Unit 8 momentum review
advertisement

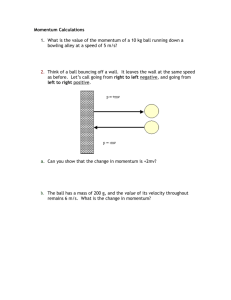
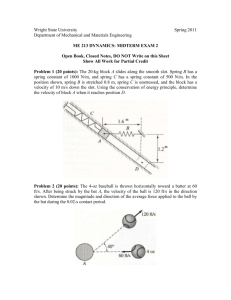
Momentum, Impulse, and Collision Review Fill in the following UNITS only table Quantity Mass Units Name: __________________________________ Quantity Kinetic Energy Velocity Potential Energy Force Momentum Weight Impulse _____ 2) The quantity 8 kg m/s is equivalent to which of the following A) 8 N B) 8 N * s C) 8 N / s Units D) 8 N / m _____ 3) A force applied over time would create which of the following? A) impulse C) Both A and B B) change in momentum D) Neither A nor B _____4) You're driving down the highway and a bug spatters into your windshield. Which undergoes the greater change is momentum? A) the bug B) the car C) both the same ____ 5) The momentum of a punch is changed by a fighter’s jaw. The fighter receiving the punch “rolls with the punch” so as to: A) increases the time of contact, and therefore decrease the average force of the punch B) decrease the time of contact, and therefore increase the average force of the punch C) decrease the mass of the boxing glove D) increase the mass of the boxing glove. ____6) Which of the following scenarios would be considered approximately an elastic collision? A) playing tennis C) an archer’s arrow piercing a target B) coupling two train cars together D) Both B and C _____7) You are driving a truck on a highway from a velocity of 25 m/s, you apply the brakes and stop the truck in 1.5 seconds. Later, when the brakes are wet you stop the same car from the same velocity but the time it takes 2.0 seconds, what is the difference in the impulse? A) The impulse increased, because the time increased B) The impulse decreased, because the time decreased. C) The impulse remained the same D) You can’t tell because you don’t know the stopping force. ______ 8) Superman is asked to calculate the momentum of two objects in motion, a speeding bullet and a locomotive. He finds that the momentum of the two objects is equal. What is the best explanation for this? A) The bullet and locomotive have the same mass. B) The bullet and the locomotive must have the same velocity. C) The locomotive is moving at much higher velocity than the bullet. D) The bullet is moving at a much higher velocity than the locomotive. ______ 9) If the momentum of an object triples with the mass remaining constant, what happens to the velocity? A) Velocity triples. B) Velocity is reduced by 1/3. C) Velocity remains constant. _____ 10) Suppose that the change of momentum of an car remains constant, increasing the time the average force is applied will have what effect on the average force. A) The average force remains constant. B) The average force will increase. C) The average force will decrease. D) The average force will vary. 11) After calculating the Kinetic Energy for the carts in the lab, a student records that he had a total of 10J of Kinetic energy before the collision and only 4.8J of Kinetic Energy after the collision. By looking at this data, what type of collision (elastic or inelastic) was this? How do you know? Type of Collision: Why: 12) A 25,000 kg tractor trailer traveling 3 m/s towards the north crashes into a 1200 kg Corvette traveling 2m/s towards the north. The velocity of the tractor trailer after the collision is 1 m/s to the north. Calculate the velocity of the Corvette after the collision if the tractor trailer and Corvette do not stick together. Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: 13) Using the picture below, rank from least to greatest the ball’s momentum at each point. The ball is rolling down and along the curved slope. 14) Airplanes maneuver on the ground by using thrust from their jet engines. A fully loaded 400,000 kg Boeing 747 gets a total of 1.1 x 106 N of thrust from it jet engines. Suppose that liftoff for a plane will occur at 78 m/s. Determine the time the plane takes to go from rest to 78 m/s. Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: ____ 15) In the diagram below, scaled vectors represent the momentum of each of two masses, A and B, sliding towards each other on a frictionless horizontal surface. Which scaled vector best represents the momentum of the system after they collide? A) C) B) D) 16) Keith Hernandez’s 0.010 kg spit ball was traveling at 12 m/s when it hit Kramer’s forehead. If the spit ball took .002 seconds to come to a complete stop, how much force did Kramer’s forehead provide? Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: 17) Hobbes, the stuffed tiger, has a mass of 31.8 kg. Calvin, the little boy, has a mass of 25.1 kg. In a game of football, Hobbes runs at Calvin at 11 m/s. Calvin is running in the same direction as Hobbes, away from Hobbes, at 8.33 m/s. If the two collide and stick together, what would be their final velocity? Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: 18) A baseball, .175 kg, is pitched at 50 m/s ( t o t h e l e f t ) when is hit by the batter. The ball travels in the opposite direction it was thrown from with a speed of 70 m/s. What is the impulse of the baseball? 19) A 2200 kg car moving with a velocity of 5 m/s to the east crashes into a 1500 kg car stopped at a light. What is the velocity of the wreckage immediately after the collision, assuming the cars stick together? What type of collision is this? Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: 20) A 100 Kg cannon initially at rest fires a 1 Kg cannon ball at 200 m/s. What is the recoil velocity of cannon? Diagram: (Given + Unknowns) Equation: Substitute: Solve: 21) Use Newton’s Laws to explain what is occurring in question #21. _____ 22) A woman with horizontal velocity v 1 jumps off a dock into a stationary boat. After landing in the boat, the woman and the boat move with velocity v 2. Compared to velocity v1, velocity v2 has A) The same magnitude and same direction B) The same magnitude and the opposite direction C) Smaller magnitude and the same direction D) Larger magnitude and the same direction.