Math Reference - BMAPreCalculus
advertisement

Burke Mountain Academy
Algebra Cheat Sheet
Math Reference
Basic Properties & Facts
Arithmetic Operations
Properties of Inequalities
If a < b then a + c < b + c and a ' c < b ' c
a b
If a < b and c > 0 then ac < bc and <
c c
a b
If a < b and c < 0 then ac > bc and >
c c
! b " ab
a# $ =
%c& c
ab + ac = a ( b + c )
!a"
# $ a
%b& =
c
bc
a
ac
=
!b" b
# $
%c&
a c ad + bc
+ =
b d
bd
a c ad ' bc
' =
b d
bd
a 'b b'a
=
c'd d 'c
a+b a b
= +
c
c c
!a"
# $ ad
%b& =
! c " bc
# $
%d&
ab + ac
= b + c, a ( 0
a
Properties of Absolute Value
if a ) 0
*a
a =+
if a < 0
, 'a
'a = a
a )0
a+b - a + b
n m
(a )
an
1
= a n'm = m'n
m
a
a
= a nm
a 0 = 1, a ( 0
n
a 'n =
!a"
# $
%b&
'n
1
an
n
bn
!b"
=# $ = n
a
%a&
n
1
a = an
m n
a = nm a
2
( x2 ' x1 ) + ( y2 ' y1 )
2
n
( )
1
am = am
Properties of Radicals
n
d ( P1 , P2 ) =
a
!a"
# $ = n
b
%b&
1
= an
'n
a
n
( ab ) = a nb n
Triangle Inequality
Distance Formula
If P1 = ( x1 , y1 ) and P2 = ( x2 , y2 ) are two
points the distance between them is
Exponent Properties
a n a m = a n+m
a
a
=
b
b
ab = a b
n
Complex Numbers
i = '1
1
= ( an ) m
i 2 = '1
'a = i a , a ) 0
( a + bi ) + ( c + di ) = a + c + ( b + d ) i
( a + bi ) ' ( c + di ) = a ' c + ( b ' d ) i
( a + bi )( c + di ) = ac ' bd + ( ad + bc ) i
( a + bi )( a ' bi ) = a 2 + b 2
n
ab = n a n b
a + bi = a 2 + b 2
n
a na
=
b nb
( a + bi ) = a ' bi Complex Conjugate
2
( a + bi )( a + bi ) = a + bi
n
a n = a, if n is odd
n
a n = a , if n is even
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
Complex Modulus
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Logarithms and Log Properties
Definition
y = log b x is equivalent to x = b y
Logarithm Properties
log b b = 1
log b 1 = 0
blogb x = x
log b b x = x
Example
log 5 125 = 3 because 53 = 125
log b ( x r ) = r logb x
log b ( xy ) = log b x + log b y
Special Logarithms
ln x = log e x
natural log
!x"
log b $ % = log b x # log b y
& y'
log x = log10 x common log
where e = 2.718281828K
The domain of log b x is x > 0
Factoring and Solving
Factoring Formulas
x 2 # a 2 = ( x + a )( x # a )
x 2 + 2ax + a 2 = ( x + a )
2
x 2 # 2ax + a 2 = ( x # a )
2
Quadratic Formula
Solve ax 2 + bx + c = 0 , a ( 0
#b ± b 2 # 4ac
2a
2
If b # 4ac > 0 - Two real unequal solns.
If b 2 # 4ac = 0 - Repeated real solution.
