule
D3-Simple diffusion not require a semi- permeable membrane, Osmosis occurs through a semi
1
permeable membrane
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
2
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Facillitated Diffusion
2014
Trial Johor 2011
Trial Negeri Sembilan 2011
X
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Based on the diagram, name the process occur
Facilitated diffusion
(b)
1
1
1
1
Name molecule X
Amino acid/glucose/small protein
(c)
Marks
Describe and explain the following:
The uptake of potassium ions by algae even that concentration of potassium ions is higher in
the cell sap the external environment
E1-Water enter plant roots by osmosis
E2-The concentration of solutes is lower in the soil in than root cell
E3-Water molecule moves across the semi preamble membrane and enter the root cell
(d)
1
1
1
3
Explain how amino acid molecule are transported across the plasma membrane by the process
shown in diagram 1.1
S1-Amino acid binds to a specific site on the carrier protein
S2-Carier protein changes its shape and releases the amino acid on the other side
S3-The movement of amino acid is down/follow the concentration gradient
1
1
1
3
25
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Essay Enhancement Coner
(a)The following information is about plasma membrane.
The plasma membrane is semi-permeable and allows certain substances to move across.
Based on the above statement, describe how an amino acid molecule is transported across the
plasma membrane into the cell.
P1-Amino acid is a large water soluble molecule
P2-It requires carrier protein to move across the membrane
P3-Amino acid will bind to the carrier protein which is specific to it
P4-Carrier protein will change its shape to bring the amino acid molecule across the membrane
P5-Lastly the carrier protein will release the amino acid and returns to its original shape
1
1
1
1
1
(b)State the similarities and differences between passive transport (facilitated diffusion) and
active transport in the movement of molecules across the cell membrane.
Similarities :
S1-Both occurs in living cells
S2-Both occurs through a semi-permeable membrane
S3-Both require carrier protein to bind with the substances
ANY 2
1
1
1
Differences :
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Molecules move down the concentration
Molecules move against the concentration
gradient
gradient
Molecules move through pore proteins or
Molecules move through carrier proteins
carrier proteins
only
Occurs until a dynamic equilibrium is
Results in accumulation of substances in the
achieved
cell or removal of substances from the cell
ATP or energy is not required
ATP or energy is required
Not dependent on cellular respiration
Dependent on cellular respiration
Not affected by inhibitors
Inhibited by inhibitors such as respiratory
1
1
poisons
1
1
1
26
1
Each differences 1 mark
8
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
Trial Johor 2009
P
No
(c)
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain how molecule P move across the plasma membrane
F -Molecule P moves across the plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion
P1-Molecule P is water soluble/not soluble in lipid
P2-Molecule P moves from higher concentration region to lower concentration
region//against concentration gradient
P3-Molecule P binds to the specific site of the carrier protein
P4-Carier protein change its shape
P5-Molecule P move through Carrier protein ( F + any 3P)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
Explain how gaseous exchange occur across the alveolus
P1 : Oxygen diffuse/ moves across a( plasma membrane/through ( plasma membrane) to
blood capillary
P2: From higher (oxygen ) concentration ( in alveolus )to lower concentration ( in blood
capillary)
P3: On the other hand the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is lower in the air of the alveoli
compared to the blood capillaries.
P4: Carbon dioxide diffuse out of the blood capillaries into the alveoli.
P5 : expelled through the nose or mouth into the atmosphere .
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
1
1
1
1
1
27
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Active Transport
2014
Kedah Trial 2008
JUJ 2009
Trial Johor 2011
Trial Kelantan 2011
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Marks
Define active transport
Movement of molecule or ions, against the concentration gradient across plasma membrane
1
1
with the help of carrier protein and energy / ATP
(b)
State the process that involved in the uptake of mineral ions
Active transport
(c)
1
1
Explain what will happen to the uptake of mineral ions by the root hair if the roots are
immersed into the solution containing metabolic poisons such as cyanide.
