Module 5 Lesson 2
advertisement

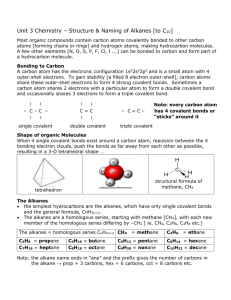
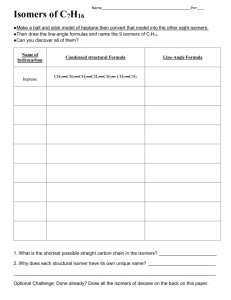
CHEMISTRY 30S – MODULE 5 Organic chemistry LESSON 2 STRUCTURAL ISOMERS Outcomes When you have completed this lesson, you will be able to: Construct, illustrate and name isomers of alkanes (up to 10 C atoms) using IUPAC nomenclature. Defining Structural Isomers You may recall the example from the previous lesson where two 4 carbon alkanes were compared. butane 2-methylpropane Both of these alkanes have the same molecular formula, C4H10, but a different structural formula. Molecules, like the two above, that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are called structural isomers. So, butane and 2methylpropane are structural isomers. The more carbon atoms a compound contains, the greater the number of structural CHEM 30S Mod 3 Chemical Reactions Lesson 6 1 TALC 2010 isomers that can exist. For example, octane has 18 different structural isomers, decane has 75, pentadecane (a 15 carbon alkane) has 4 347, and eicosane (a 20 carbon alkane) has 366 319 isomers! Constructing Structural Isomers When constructing structural isomers, it is always a good practice to begin by drawing the carbon chains without the hydrogen atoms, then rearranging to find new patterns or arrangements. You should also try naming them to ensure they are different. Once you have structural isomers drawn, fill in the hydrogen atoms to give each carbon 4 bonds. Example 1. Draw and name 2 structural isomers of pentane, not including pentane. Solution. Step 1: Write the molecular formula. Pentane is a 5-carbon alkane, so its molecular formula is C5H12. CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH3 We are looking for 2 different arrangements of 5 carbons. Step 2: Draw different arrangements of carbons. We can start by taking one carbon off the end and making it a branch. Remember, we are just drawing the carbons. Then name it. If we put a branch on the end, we have not created an isomer. The longest continuous chain has 5 carbons. This structure is the same as the original pentane. We must place the branches off internal carbons, not carbons on the end of the chain. 2-methylbutane We could try putting the branch on the other end. This structure is still 2-methylbutane, so we don't have a different structure. It CHEM 30S Mod 3 Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 2 TALC 2010 appears we cannot make any more new structure with a single branch, so we take another carbon off the end and make it a second branch. 2,2-dimethylpropane These are the only 2 structural isomers of pentane: Identifying Isomers Example 2. 3-ethyl-2-methylhexane is a structural isomer of which straight chained alkane? Solution. Step 1: Identify the parent chain. The parent chain is hexane, 6 carbons. Step 2: Identify each branch and the number of carbons. There is one ethyl group (2 carbons) and 1 methyl group (1 carbon) Step 3: Add up the carbons. 6 carbons + 2 carbons + 1 carbon = 9 carbons The alkane with 9 carbons is nonane. 3-ethyl-2-methylhexane is a structural isomer of nonane. Lesson Summary In this lesson we have learned Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. CHEM 30S Mod 3 Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 3 TALC 2010 Exercise Answer the following questions: 1. Draw and name all the structural isomers of hexane. 2. Draw and name all the structural isomers of heptane. 3. Indicate which straight-chain alkane is a structural isomer of each of the following. a) 3-propylheptane b) 3-methylpentane c) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpentane d) 2-methylbutane e) 3-ethylhexane f) 2-methylhexane g) 2,2-dimethylpentane CHEM 30S Mod 3 Chemical Reactions Lesson 3 4