If b 2 # 4ac < 0 - Two complex solutions.
x=
x 2 + ( a + b ) x + ab = ( x + a )( x + b )
x3 + 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x + a 3 = ( x + a )
x3 # 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x # a 3 = ( x # a )
3
3
Square Root Property
If x 2 = p then x = ± p
x3 + a 3 = ( x + a ) ( x 2 # ax + a 2 )
x3 # a 3 = ( x # a ) ( x 2 + ax + a 2 )
2n
x #a
2n
= (x #a
n
n
)( x
n
+a
n
)
If n is odd then,
x n # a n = ( x # a ) ( x n #1 + ax n # 2 + L + a n #1 )
xn + a n
Absolute Value Equations/Inequalities
If b is a positive number
p =b
)
p = #b or p = b
p <b
)
#b < p < b
p >b
)
p < #b or
p>b
= ( x + a ) ( x n #1 # ax n # 2 + a 2 x n #3 # L + a n #1 )
Completing the Square
(4) Factor the left side
Solve 2 x 2 # 6 x # 10 = 0
2
2
(1) Divide by the coefficient of the x
x 2 # 3x # 5 = 0
(2) Move the constant to the other side.
x 2 # 3x = 5
(3) Take half the coefficient of x, square
it and add it to both sides
2
2
9 29
! 3"
! 3"
x 2 # 3x + $ # % = 5 + $ # % = 5 + =
4 4
& 2'
& 2'
3"
29
!
$x# % =
2'
4
&
(5) Use Square Root Property
3
29
29
x# = ±
=±
2
4
2
(6) Solve for x
3
29
x= ±
2
2
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Functions and Graphs
Constant Function
y = a or f ( x ) = a
Graph is a horizontal line passing
through the point ( 0, a ) .
Line/Linear Function
y = mx + b or f ( x ) = mx + b
Graph is a line with point ( 0,b ) and
slope m.
Slope
Slope of the line containing the two
points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is
y2 ! y1 rise
=
x2 ! x1 run
Slope – intercept form
The equation of the line with slope m
and y-intercept ( 0,b ) is
y = mx + b
Point – Slope form
The equation of the line with slope m
and passing through the point ( x1 , y1 ) is
m=
y = y1 + m ( x ! x1 )
Parabola/Quadratic Function
2
2
y = a ( x ! h) + k
f ( x) = a ( x ! h) + k
The graph is a parabola that opens up if
a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex
at ( h, k ) .
Parabola/Quadratic Function
y = ax 2 + bx + c f ( x ) = ax 2 + bx + c
The graph is a parabola that opens up if
a > 0 or down if a < 0 and has a vertex
" b
" b ##
at $ ! , f $ ! % % .
& 2a & 2 a ' '
Parabola/Quadratic Function
x = ay 2 + by + c g ( y ) = ay 2 + by + c
The graph is a parabola that opens right
if a > 0 or left if a < 0 and has a vertex
" " b # b #
at $ g $ ! % , ! % .
& & 2a ' 2 a '
Circle
2
2
( x ! h) + ( y ! k ) = r2
Graph is a circle with radius r and center
( h, k ) .
Ellipse
( x ! h)
2
( y !k)
+
2
=1
a2
b2
Graph is an ellipse with center ( h, k )
with vertices a units right/left from the
center and vertices b units up/down from
the center.
Hyperbola
( x ! h)
2
( y !k)
!
2
( x ! h)
!
2
=1
a2
b2
Graph is a hyperbola that opens left and
right, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices a
units left/right of center and asymptotes
b
that pass through center with slope ± .
a
Hyperbola
(y !k)
2
=1
b2
a2
Graph is a hyperbola that opens up and
down, has a center at ( h, k ) , vertices b
units up/down from the center and
asymptotes that pass through center with
b
slope ± .
a
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Common Algebraic Errors
Error
Reason/Correct/Justification/Example
2
2
! 0 and ! 2
0
0
Division by zero is undefined!
"32 ! 9
"32 = "9 ,
2 3
(x )
2 3
(x )
! x5
a
a a
! +
b+c b c
1
! x "2 + x "3
2
x + x3
" a ( x " 1) ! " ax " a
2
! x2 + a2
x+a ! x + a
n
= 9 Watch parenthesis!
= x2 x2 x2 = x6
( x + a)
x2 + a2 ! x + a
( x + a)
2
1
1
1 1
=
! += 2
2 1+1 1 1
A more complex version of the previous
error.
a + bx a bx
bx
= +
= 1+
a
a a
a
Beware of incorrect canceling!