P1-metabolic poisons stopped the cell respiration
1
1
1
1
P2-no energy/ATP is produced
P3-active transported cannot occur
P4-no uptake of mineral ions by roots cell (any 3)
3
(d)
Sodium ions found to be higher in concentration outside a human cell while potassium ions is
found to be higher outside the cell
Describe the process that leads to the occurrence of the above situation
P1-The carrier protein‘s opening end has active site, which are filled by the sodium ions.
P2-An ATP molecule then attaches on the protein and release energy
P3-The carrier Protein \change shape (and open to the other end, Where),it release the sodium
ion
1
1
1
28
to outside
P4-Carier Protein Returns to its original shape and release the potassium ions
1
Any 3
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(e)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain why paramecium has to pump it’s contractile vacuole when placed in 0.25 sucrose
solution
P1-0.25%sucrose solution is hypotonic to cytoplasm
P2-Water diffuses into that paramecium through osmosis
P3-Excess water has to be expelled, otherwise the paramecium will burst
(f)
1
1
1
3
Paramecium will and die when placed in the 0.25% sucrose solution added with respiratory
poison
Explain the above statement
P1-The poison will inhibit cellular respiration
1
1
1
1
P2-No energy is produced
P3-Contractile vacuole will not work/pump
P4-Excess water cannot be expelled
(g)
4
How unicellular organisms living in freshwater maintain the water balance?
P1-Gaseous exchange in the alveoli occurs through diffusion
1
P2-The concentration of oxygen in the alveoli is higher than that of the blood capillaries
1
surrounding the alveoli
P3-This causes oxygen to diffuses into the blood
P4-Likewise, the higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood capillaries causes carbon
dioxide to diffuse into the blood capillaries
(h)
1
1
4
1
1
What is the important of the process in (a) to an organism
It helps the organism to take in / accumulate glucose/amino acid
29
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
3.2 The movement of substances across the plasma membrane in everyday life
Plant Cell
In an experiment, the palisade mesophyl cell is immersed in distilled water for a certain period of
time
Trial SBP 2012
Trail Johor 2011
Type of solution
Solution A
Question & Marking Scheme
(a) Based on the diagram, name the term use to describe the following/State the
properties of the following solution/state the type of solution
Hypotonic/’hypotonic solution
(b)
State the condition of the cell in the following solution
Turgid
(c) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will happen
to this cellular component
F1- This cellular component/ plasma membrane is pushed against the cell wall
F2-The distilled water /solution is hypotonic to the cell sap
Trail Johor 2011
E1-Distilled water is hypotonic to the cell sap // cell sap hypertonic to distilled
water
E2- Water molecule diffuses into the cell by osmosis
E3-Vacuole Expand /swell up
E4- the cell are highly turgid /Any 3
Solution C
(a) Based on the diagram, name the term use to describe the following/State the
properties of the following solution/ state the type of solution
Hypertonic/Hypertonic solution
(b) State the condition of the cell in the following solution
Flaccid
(c)
Name a physical process of plant cell in solution C
Plasmolysis
(d) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will happen to
this cellular component
P1-The …solution is hyper tonic to cell sap
P2-Water molecule diffuses out of the large central vacuole by osmosis
P3-the plasma membrane pull away from the cell wall
P4-Plant cell become flaccid /any3
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
30
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Type of solution
Solution B
2014
Question & Marking Scheme
(a) Based on the diagram, name the term use to describe the following/State the
properties of the following solution/ state the type of solution
Isotonic/ Isotonic solution
(b) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will happen to
this cellular component
P1-the solution outside the cell is isotonic to the cell sap
P2-Water diffuse in and out the cell at equal rate
P3-the cell maintain its shape/not change
P4- no plant cell shrinks /.any 3
A plasmolysed plant cell become turgid when immersed in distilled water
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Marks
What process does the plant cell experienced?