" a ( x " 1) = " ax + a
Make sure you distribute the “-“!
a + bx
! 1 + bx
a
( x + a)
( "3 )
! x n + a n and
n
x+a ! n x + n a
2
= ( x + a )( x + a ) = x 2 + 2ax + a 2
5 = 25 = 32 + 42 ! 32 + 42 = 3 + 4 = 7
See previous error.
More general versions of previous three
errors.
2
2
2 ( x + 1) ! ( 2 x + 2 )
( 2 x + 2)
2
! 2 ( x + 1)
2 ( x + 1) = 2 ( x 2 + 2 x + 1) = 2 x 2 + 4 x + 2
2
2
= 4 x2 + 8x + 4
Square first then distribute!
See the previous example. You can not
factor out a constant if there is a power on
the parethesis!
( 2 x + 2)
2
1
2
2
2
"x + a ! " x + a
a
ab
!
#b$ c
% &
'c(
#a$
% & ac
'b( !
c
b
2
" x2 + a2 = ( " x2 + a 2 ) 2
Now see the previous error.
#a$
% &
a
1
# a $# c $ ac
= ' ( = % &% & =
# b $ # b $ ' 1 (' b ( b
% & % &
'c( 'c(
#a$ #a$
% & % &
' b ( = ' b ( = # a $# 1 $ = a
% &% &
c
# c $ ' b (' c ( bc
% &
'1(
For a complete set of online Algebra notes visit http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu.
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
2D GEOMETRY FORMULAS
SQUARE
s = side
Area: A = s2
Perimeter: P = 4s
CIRCLE
r = radius, d = diameter
Diameter: d = 2r
Area: A = πr 2
Circumference: C = 2πr = πd
s
s
RECTANGLE
l = length, w = width
Area: A = lw
Perimeter: P = 2l + 2w
w
l
TRIANGLE
b = base, h = height
Area: A = 12 bh
Perimeter: P = a + b + c
a
Area: A =
r
SECTOR OF CIRCLE
r = radius, θ = angle in radians
Area: A = 12 θr 2
Arc Length: s = θr
s
θ
r
ELLIPSE
c
h
a = semimajor axis
b = semiminor axis
Area: A = πab
b
EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE
s = side
√
Height: h = 23 s
d
s
b
a
Circumference:
!
#
"
C ≈ π 3(a + b) − (a + 3b)(b + 3a)
s
h
√
3 2
4 s
s
PARALLELOGRAM
b = base, h = height, a = side
Area: A = bh
Perimeter: P = 2a + 2b
a
h
ANNULUS
r = inner radius,
R = outer radius
Average Radius: ρ = 12 (r + R)
Width: w = R − r
Area: A = π(R2 − r 2 )
or A = 2πρw
r
R
b
TRAPEZOID
a, b = bases; h = height;
c, d = sides
Area: A = 21 (a + b)h
Perimeter:
P = a+b+c+d
a
c
d
h
b
REGULAR POLYGON
s = side length,
n = number of sides
Circumradius: R = 12 s csc( πn )
Area: A = 41 ns2 cot( πn )
or A = 21 nR2 sin( 2π
n )
s
R
3D GEOMETRY FORMULAS
GENERAL CONE
OR PYRAMID
A = area of base, h = height
Volume: V = 13 Ah
CUBE
s
s = side
Volume: V = s3
Surface Area: S = 6s2
h
A
s
s
RECTANGULAR SOLID
l = length, w = width,
h = height
Volume: V = lwh
Surface Area:
S = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh
RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE
h
w
r = radius, h = height
Volume: V = 13 πr 2 h
Surface√Area:
S = πr r 2 + h2 + πr 2
h
r
l
SPHERE
r = radius
Volume: V = 43 πr 3
Surface Area: S = 4πr 2
RIGHT CIRCULAR
CYLINDER
r = radius, h = height
Volume: V = πr 2 h
Surface Area: S = 2πrh + 2πr 2
FRUSTUM OF A CONE
r = top radius, R = base radius,
h = height, s = slant height
Volume: V = π3 (r 2 + rR + R2 )h
Surface Area:
S = πs(R + r) + πr 2 + πR2
r
r
r
s
h
R
SQUARE PYRAMID
h
s = side, h = height
Volume: V = 13 s2 h
Surface Area:
√
S = s(s + s2 + 4h2 )
h
s
s
R
TORUS
r = tube radius,
R = torus radius
Volume: V = 2π 2 r 2 R
Surface Area: S = 4π 2 rR
r
REGULAR TETRAHEDRON
s = side
√ 3
1
2s
Volume: V = 12
√
Surface Area: S = 3s2
s
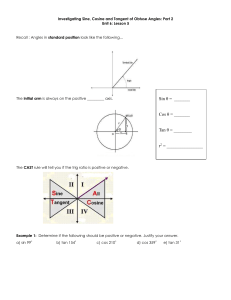
Trig Cheat Sheet
Definition of the Trig Functions
Right triangle definition
For this definition we assume that
0 #" #
!
2
or 0$ # " # 90$ .
Unit circle definition
For this definition " is any angle.
y
3 x, y 4
hypotenuse
y
opposite
1
"
x
x
"
adjacent
opposite
hypotenuse
adjacent
cos " %
hypotenuse
opposite
tan " %
adjacent
sin " %
hypotenuse
opposite
hypotenuse
sec " %
adjacent
adjacent
cot " %
opposite
csc " %
y
%y
1
x
cos " % % x
1
y
tan " %
x
sin " %
1
y
1
sec " %
x
x
cot " %
y
csc " %
Facts and Properties
Domain
The domain is all the values of " that
can be plugged into the function.
sin " , " can be any angle
cos " , " can be any angle
1'
&
tan " , " ( + n ) , ! , n % 0, * 1, * 2,!
2.
csc " , " ( n ! , n % 0, * 1, * 2,!
1'
&
sec " , " ( + n ) , ! , n % 0, * 1, * 2,!
2.
cot " , " ( n ! , n % 0, * 1, * 2,!
Range
The range is all possible values to get
out of the function.
csc " 1 1 and csc" 0 /1
/1 0 sin " 0 1
/1 0 cos " 0 1 sec " 1 1 and sec" 0 /1
/2 0 tan " 0 2
/2 0 cot " 0 2
Period
The period of a function is the number,
T, such that f 3" ) T 4 % f 3" 4 . So, if 5
is a fixed number and " is any angle we
have the following periods.
sin 35" 4 6
T%
cos 35" 4 6
T
tan 35" 4 6
T
csc 35" 4 6
T
sec 35" 4 6
T
cot 35" 4 6
T
2!
5
2!
%
5
!
%
5
2!
%
5
2!
%
5
!
%
5
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Formulas and Identities
Tangent and Cotangent Identities
sin !
cos !
tan ! "
cot ! "
cos !
sin !
Reciprocal Identities
1
1
csc ! "
sin ! "
sin !
csc !
1
1
sec ! "
cos ! "
cos !
sec !
1
1
cot ! "
tan ! "
tan !
cot !
Pythagorean Identities
sin 2 ! # cos 2 ! " 1
tan 2 ! # 1 " sec2 !
1 # cot 2 ! " csc2 !
Even/Odd Formulas
sin $ &! % " & sin !
csc $ &! % " & csc!
cos $ &! % " cos !
sec $ &! % " sec!
tan $ &! % " & tan !
cot $ &! % " & cot !
Periodic Formulas
If n is an integer.
sin $! # 2' n % " sin !
csc $! # 2' n % " csc!
cos $! # 2' n % " cos ! sec $! # 2' n % " sec!
tan $! # ' n % " tan ! cot $! # ' n % " cot !