depalsmolysis
(b)
1
1
1
2
Explain your answer
P1-plasmolysed cell can become turgid again by immersing in a hypotonic solution
P2-water molecule diffuses in and the cell become turgid again
(c)
1
Draw a labeled diagram of the condition of palisade mesophyl cell after being immersed in the
distilled water
1
D- The shape of the cell must be rectangular
The cell wall is drawn with double line
The vacuole must be large
L-Label vacuole
1
Reject other shape of the cell
2
[2 marks]
31
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
Animal Cell
Trial Kelantan SPM
Type of solution
Solution M
Question& Marking sche me
(a) Name a physical process that causes the changes in erythrocyte cells L and M.
Haemolysis
(b) What are the characteristics /properties of the solutions used to soak :/ state
the type of solution(must have word SOLUTION)
Hypotonic
(c) State the condition of the cell
State what your
observe( / ) before
P1
Normally get 1
marks
Eg.P1-raw egg is
floating
Crenated
(c) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will
happen to this cellular component/ Explain what happen on the red blood cells
in solution M/Explain the phenomena(state the phenomena)
P1-the solution is hypertonic to the red blood cell
P2-Osmosis occur
P3-Water molecule diffuses in the cells
P4-the cell start to swell and eventually burst
P5-Haemolysis occur
P6-cytoplasmic fluid of red blood cells cause the solution change into clear red
ANY 3
Solution K
(a) What are the characteristics /properties of the solutions used to soak : state
the type of solution
Isotonic
(b) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will
happen to this cellular component/ Explain what happen on the red blood cells
in solution/ Explain the phenomena(state the phenomena)
State what your
observe( / ) before
P1
Normally get 1
marks
P1-the solution outside the cell is isotonic to the cell sap
P2-Water diffuse in and out the cell at equal rate
P3-the cell maintain its shape/not change
P4- no red blood cell shrinks /burst ANY 3
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
32
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Type of solution
Solution L
2014
Question& Marking sche me
(a) Name a physical process that causes the changes in erythrocyte cells L and M.
/state the type of solution
crenation
(b) What are the characteristics /properties of the solutions used to soak :// state
the type of solution(must have word SOLUTION)
Hypertonic
Trial Kedah 2008
(c) State the condition of the cell
Haemolysed
State what your
observe( / )before
P1
Normally get 1
marks
(c) Explain the effect of the following solution to plant cell/ Explain what will
happen to this cellular component/ Explain what happen on the red blood cells
in solution L/ Explain the phenomena(state the phenomena)
P1-The solution is hypertonic to the red blood cell
P2-Water molecule diffuses out of the cells by osmosis
P3-creanation occurs
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Marks
Use a tick (/) in the correct column to identify solution L and solution M
Name of solution
Distilled water
Solution L
10% salt solution
/
Solution M
/
1
1
2
1
1
1
3
Explain why paramecium has to pump its contractile vacuole when placed in 0.25 sucrose
solution
P1-0.25%sucrose solution is hypotonic to cytoplasm
P2-Water diffuses into that paramecium through osmosis
P3-Excess water has to be expelled, otherwise the paramecium will burst
(b)
Cells P is mixed with detergent. The detergent dissolves lipids.
After 10 minutes, the mixture is examined under a microscope; no cells P were seen but the
mixture turn red and cloudy.
Explain why?
P1- Detergent dissolves the lipid in the plasma membrane.
P2- Plasma membrane disintegrate/destroyed
P3- Cytoplasm (of red blood cell) mix into the solution
P4- Cell P is haemolysed AYN 3
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
33
1
1
1
1
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Trial Kedah 2008
Trial Kedah 2010
No
(a)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Graph in Diagram 1.2 shows the percentage of red blood cells that are burst or shrink when
placed in salt solution of different concentration.
Based on the graph given, state the concentration which is isotonic to
blood plasma.
0.45 g/100 cm3
1
(b)
1
Explain your answer in (b)(ii).