Double Angle Formulas
sin $ 2! % " 2sin ! cos !
cos $ 2! % " cos 2 ! & sin 2 !
" 2 cos 2 ! & 1
" 1 & 2sin 2 !
2 tan !
tan $ 2! % "
1 & tan 2 !
Degrees to Radians Formulas
If x is an angle in degrees and t is an
angle in radians then
'
t
'x
180t
"
( t"
and x "
180 x
180
'
Half Angle Formulas
1
sin 2 ! " $1 & cos $ 2! % %
2
1
cos 2 ! " $1 # cos $ 2! % %
2
1 & cos $ 2! %
tan 2 ! "
1 # cos $ 2! %
Sum and Difference Formulas
sin $) + * % " sin ) cos * + cos ) sin *
cos $) + * % " cos ) cos * ! sin ) sin *
tan ) + tan *
1 ! tan ) tan *
Product to Sum Formulas
1
sin ) sin * " ,.cos $) & * % & cos $) # * % -/
2
1
cos ) cos * " ,. cos $) & * % # cos $) # * % -/
2
1
sin ) cos * " ,.sin $) # * % # sin $) & * % -/
2
1
cos ) sin * " ,.sin $) # * % & sin $) & * % -/
2
Sum to Product Formulas
0) # * 1
0) & * 1
sin ) # sin * " 2sin 2
3 cos 2
3
4 2 5
4 2 5
0) # * 1 0) & * 1
sin ) & sin * " 2 cos 2
3 sin 2
3
4 2 5 4 2 5
0) # * 1
0) & * 1
cos ) # cos * " 2 cos 2
3 cos 2
3
4 2 5
4 2 5
0) # * 1 0) & * 1
cos ) & cos * " &2sin 2
3 sin 2
3
4 2 5 4 2 5
Cofunction Formulas
tan $) + * % "
0'
1
sin 2 & ! 3 " cos !
2
4
5
'
0
1
csc 2 & ! 3 " sec !
42
5
0'
1
cos 2 & ! 3 " sin !
2
4
5
'
0
1
sec 2 & ! 3 " csc!
42
5
0'
1
tan 2 & ! 3 " cot !
2
4
5
0'
1
cot 2 & ! 3 " tan !
2
4
5
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Unit Circle
y
%
& 1 3'
)( , *
+ 2 2 ,
&
2 2'
,
)(
*
+ 2 2 ,
&
3 1'
)( , *
+ 2 2,
! (1,0 "
3%
4
5%
6
! 0,1"
2
2%
3
%
90120-
&1 3'
)) , **
+2 2 ,
3
%
60-
4
%
45-
135-
30-
& 3 1'
)) , **
+ 2 2,
6
150-
% 180-
&
3 1'
)( ,( *
2,
+ 2
& 2 2'
,
))
**
+ 2 2 ,
7%
6
&
2
2'
,(
)(
*
2 ,
+ 2
210-
5%
4
0-
0
360-
2%
330225-
4%
3
240-
& 1
3'
) ( ,(
*
2
2
+
,
3157%
3002704
5%
3%
3
2
&
11%
6
!1,0 "
x
& 3 1'
) ,( *
+ 2 2,
& 2
2'
,(
)
*
2
2
+
,
1
3'
) ,(
*
+2 2 ,
! 0,(1"
For any ordered pair on the unit circle ! x, y " : cos # $ x and sin # $ y
Example
& 5%
cos )
+ 3
' 1
*$
, 2
& 5%
sin )
+ 3
3
'
*$(
2
,
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
Inverse Trig Functions
Definition
y " sin !1 x is equivalent to x " sin y
Inverse Properties
cos ' cos !1 ' x ( ( " x
cos!1 ' cos ') ( ( " )
y " cos !1 x is equivalent to x " cos y
sin ' sin !1 ' x ( ( " x
sin !1 ' sin ') ( ( " )
tan ' tan !1 ' x ( ( " x
tan !1 ' tan ') ( ( " )
!1
y " tan x is equivalent to x " tan y
Domain and Range
Function
Domain
y " sin !1 x
!1
!1 # x # 1
y " cos x
!1 # x # 1
y " tan !1 x
!% & x & %
Range
!
!
$
# y#
Alternate Notation
sin !1 x " arcsin x
$
cos !1 x " arccos x
2
2
0# y #$
$
2
& y&
tan !1 x " arctan x
$
2
Law of Sines, Cosines and Tangents
c
+.
a
,.
*.
b
Law of Sines
sin * sin + sin ,
"
"
a
b
c
Law of Tangents
a ! b tan 12 '* ! + (
"
a - b tan 12 '* - + (
Law of Cosines
a 2 " b 2 - c 2 ! 2bc cos *
b ! c tan 12 ' + ! , (
"
b - c tan 12 ' + - , (
b 2 " a 2 - c 2 ! 2ac cos +
c 2 " a 2 - b 2 ! 2ab cos ,
a ! c tan 12 '* ! , (
"
a - c tan 12 '* - , (
Mollweide’s Formula
a - b cos 12 '* ! + (
"
c
sin 12 ,
© 2005 Paul Dawkins
f ( x) = x3
f ( x) = x 0 = 1
!
!
f ( x) = x 3 " x
f ( x) = x1 = x
!
!
f ( x) = x2
f ( x) = x 4
!
!
1
f ( x) = x 2 = x
f ( x) = x 4 " x 2
!
!
x2 + y2 = 1
y = sin x
x2 " y2 = 1
y = cos x
2
2
x
y
+
= 1
9
4
y = tan x
f ( x) = log x
f ( x) = 2 x
!
!
Differentiation Formulas
d
k=0
dx
d
[f (x) ± g(x)] = f ⇥ (x) ± g ⇥ (x)
dx
d
[k · f (x)] = k · f ⇥ (x)
dx
d
[f (x)g(x)] = f (x)g ⇥ (x) + g(x)f ⇥ (x)
dx
⇥
d f (x)
g(x)f ⇥ (x) f (x)g ⇥ (x)
=
2
dx g(x)
[g(x)]
d
f (g(x)) = f ⇥ (g(x)) · g ⇥ (x)
dx
d n
x = nxn 1
dx
d
sin x = cos x
dx
d
cos x = sin x
dx
d
tan x = sec2 x
dx
d
cot x = csc2 x
dx
d
sec x = sec x tan x
dx
d
csc x = csc x cot x
dx
d x
e = ex
dx
d x
a = ax ln a
dx
d
1
ln |x| =
dx
x
d
1
sin 1 x = ⇥
dx
1 x2
1
d
cos
dx
1
d
tan
dx
d
cot
dx
d
sec
dx
1
+1
1
1
x= 2
x +1
1
1
⇥
x=
|x| x2
d
csc
dx
1
1
x= ⇥
x=
x=
1
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
x2
(19)
x2
1
⇥
|x| x2
Integration Formulas
(20)
1
1
(21)
(22)
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
⇤
dx = x + C
xn dx =
(1)
xn+1
+C
n+1
(2)
dx
= ln |x| + C
x
(3)
ex dx = ex + C
(4)
ax dx =
1 x
a +C
ln a
ln x dx = x ln x
sin x dx =
(5)
x+C
cos x + C
(6)
(7)
cos x dx = sin x + C
(8)
tan x dx =
(9)
ln | cos x| + C
cot x dx = ln | sin x| + C
(10)
sec x dx = ln | sec x + tan x| + C
(11)
csc x dx =
ln | csc x + cot x| + C (12)
sec2 x dx = tan x + C
(13)
csc2 x dx =
(14)
cot x + C
sec x tan x dx = sec x + C
(15)
csc x cot x dx =
csc x + C
(16)
x
+C
a
(17)
⇥
dx
= sin
a2 x2
dx
1
= tan
a2 + x2
a
1
1
dx
1
⇥
= sec
2
2
a
x x
a
x
+C
a
1
|x|
+C
a
(18)
(19)
Standard Normal Distribution Table
0
z
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.9
3.0
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
.00
.0000
.0398