Both percentage of haemolysis of red blood cells and percentage of crenation of red blood
1
1
1
1
1
3
Cells are zero (0%).
(c)
Comment on the osmotic pressure at Q.
F: The osmotic pressure inside the red blood cells is equivalent to its environment.
P2 : Amount of water moving in and out of the cells are the same,
P3 : therefore the size and structure of the red blood cells
does not change
34
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
Trial Kedah 2010
No
(a)
Marking scheme
Name the process that causes the level of sucrose solution in the capillary tube change.
Osmosis
(b)
Marks
1
1
Explain the process
P1-Sucrose solution is hypertonic /more concentrated
P2-water diffuse from distilled water into the sucrose solution
P3-the level of sucrose solution in the capillary tube stop rising at the equilibrium stage/the
1
1
1
3
1
1
2
concentration inside and outside the visking tube is the same /the amount of water diffuse into
and out from the visking tubing is the same
(c)
A laboratory test shows that at the end of the experiment, the distilled water in the beaker did
not consist of sucrose
Explain why
F-sucrose molecule is too large
E-The visking tubing is a semi-permeable membrane/which only allow certain substances to
pass through
(c)
The red blood cell in solution Z is replaced with a plant cell
Does the plant cell burst as the red blood cell did
Explain why
35
1
1
1
F - No
P1-plant cell consist of cell wall
P2-cell wall made up of cellulose
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
3
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
2014
Trial Johor 2010
A strip of mustard green stem was placed in different of concentrations of sucrose solution
Type of solution
Solution A
Question& Marking scheme
(a) State the type solution A, when compared to the cell mustard
Hypotonic Solution
(b) Explain why do the strips placed in solution J and solution L curved
F1-the strips in solution J curved outward /toward the epidermis/epidermis layer
P1-(Cortex) cells / (parenchyma) cell becomes turgid ‘longer because
water diffuses into the cell /protoplasm/cytoplasm by osmosis
P2- Epidermal cells have a layer of cuticle on the outside
P3- Which resist/ restrict the entry of water (and retain its normal size) Any 2
Solution B
(a) State the type solution B, when compared to the cell mustard
Isotonic Solution
c)
State the solution which has osmotic concentration nearest to the cell sap
of mustard green
Solution B
(ii) Explain your answer(c) (i)
P1-The strip in solution B remain straight
P2-because the (cortex/ Parenchyma) cell have not increase in turgidity
/flaccidity //no change in size / remain the same
P3-Water diffuses in and out at the same rate/Any 2
36
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Type of solution
Solution C 2008
2014
Question& Marking scheme
(a) State the type solution c, when compared to the cell mustard
Hypertonic solution
(b) Explain why do the strips placed in solution J and solution L curved as shown
F1 – the strip in solution L curved inward /toward the cortex/parenchyma layer
P1- Water diffuses out of the cytoplasm /protoplasm /cell sap of the (cortex ) cell
/ (Parenchyma) cells will shrink
P2- The cytoplasm and /or the vacuole of the cell will shrink
(d) Draw and labeled diagram of the condition of one of the mustard green cells after being
immersed in solution A, B, C for 20 minutes
D-Correct drawing
-With vacuole
-Doubled- line cell wall
-Plasma membrane pulled away with some parts attached to the cell wall( totally detached
from the cell wall is not accept)
L-Correct Labels
-Plasma /cell membrane
-vacuole
37
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Wilting of plant
No
(a)
2014
Trial Terrenganu 2010
Marking scheme
Marks
Name the process that is occurs in the diagram
Osmosis
1
1
(b)
What is the factors that affects that direction in (a)(i)
1
1
(c)
Relative concentration (of solute) inside and outside the cell
Give an explanation what will happen to the plant of there is no water
P1-soil become hypertonic
1
1
1
1
5
P2-water molecule diffuses out of the root cell by osmosis
P3-the plant cell become flaccid
(d)
P4-the plant become wilt
Explain the condition of plant after being spread with excess fertilizers
P1-excess fertilizers cause the soil becomes hypertonic
P2-water diffuses out from (cell) via osmosis
P3-palnt cell loses water and cells are plasmolysed
P4-hence plant wilt
(e)
A Chemical substance inhibits the respiration process in the root hairs cells of the plant.