.0793
.1179
.1554
.1915
.2257
.2580
.2881
.3159
.3413
.3643
.3849
.4032
.4192
.4332
.4452
.4554
.4641
.4713
.4772
.4821
.4861
.4893
.4918
.4938
.4953
.4965
.4974
.4981
.4987
.4990
.4993
.4995
.4997
.4998
.01
.0040
.0438
.0832
.1217
.1591
.1950
.2291
.2611
.2910
.3186
.3438
.3665
.3869
.4049
.4207
.4345
.4463
.4564
.4649
.4719
.4778
.4826
.4864
.4896
.4920
.4940
.4955
.4966
.4975
.4982
.4987
.4991
.4993
.4995
.4997
.4998
.02
.0080
.0478
.0871
.1255
.1628
.1985
.2324
.2642
.2939
.3212
.3461
.3686
.3888
.4066
.4222
.4357
.4474
.4573
.4656
.4726
.4783
.4830
.4868
.4898
.4922
.4941
.4956
.4967
.4976
.4982
.4987
.4991
.4994
.4995
.4997
.4998
Gilles Cazelais. Typeset with LATEX on April 20, 2006.
.03
.0120
.0517
.0910
.1293
.1664
.2019
.2357
.2673
.2967
.3238
.3485
.3708
.3907
.4082
.4236
.4370
.4484
.4582
.4664
.4732
.4788
.4834
.4871
.4901
.4925
.4943
.4957
.4968
.4977
.4983
.4988
.4991
.4994
.4996
.4997
.4998
.04
.0160
.0557
.0948
.1331
.1700
.2054
.2389
.2704
.2995
.3264
.3508
.3729
.3925
.4099
.4251
.4382
.4495
.4591
.4671
.4738
.4793
.4838
.4875
.4904
.4927
.4945
.4959
.4969
.4977
.4984
.4988
.4992
.4994
.4996
.4997
.4998
z
.05
.0199
.0596
.0987
.1368
.1736
.2088
.2422
.2734
.3023
.3289
.3531
.3749
.3944
.4115
.4265
.4394
.4505
.4599
.4678
.4744
.4798
.4842
.4878
.4906
.4929
.4946
.4960
.4970
.4978
.4984
.4989
.4992
.4994
.4996
.4997
.4998
.06
.0239
.0636
.1026
.1406
.1772
.2123
.2454
.2764
.3051
.3315
.3554
.3770
.3962
.4131
.4279
.4406
.4515
.4608
.4686
.4750
.4803
.4846
.4881
.4909
.4931
.4948
.4961
.4971
.4979
.4985
.4989
.4992
.4994
.4996
.4997
.4998
.07
.0279
.0675
.1064
.1443
.1808
.2157
.2486
.2794
.3078
.3340
.3577
.3790
.3980
.4147
.4292
.4418
.4525
.4616
.4693
.4756
.4808
.4850
.4884
.4911
.4932
.4949
.4962
.4972
.4979
.4985
.4989
.4992
.4995
.4996
.4997
.4998
.08
.0319
.0714
.1103
.1480
.1844
.2190
.2517
.2823
.3106
.3365
.3599
.3810
.3997
.4162
.4306
.4429
.4535
.4625
.4699
.4761
.4812
.4854
.4887
.4913
.4934
.4951
.4963
.4973
.4980
.4986
.4990
.4993
.4995
.4996
.4997
.4998
.09
.0359
.0753
.1141
.1517
.1879
.2224
.2549
.2852
.3133
.3389
.3621
.3830
.4015
.4177
.4319
.4441
.4545
.4633
.4706
.4767
.4817
.4857
.4890
.4916
.4936
.4952
.4964
.4974
.4981
.4986
.4990
.4993
.4995
.4997
.4998
.4998