Explain the effect to the transport of the mineral ions into the root hair cells of the plant
P1: The cell unable to produce energy // energy is not generated
P2: Active transport does not occur.
P3: Thus, mineral ions cannot be transported into the cell. /any 2
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
1
1
1
1
3
38
1
1
1
2
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(f)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain how water move to structure T xylem tissue
P2-So, water diffuses into root hairs by osmosis
1
1
P3-The entry o dater dilutes cell sap of root hairs // cell sap of root hairs become hypotonic
compared to the cell sap of spongy mesophyll cell
1
P4- water diffuses into spongy mesophyll cell /o these adjacent cells which become more
diluted themselves, so osmosis continues across the S
1
P5-the continuous flow of water in S creates a force known as root pressure to push water into
xylem
1
P1-The cell sap of the root hair is hypetonic to the soil water
4
Essay enhancement coner
Diagram A
No
(a)
Diagram B
Marking scheme
Marks
Diagram A shows a well –watered plant .diagram B shows the same plants have not been
watered for week. Based on biological knowledge, explain what happens to the plants in
diagram A and B
Diagram A
P1-The soil solution is hypotonic to the cell sap o the plants cell
P2-water diffuses into the cell by osmosis
P3-Vacoule expand/swell up //cytoplasm to press outwards against the cell wall
P4-Cell becomes turgid, supporting the plant upright
1
1
1
1
Diagram B
P1-The soil solution becomes hypotonic to the cell sap of the plant cell
P2-water diffuses out from the cell by osmosis
P3-Vacoule/cytoplasm shrink//plasma membrane pull away from the cell wall
P4-the plasmolysed/flaccid cells causing the plant to wilt
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
1
1
1
1
39
8
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
Food Preservation
No
(a)
2014
Trial Negeri Sembilan
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain the concept of osmosis in the preservation of mango
P-The addition of preservatives such as concentrated salt/ sugar solution makes the
1
surrounding solution hypertonic to the cell sap of the mango
S1-Causing water to diffuse out from the cucumber cell by osmosis
S2-The dehydrated condition of the mango prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi
S3-Causes water to diffuse out the bacteria /fungi
S4-Bacteria/fungi dehydrates and dies
ANY 3
Essay enhancement corner
No
(a)
1
1
1
1
1
3
Trial Pahang 2011
Marking scheme
Marks
Explain how natural preservation can preserves the cucumber for a long per iod of time
P1-Immersed in salt and sugar solutions
P2-Solution outside of the food is hypertonic compared to the cytoplasm
P3-Water in the food diffuse out by osmosis
P4-The cells in the food become dehydrated
P5-microoraganism/bacteria/fungi lose water
P6-these conditions are not favorable for the growth of microorganism
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
40
6
SULIT
4551/2
Chapter 3: Movement Of Substances Across the Substances
No
(b)
2014
Marking scheme
Marks
Diagram 3.1.2 and 3.1.3 show two types of food which can be preserved.
Diagram 3.1.2
Diagram 3.1.3
Explain how vinegar and concentrated salt solution can be used in the food preservation.
P1-Vinegar is acidic and has low pH
P2-This prevent the growth of microorganisms in mangoes
P3-The mangoes can be preserved to last longer
P4-Concentrated salt solutions hypertonic to the tissue of fish
P5-Water diffuse out of fish cell by osmosis
P6-Water also diffuse out of bacteria cell to the surroundings
P7-The bacteria cells become plasmolysed
P8-This prevent the growth of bacteria which cause food spoilage
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
8
41
4551/2© All Right Reserved
Module Biology Trial Paper Collection
SULIT